Table of Contents
Introduction:
- DNA cloning refers to the process of producing multiple identical copies of a specific DNA fragment.
- It is a powerful tool in molecular biology, enabling researchers to study the function of individual genes and to produce large amounts of a specific protein for use in biotechnology and medicine.
- There are various methods for cloning DNA, including restriction enzyme cloning, PCR cloning, and gene synthesis.
Restriction Enzyme Cloning:
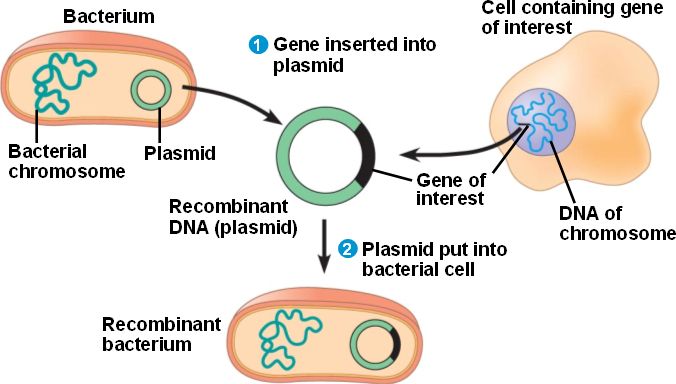
- Restriction enzyme cloning is a method for cloning DNA that uses restriction enzymes to cut the DNA molecule into specific fragments.
- The DNA fragment of interest is then ligated into a vector, such as a plasmid, which is a circular piece of DNA that can replicate independently in a host cell.
- The vector and insert are then introduced into a host cell, such as E. coli, where the vector is replicated and the insert is expressed.
- Restriction enzyme cloning is a widely used method for cloning DNA fragments, particularly in the study of gene function and in the production of recombinant proteins.
PCR Cloning:
- PCR cloning is a method for cloning DNA that uses the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to amplify a specific DNA fragment.
- The DNA fragment is amplified using primers that are complementary to the ends of the fragment, and the resulting PCR product is then ligated into a vector.
- The vector and insert are then introduced into a host cell, where the vector is replicated and the insert is expressed.
- PCR cloning is a fast and efficient method for cloning DNA fragments, particularly for cloning cDNA, which is a complementary DNA copy of mRNA.
Gene Synthesis:
- Gene synthesis is a method for synthesizing a specific DNA fragment from scratch, using a combination of chemical and biological processes.
- The DNA sequence of interest is first designed on a computer, and the individual nucleotides are then chemically assembled to produce the desired DNA fragment.
- The DNA fragment is then ligated into a vector, and the vector and insert are introduced into a host cell, where the vector is replicated and the insert is expressed.
- Gene synthesis is a useful method for cloning DNA fragments that are difficult or impossible to obtain through other methods, such as non-coding RNA or artificial genes.
Conclusion:
- DNA cloning is a powerful tool in molecular biology, enabling researchers to study the function of individual genes and to produce large amounts of a specific protein.
- There are several methods for cloning DNA, including restriction enzyme cloning, PCR cloning, and gene synthesis.
- Advances in DNA cloning technology continue to make it more efficient and less expensive, enabling new breakthroughs in our understanding of genetics and the biological world.