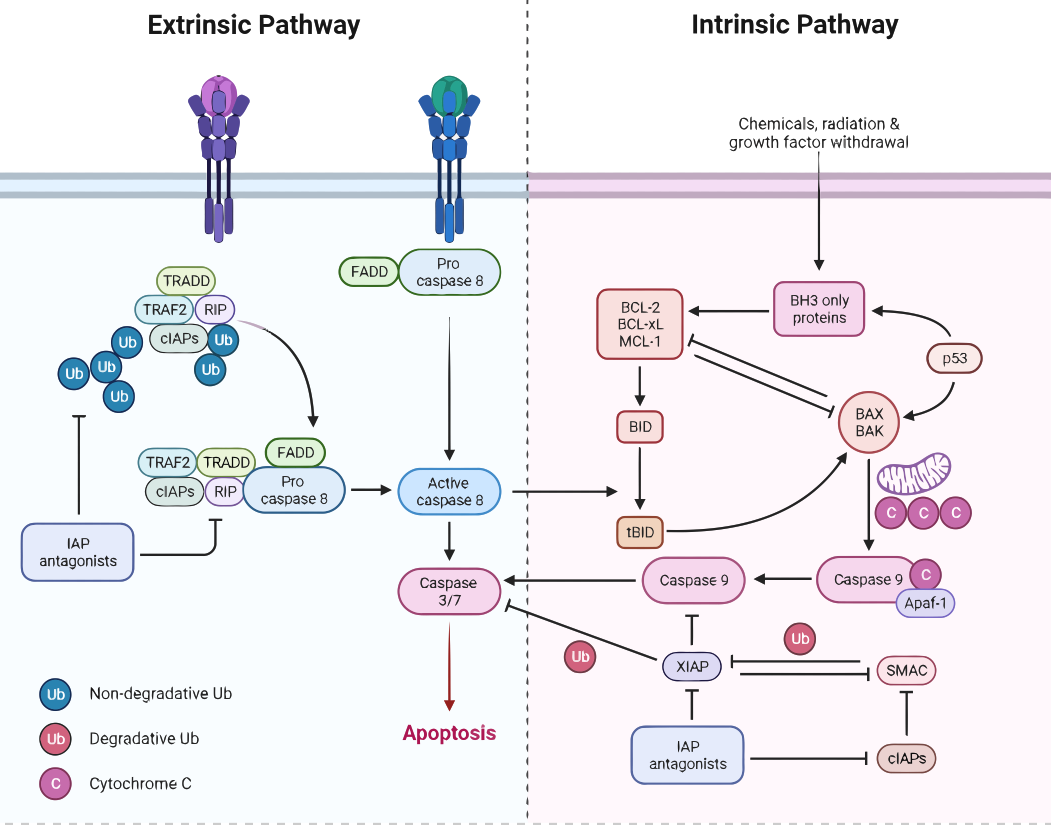
Apoptotic pathways are a series of cellular events that result in programmed cell death, or apoptosis. There are two main pathways: the extrinsic pathway, which is triggered by signals from outside the cell, and the intrinsic pathway, which is activated by signals from within the cell.
Table of Contents
I. Extrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis/ Extrinsic apoptotic pathway
- The extrinsic pathway is triggered by signals from outside the cell, such as death receptors on the cell surface.
- These receptors, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and Fas (CD95) receptors, bind to their respective ligands and undergo a conformational change that allows them to recruit adaptor proteins.
- These adaptor proteins, such as FADD and TRADD, recruit and activate the caspase cascade, which is a series of proteases that ultimately lead to the destruction of the cell.
- The initiator caspase in this pathway is caspase 8, which is activated by the adaptor proteins.
- Caspase 8 in turn activates the executioner caspases, caspase 3 and caspase 7, which cleave and degrade a variety of cellular proteins, leading to the characteristic morphological changes of apoptosis.
II. Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis/ Intrinsic apoptotic Pathway
- The intrinsic pathway is activated by signals from within the cell, such as DNA damage or mitochondrial dysfunction.
- This pathway involves the release of pro-apoptotic molecules, such as cytochrome c and SMAC/DIABLO, from the mitochondria into the cytosol.
- These molecules bind to and activate the initiator caspase, caspase 9, which is a part of the Apaf-1 complex.
- Caspase 9 in turn activates the executioner caspases, caspase 3 and caspase 7, which cleave and degrade a variety of cellular proteins, leading to the characteristic morphological changes of apoptosis.
- The intrinsic pathway is also regulated by the Bcl-2 family of proteins, which can either promote or inhibit the release of pro-apoptotic molecules from the mitochondria.
- It is important to note that the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway converge at the activation of executioner caspases, caspase 3 and caspase 7, which leads to the apoptotic process.