Table of Contents
Introduction
- Protozoa are a diverse group of single-celled, eukaryotic organisms that are found in a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, marine, and terrestrial environments.
- In 1980, Levine et al. proposed a classification system for protozoa that is based on their morphological and physiological characteristics.
General Characteristics of Protozoa
- Protozoa are unicellular eukaryotic organisms that can be heterotrophic or autotrophic.
- They possess a variety of organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.
- They are characterized by the presence of a cytoskeleton, which provides them with shape and motility.
- They can reproduce asexually or sexually.
Classification of Protozoa
- According to Levine et al. (1980), protozoa can be classified into seven main phyla:
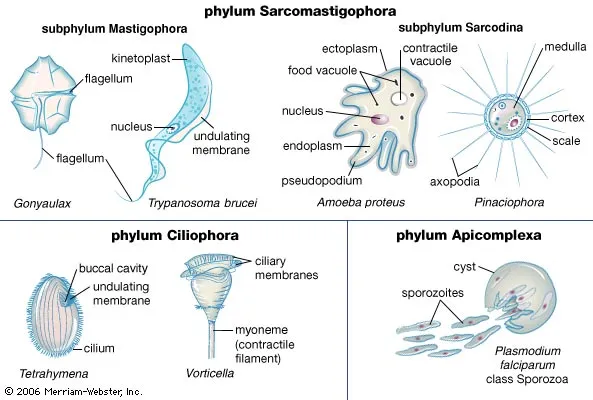
Phylum Sarcomastigophora
- Organisms in this phylum have flagella or pseudopodia for motility.
- They possess one or more nuclei.
- They are typically heterotrophic.
- Examples include the genera Trypanosoma and Leishmania.
Phylum Mastigophora
- Organisms in this phylum have flagella for motility.
- They possess one or more nuclei.
- They can be heterotrophic or autotrophic.
- Examples include the genera Euglena and Dinoflagellates.
Phylum Opalinata
- Organisms in this phylum have opaline silica scales.
- They possess one or more nuclei.
- They can be heterotrophic or autotrophic.
- Examples include the genera Opalina and Difflugia.
Phylum Ciliophora
- Organisms in this phylum have cilia for motility.
- They possess one or more nuclei.
- They can be heterotrophic or autotrophic.
- Examples include the genera Paramecium and Tetrahymena.
Phylum Apicomplexa
- Organisms in this phylum have specialized organelles called apical complex for motility.
- They possess one or more nuclei.
- They are typically heterotrophic.
- Examples include the genera Plasmodium and Toxoplasma.
Phylum Microspora and Myxozoa
- Organisms in this phylum are obligate parasites, typically of invertebrates or fish.
- They possess one or more nuclei.
- Examples include the genera Enterocytozoon and Myxobolus.
Phylum Acanthamoeba
- Organisms in this phylum have filopodia and lobopodia for motility.
- They possess one or more nuclei.
- They can be heterotrophic or autotrophic.
- Examples include the genera Acanthamoeba and Hartmannella.
Conclusion
- Protozoa are a diverse group of unicellular eukaryotic organisms that are found in a wide range of habitats.
- Levine et al. (1980) proposed a classification system for protozoa that is based on their morphological and physiological characteristics.
- This classification system recognizes seven main phyla of protozoa, each with its own unique characteristics and examples of representative genera.