Table of Contents
Introduction:
DNA fingerprinting is also known as DNA profiling or genetic fingerprinting. It is a technique used to identify an individual based on their unique DNA pattern. It was first developed by Alec Jeffreys in 1985 and has since been used in a variety of applications, including criminal investigations, paternity testing, and medical research.
Principle of DNA Fingerprinting:
- The principle is based on the fact that everyone’s DNA is unique, with the exception of identical twins.
- It is performed by analyzing specific regions of the DNA known as short tandem repeats (STRs) or minisatellites.
- These regions are located in non-coding areas of the DNA and do not contain information for the development of an organism, but they are highly variable among individuals.
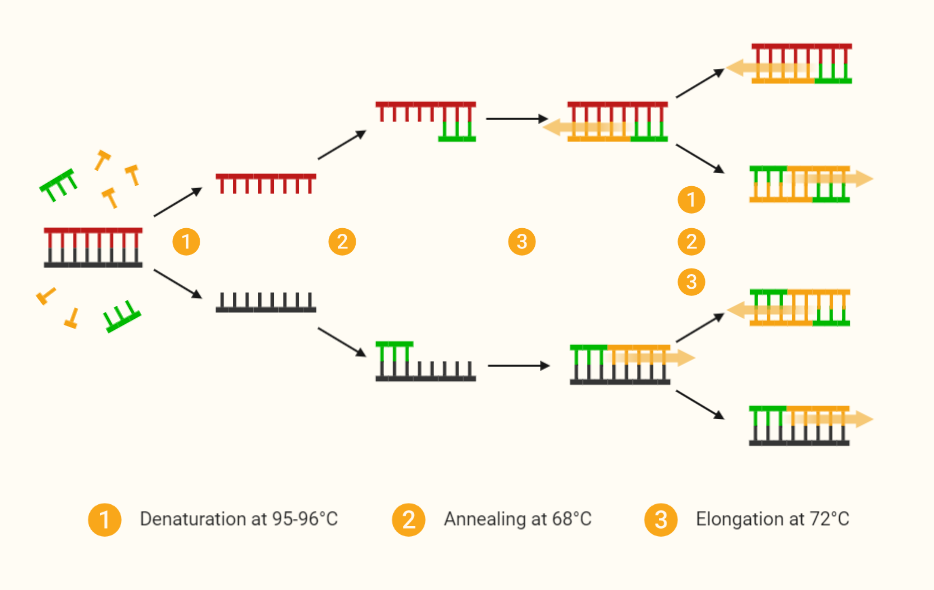
Methods of DNA Fingerprinting:
There are several methods of this, but the most common ones are:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): This method amplifies specific regions of the DNA using enzymes.
- Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP): This method cuts the DNA at specific locations using enzymes known as restriction endonucleases.
Applications:
- Criminal investigations: It is used to identify suspects and link them to crimes by comparing their DNA to samples found at crime scenes.
- Paternity testing: It can be used to determine the father of a child by comparing the child’s DNA to that of the alleged father.
- Medical research: It is used in medical research to study inherited diseases and to track the spread of infectious diseases.
Advantages:
- DNA fingerprinting is a highly accurate method of identification.
- It can be used to link suspects to crimes even if they have no prior criminal record.
- It can also be used to identify human remains in cases of mass disasters or unidentified remains.
Disadvantages:
- DNA fingerprinting can be expensive and time-consuming.
- It requires specialized equipment and trained personnel.
- The collection of DNA samples can be invasive and may raise ethical concerns.
- Conclusion:
- It is a powerful tool for identification. It has many important applications in forensic science, paternity testing, and medical research.
- However, it also raises important ethical and legal issues and must be used with caution.