Table of Contents
Introduction
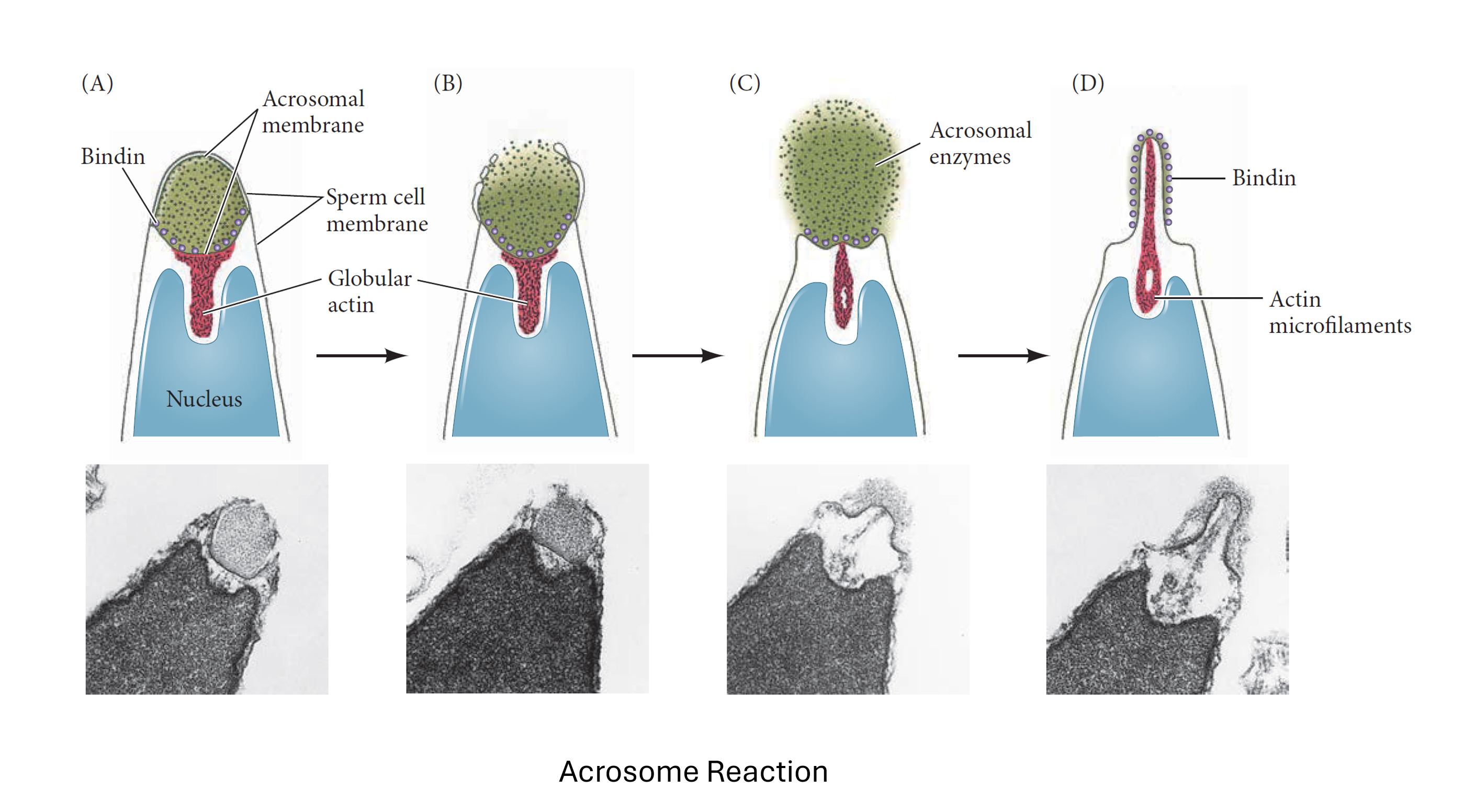
The acrosome reaction is a crucial process in fertilization, enabling the sperm to penetrate the egg’s protective layers and achieve fertilization. This reaction involves a series of biochemical and structural changes in the sperm’s acrosome, a cap-like structure covering the anterior part of the sperm head.
Structure of the Acrosome
- Location: The acrosome is located at the tip of the sperm head, between the plasma membrane and the nuclear membrane.
- Origin: It is derived from the Golgi apparatus during spermiogenesis.
- Contents: The acrosome contains hydrolytic enzymes such as hyaluronidase and acrosin, which are essential for breaking down the egg’s outer layers.
Steps of the Acrosome Reaction
- Contact with the Zona Pellucida:
- The sperm binds to the zona pellucida, a glycoprotein layer surrounding the egg.
- This binding is mediated by specific receptors on the sperm surface.
- Fusion of Membranes:
- The plasma membrane of the sperm fuses with the outer acrosomal membrane.
- This fusion results in the formation of vesicles and the release of acrosomal contents.
- Release of Enzymes:
- Enzymes such as hyaluronidase and acrosin are released from the acrosome.
- These enzymes digest the zona pellucida, creating a pathway for the sperm to reach the egg’s plasma membrane.
- Penetration of the Zona Pellucida:
- The sperm moves through the digested zona pellucida.
- The inner acrosomal membrane remains intact and facilitates further binding to the egg’s plasma membrane.
- Fusion with the Egg Membrane:
- The sperm’s inner acrosomal membrane binds to the egg’s plasma membrane.
- This binding triggers the fusion of the sperm and egg membranes, allowing the sperm nucleus to enter the egg.
Significance of the Acrosome Reaction
- Fertilization: The acrosome reaction is essential for the sperm to penetrate the egg and achieve fertilization.
- Species-Specificity: The reaction ensures that only sperm from the same species can fertilize the egg, preventing cross-species fertilization.
- Activation of the Egg: The fusion of sperm and egg membranes triggers the egg’s activation, leading to the completion of meiosis and the beginning of embryonic development.
Variations Among Species
- Echinoderms: In species like sea urchins, the acrosome reaction involves the formation of an acrosomal process supported by actin microfilaments.
- Mammals: In mammals, the reaction is characterized by the release of enzymes that facilitate the penetration of the zona pellucida.
Conclusion
The acrosome reaction is a complex and highly regulated process that plays a critical role in fertilization. Understanding this process provides insights into reproductive biology and potential applications in assisted reproductive technologies.