Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chromosomal aberrations are variations in the structure or quantity of chromosomes that can occur in an organism’s cells.
- Chromosomal abnormalities can cause a variety of health problems, including genetic illnesses, developmental abnormalities, and cancer.
- Chromosomal Aberration Types
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormally large number of chromosomes in a cell.
This can happen because of:
Nondisjunction: when chromosomes fail to split properly during meiosis, resulting in cells with an additional or missing chromosome. Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is one such condition caused by the existence of an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Chromosome duplication: an extra copy of one or more chromosomes.
Chromosome deletion: the elimination of one or more chromosomes.
Polyploidy
The presence of more than two sets of chromosomes in a cell is referred to as polyploidy.
Nondisjunction: the inability of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis, resulting in cells with more than two sets of chromosomes.
Endoreduplication: chromosomal replication without cell division.
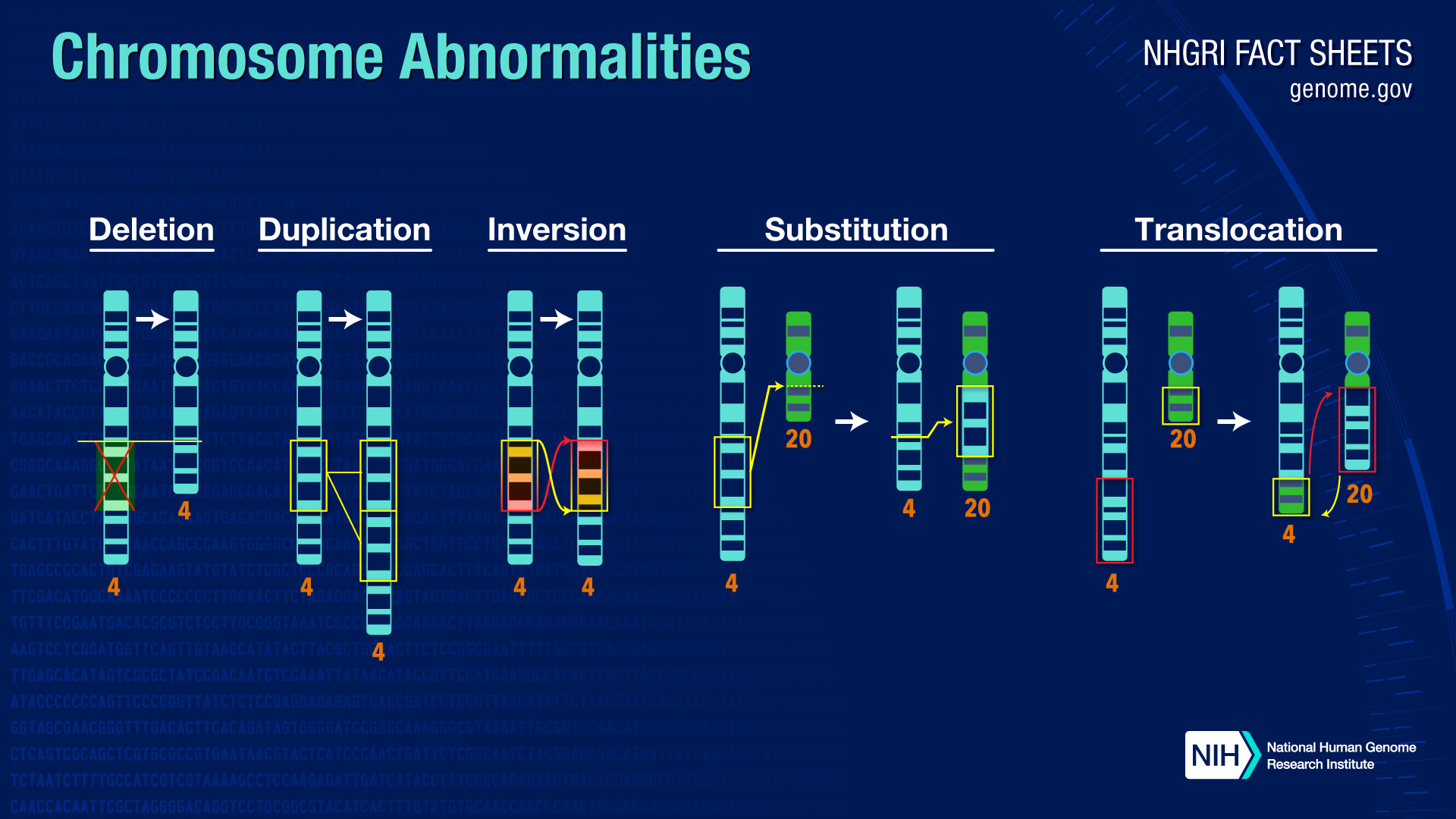
Chromosomal abberations
Changes in the structure of chromosomes are examples of structural aberrations.
This can happen as a result of:
Deletions: the loss of a chromosomal segment.
Duplications: the presence of an additional copy of a chromosomal segment.
Inversions: the reversal of the order of a chromosomal segment.
Translocations: the transfer of a segment of one chromosome to another.
Chromosomal Aberration Causes
- Spontaneous mutation: Chromosomal abnormalities can occur as a result of DNA replication or repair mistakes.
- Induced mutation: Chromosomal abnormalities can also be produced by environmental causes like radiation or toxins.
- Cancer: Chromosomal abnormalities are frequently detected in cancer cells and are assumed to play a role in the disease’s development and progression.
The Impact of Chromosomal Aberration
- Chromosomal abnormalities can cause a variety of genetic illnesses, including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome.
- Chromosomal aberrations can result in developmental problems such as birth deformities, miscarriage, and stillbirth.
- Cancer: Chromosomal abnormalities are frequently detected in cancer cells and are assumed to play a role in the disease’s development and progression.
Conclusion
- Chromosomal aberrations are variations in the structure or quantity of chromosomes that can occur in an organism’s cells.
- Chromosomal abnormalities can cause a variety of health problems, including genetic illnesses, developmental abnormalities, and cancer.
- Understanding the causes and consequences of chromosomal abnormalities is critical in domains including genetics, medicine, and cancer research.