Table of Contents
Introduction
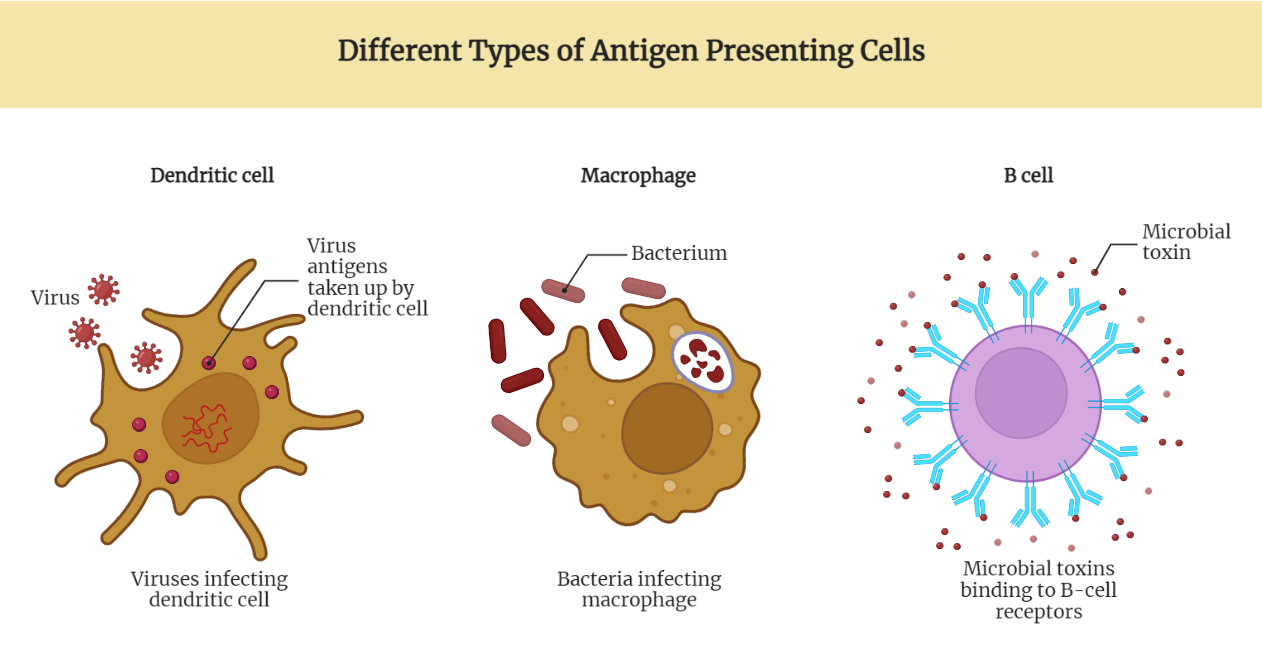
Antigen presenting cells (APCs) are a diverse group of cells that play a crucial role in the immune system by presenting antigens to T cells. They are responsible for initiating the adaptive immune response by processing and presenting antigens to T cells in a way that allows the T cells to recognize them.
APCs include dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells.
Dendritic Cells
- Dendritic cells are professional APCs that are found in various tissues, including the skin, lymphoid organs, and mucosa.
- They are able to take up antigens, process them, and present them on their surface to T cells.
- Dendritic cells can be divided into two main types: myeloid dendritic cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells.
Macrophages
- Macrophages are also professional APCs and are found in various tissues including the lungs, liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
- They play a crucial role in the immune response by phagocytosis, the process of engulfing and digesting pathogens and cellular debris.
- Macrophages also have the ability to process and present antigens on their surface to T cells.
B cells
- B cells are important for the immune response against pathogens by producing antibodies.
- They are also able to act as APCs by presenting antigens on their surface to T cells, which can lead to the activation of CD4+ T cells.
- B cells can also differentiate into plasma cells, which secrete high-affinity antibodies against specific antigens.
Maturation of APCs
- APCs undergo a process of maturation that allows them to become more efficient at presenting antigens to T cells.
- This process is characterized by the upregulation of co-stimulatory molecules, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and the increased expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
- Maturation of APCs is essential for the initiation of a robust adaptive immune response.
Conclusion
Antigen presenting cells (APCs) are a diverse group of cells. They play a crucial role in the immune system by presenting antigens to T cells.
APCs include dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells.
They are responsible for initiating the adaptive immune response by processing. They present antigens to T cells in a way that allows the T cells to recognize them.
APCs also undergo maturation process that allows them to become more efficient in presenting antigens to T cells, which is essential for the initiation of a robust adaptive immune response.