Table of Contents
I. Introduction
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), are a class of proteins that are produced by the immune system in response to foreign antigens.
They are an important component of the humoral immune response and play a key role in fighting infection and disease.
Antibodies are highly specific to a particular antigen and can bind to it with high affinity.
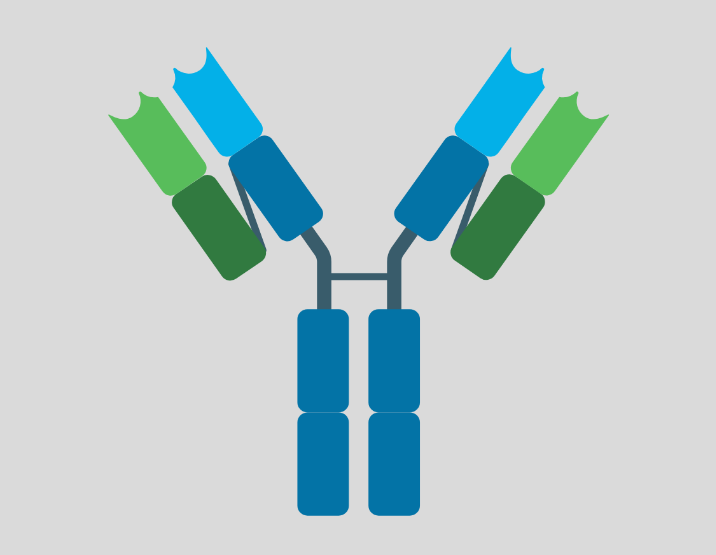
II. Structure
- Antibodies are composed of four polypeptide chains: two heavy chains and two light chains.
- The heavy chains are responsible for the antibody’s class or isotype, which determines its effector function.
- The light chains are responsible for the antibody’s specificity, which determines its ability to bind to a particular antigen.
III. Classes and Isotypes
- There are five main classes of antibodies: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD, and IgE.
- Each class has a unique structure and function.
- IgM is the first class of antibody to be produced in response to an infection and is the largest antibody.
- IgG is the most common antibody and is responsible for long-term immunity.
- IgA is found in secretions such as tears, saliva, and breast milk and plays a role in protecting mucosal surfaces.
- IgD is found on the surface of B cells and plays a role in the activation of the immune response.
- IgE is responsible for allergic reactions.

IV. Mechanisms of Action
- Antibodies can neutralize pathogens by binding to them and making it difficult for them to infect host cells.
- They can also bind to toxins and prevent them from causing harm.
- Antibodies can also activate the complement system, which leads to the lysis of pathogens.
- They can also recruit other immune cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells to the site of infection.
V. B cell Development and Differentiation
- B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are responsible for producing antibodies.
- B cells develop from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
- They differentiate into immature B cells and then mature B cells, which enter the circulation.
- B cells can also differentiate into memory B cells and plasma cells.
VI. Conclusion
- Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), are a class of proteins that are produced by the immune system in response to foreign antigens.
- They are an important component of the humoral immune response and play a key role in fighting infection and disease.
- Antibodies are highly specific to a particular antigen and can bind to it with high affinity.
- There are five main classes of antibodies: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD, and IgE.
- They can neutralize pathogens by binding to them, activate the complement system, recruit other immune cells and it also play role in B cell Development and Differentiation.