Table of Contents
Introduction:
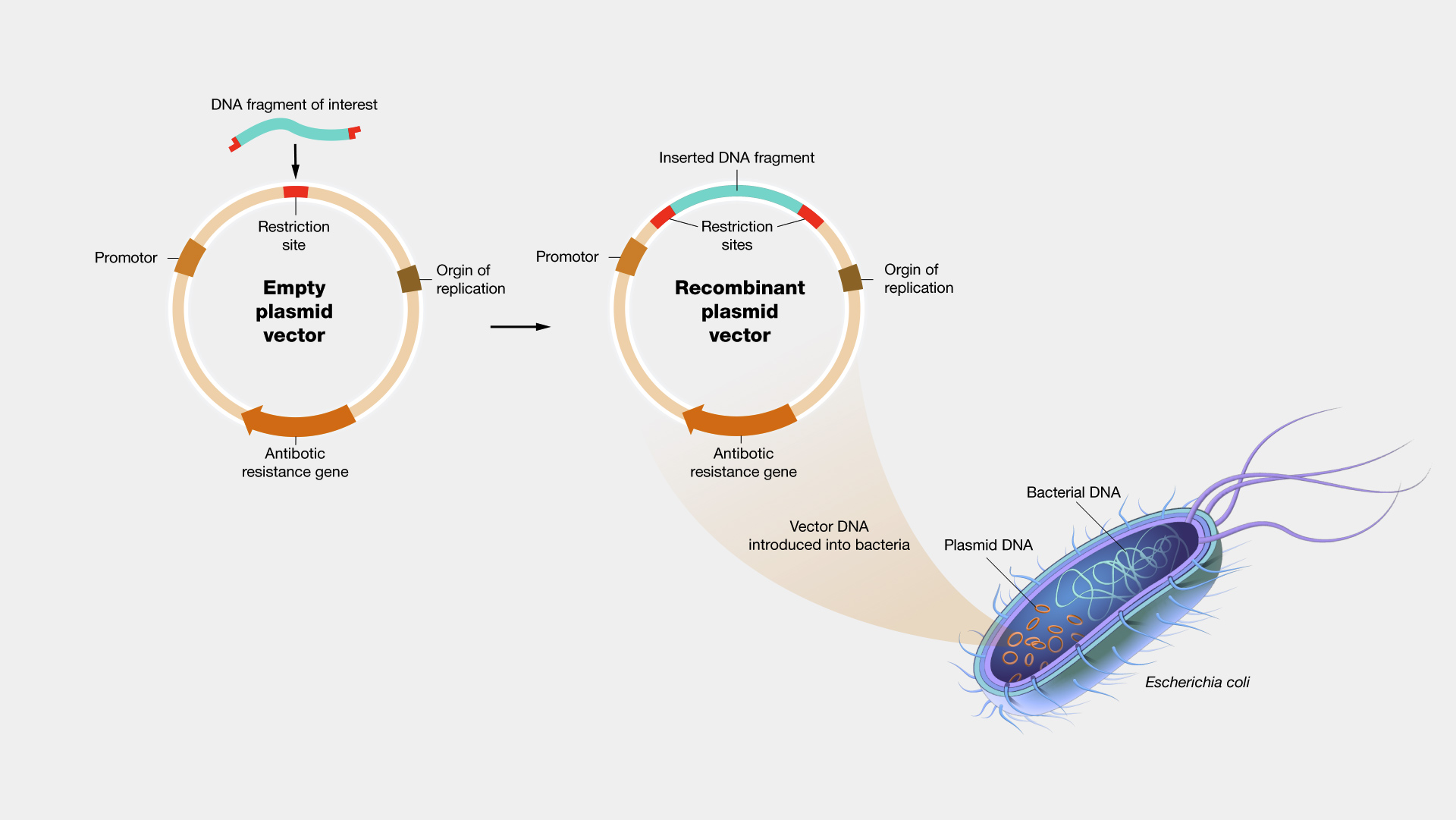
- A cloning vector is a DNA molecule that is used to introduce foreign DNA into cells for the purpose of cloning and producing large amounts of the target DNA molecule.
- Cloning vectors are typically derived from bacteria, yeast, or viruses, and they contain genetic elements that allow them to replicate and maintain their stability within host cells.
- Cloning vectors play a critical role in modern molecular biology and biotechnology, allowing scientists to study the function of genes, develop new medicines, and engineer crops with improved traits.
Types of Cloning Vectors:
- Cloning vectors can be classified into two main categories: plasmids and phages.
Plasmids:
- Plasmids are small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecules that are found in many bacteria and yeast.
- They can replicate independently of the host cell’s chromosome, making them ideal for cloning large amounts of DNA.
- Common plasmid cloning vectors include pBR322, pUC18, and pET vectors.
Phages:
- Phages are viruses that infect bacteria and can be used as cloning vectors.
- Phage cloning vectors are typically less commonly used than plasmid vectors, but they have some advantages, such as the ability to package larger DNA molecules and their ability to integrate into the host cell chromosome.
- Common phage cloning vectors include lambda phage and M13 phage.
Features of Cloning Vectors:
- Cloning vectors have several key features that are important for successful cloning and expression of target DNA molecules:
- Origin of Replication:
- The origin of replication is a specific DNA sequence that is necessary for the replication of the vector in host cells.
- Selectable Markers:
- Selectable markers are genes that provide a selective advantage to host cells that have taken up the cloning vector, allowing the cells to be easily distinguished from those that have not.
- Multiple Cloning Site:
- The multiple cloning site (MCS) is a region of the cloning vector that contains a series of restriction enzyme recognition sites that can be used to insert target DNA into the vector.
- Promoter:
- The promoter is a DNA sequence that directs the transcription of a gene.
- Reporter Gene:
- The reporter gene is a gene that is used to monitor expression of the target DNA.
Uses of Cloning Vectors:
- Cloning vectors are widely used in a variety of applications, including:
- Gene cloning and expression:
- Cloning vectors are used to insert target DNA into host cells for the purpose of cloning and producing large amounts of the target DNA.
- Production of recombinant proteins:
- Cloning vectors are used to produce recombinant proteins, which are proteins that are made from genes that have been inserted into a host organism.
- Studying gene function:
- Cloning vectors are used to study the function of genes by inserting the genes into host cells and observing the effects of the gene on the cells.
- Developing vaccines and therapies:
- Cloning vectors are used to develop vaccines and therapies by inserting genes that produce therapeutic proteins into host cells.
Conclusion:
- Cloning vectors are essential tools in molecular biology and biotechnology, allowing scientists to study the function of genes, produce large amounts of target DNA, and develop new medicines and therapies.
- There are two main types of cloning vectors: plasmids and phages, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
- Key features of cloning vectors include the origin of replication, select able markers, multiple cloning site, promoter, and reporter gene.
- Cloning vectors are widely used in various applications such as gene cloning and expression, production of recombinant proteins, studying gene function, and developing vaccines and therapies.
- The use of cloning vectors has revolutionized the field of molecular biology and biotechnology, enabling scientists to make important discoveries and advancements in the fields of medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
- It is important to note that while the use of cloning vectors has many benefits, it also raises ethical concerns, particularly with regards to genetically modified organisms. The responsible and ethical use of cloning vectors is an important consideration in the field.