Table of Contents
Introduction:
- Eukaryotic DNA replication is the process of duplication of genetic material before cell division
- Semi-conservative process, meaning that each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one new strand
- Tightly regulated and coordinated to ensure accurate replication
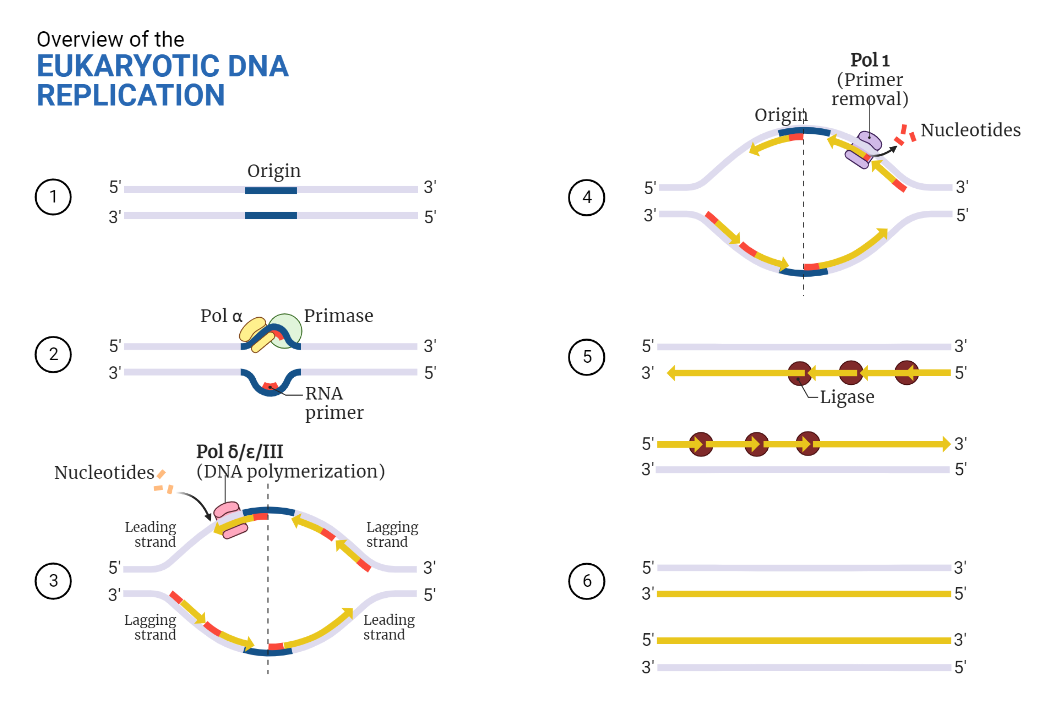
Steps of Eukaryotic DNA Replication
Pre-replication Complex formation of Eukaryotic DNA Replication:
- The first step in eukaryotic DNA replication is the formation of pre-replication complex. This is the point where the replication machinery is assembled and the origin of replication is recognized.
- The pre-replication complex includes a number of proteins such as:
- Replication Origin Binding proteins (ORC): These proteins bind to the replication origin and recruit other replication proteins to initiate replication
- Cdc6 and Cdt1: Cdc6 and Cdt1 are required for the loading of the replicative helicase, Mcm2-7 on the replication origin.
- MCM2-7: The replicative helicase, Mcm2-7 is responsible for the unwinding of the DNA double helix at the replication origin, creating replication forks.
Initiation:
- The next step is the initiation of replication, which is triggered by the binding of the helicase enzyme, Mcm2-7 to the origin of replication.
- The helicase enzyme, Mcm2-7 unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication origin and creates replication forks.
- This process is tightly regulated by the presence of replication origin binding proteins (ORC) and the replication licensing system.
Elongation:
- The elongation step is carried out by a number of enzymes, including:
- DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing strand.
- Primase: Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer, which serves as a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin adding nucleotides.
Termination:
- The final step in eukaryotic DNA replication is the termination of replication.
- Termination is not well understood in eukaryotic cells, but it is thought to involve the dissociation of the replication machinery from the chromosomes and the resolution of replication intermediates.
In summary, Eukaryotic DNA replication is a complex process that is tightly regulated and coordinated to ensure accurate replication. A number of proteins are involved in this process such as ORC, Cdc6, Cdt1, Mcm2-7 and DNA polymerase, Primase. These proteins work together to initiate replication at multiple replication origins present on the chromosomes, elongate the strands and eventually terminate the replication process.