Table of Contents
Introduction
- Classification, systematics, and taxonomy are the scientific disciplines that study the diversity of living organisms and their relationships to one another.
- They are essential for understanding the natural world and for making informed decisions about conservation, management, and biotechnology.
Classification
- Classification is the process of organizing living organisms into groups based on their characteristics.
- The goal of classification is to reflect the evolutionary relationships among organisms and to make it easier to study and understand them.
Taxonomy
- Taxonomy is the branch of biology that deals with the identification, description, and naming of living organisms.
- It involves the systematic arrangement of organisms into a hierarchy of categories, or taxa (singular: taxon), based on their characteristics.
Systematics
- Systematics is the study of the diversity of living organisms and their relationships to one another.
- It includes both the process of classification and the resulting system of classification.
Types of Classification
- There are several different types of classification, including:
- Artificial classification: Based on arbitrary criteria, such as external appearance or economic importance.
- Natural classification: Based on evolutionary relationships.
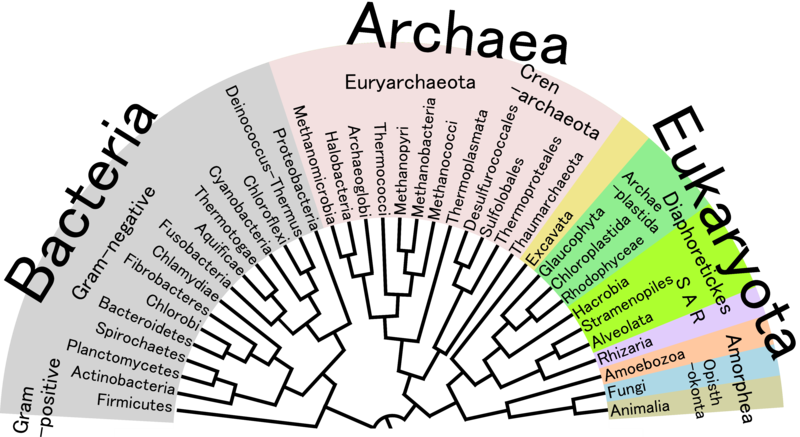
- Phylogenetic classification: Based on the evolutionary history of organisms, as inferred from molecular, morphological, and/or behavioral data.
Hierarchy of Taxa
- The hierarchy of taxa, from most inclusive to most exclusive, is:
- Domain
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
Examples
- A well-known example of classification is the Linnaean system, which was developed by Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century.
- It uses a hierarchical system of classification, with the major categories being: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
- For example, humans belong to the kingdom Animalia, the phylum Chordata, the class Mammalia, the order Primates, the family Hominidae, the genus Homo, and the species Homo sapiens.
- Another example is the use of phylogenetic classification, in which organisms are classified based on their evolutionary history.
- For example, a phylogenetic tree can be used to show the evolutionary relationships among different species of primates.
Conclusion
- Classification, systematics, and taxonomy are important fields of study that allow us to understand the diversity of life and the relationships among living organisms.
- They have many practical applications, such as in conservation, management, and biotechnology, and will continue to be important for understanding the natural world.