Table of Contents
Introduction to ECG (Electrocardiogram) :
The ECG (electrocardiogram) is a diagnostic tool that is used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. It is a non-invasive test that records the electrical impulses that travel through the heart muscle, and displays them on a graph as waves. The ECG is used to diagnose heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac disorders.
Principles of the ECG (Electrocardiogram) Technique:
- The ECG is a measurement of the electrical activity of the heart, which is generated by the depolarization and repolarization of the heart muscle.
- The electrical impulses generated by the heart are conducted through the heart muscle and then to the surface of the body where they can be recorded.
- Electrodes are placed on the skin at specific locations on the body to pick up these electrical impulses and transmit them to an ECG machine for analysis.
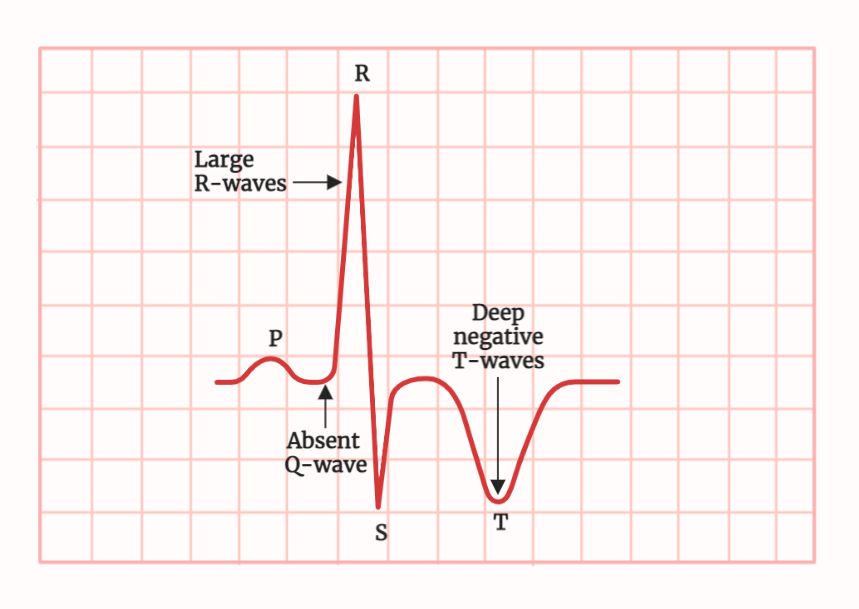
Components of an ECG (Electrocardiogram) :
- An ECG is composed of several different waves and intervals that provide information about the electrical activity of the heart.
- The P wave represents the depolarization of the atria.
- The QRS complex represents the depolarization of the ventricles.
- The T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles.
- The PR interval, QT interval, and ST segment are also important components of an ECG.
Leads and Placement:
- The ECG is recorded using electrodes that are placed at specific locations on the body, called leads.
- There are several different types of leads, including standard 12-lead ECG, which is most commonly used in clinical practice.
- The placement of the electrodes is important for accurate ECG interpretation, and they are placed on the limbs and chest in specific positions in order to capture the electrical activity of the heart from different angles.
Applications:
- The ECG is a widely used diagnostic tool for the evaluation of heart conditions.
- It is used to diagnose arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac disorders.
- It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to detect changes in cardiac function over time.
Limitations and Challenges:
- The ECG is a non-invasive test, but it does have some limitations.
- It can be affected by movement and muscle activity, and may not be able to detect certain types of heart conditions, such as those caused by structural heart disease.
- In addition, ECG interpretation can be challenging, and requires a certain level of expertise.
Conclusion:
The ECG is a widely used diagnostic tool for the evaluation of heart conditions. It is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart and displays it as waves on a graph. The ECG is used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac disorders. Despite its limitations, the ECG remains an important diagnostic tool in the field of cardiology, and its interpretation requires a certain level of expertise.