Table of Contents
Introduction to DNA microarray technique:
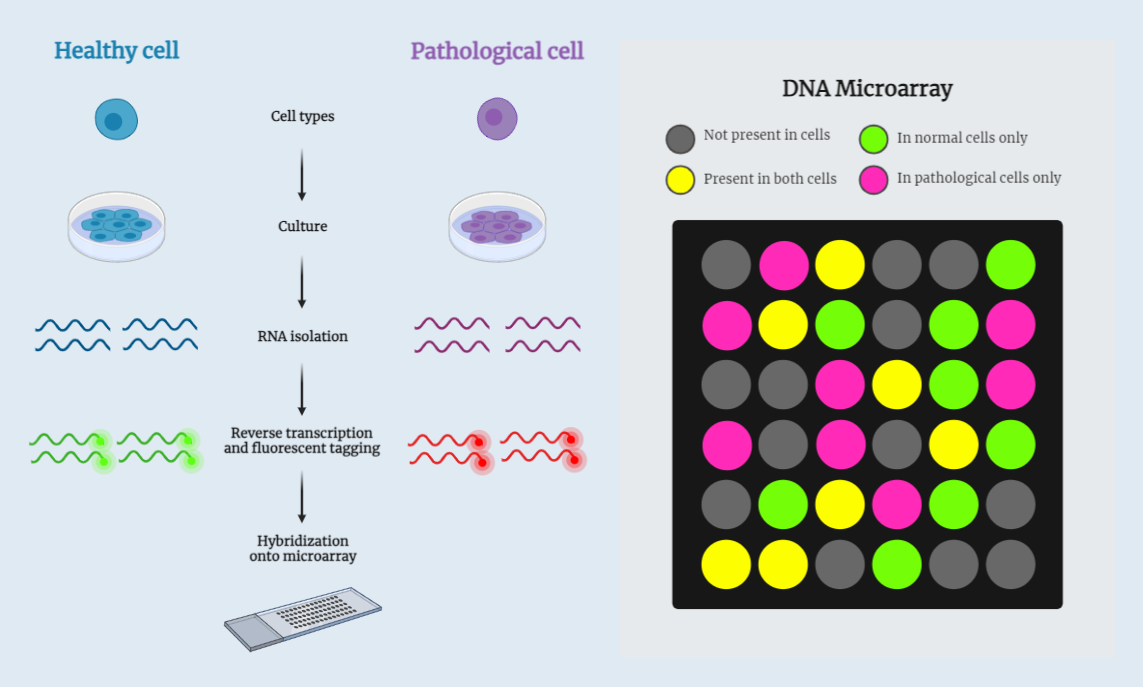
DNA microarray technique is a high-throughput technique used to study the expression levels of thousands of genes in a single experiment. DNA microarray technology allows researchers to detect the presence and quantity of specific nucleic acid sequences in a sample, such as DNA or RNA. The technique involves immobilizing known sequences of DNA, called probes, on a solid surface and hybridizing them with fluorescently labeled target sequences.
Principles of DNA Microarray technique:
- The DNA microarray technique is based on the principle of hybridization, where a labeled target sequence binds to a complementary probe sequence on the microarray.
- The intensity of the fluorescence emitted by the target sequence is proportional to the amount of the target sequence present in the sample.
- The microarray can be used to study gene expression by comparing the fluorescence intensities between different samples or conditions.
Procedure of DNA microarray technique:
- DNA microarray analysis involves the following steps:
- Isolation of total RNA or cDNA from the sample of interest
- Labeling of the RNA or cDNA with fluorescent dyes or biotin
- Hybridization of the labeled RNA or cDNA to the microarray
- Scanning of the microarray to measure the fluorescence intensity of each probe
- Data analysis to identify differentially expressed genes.
Applications:
- DNA microarray is used in a variety of fields, including genetics, genomics, and medicine.
- DNA microarray can be used to study gene expression patterns in different samples or conditions, such as disease or drug treatment.
- DNA microarray can also be used to identify genetic variations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or copy number variations (CNVs).
Limitations:
- DNA microarray is a relatively expensive and labour-intensive technique, as it requires the production of large amounts of labeled RNA or cDNA and the preparation of the microarray.
- DNA microarray may also suffer from technical biases, such as non-specific binding or variations in the labeling efficiency, which can lead to false-positive or false-negative results.
- DNA microarray also requires a large amount of sample, which may limit the application in some samples.
Conclusion:
- DNA microarray is a powerful technique that allows researchers to study the expression levels of thousands of genes in a single experiment.
- DNA microarray has been widely used to study gene expression patterns in different samples or conditions.
- However, This is a technically demanding technique and may suffer from some biases and limitations. Newer techniques such as RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) are more efficient and more sensitive, which can overcome some of the limitations of DNA microarray.