Table of Contents
Fertilization: The Fusion of Gametes
Introduction
Fertilization is the process by which male and female gametes (sperm and egg) unite to form a diploid zygote, initiating the development of a new organism. This process is crucial for sexual reproduction and involves several intricate steps.
Steps of Fertilization
- Sperm Capacitation
- Definition: The physiological changes sperm undergo to become capable of penetrating and fertilizing an egg.
- Key Changes: Increased motility, changes in the sperm membrane to facilitate binding to the egg.
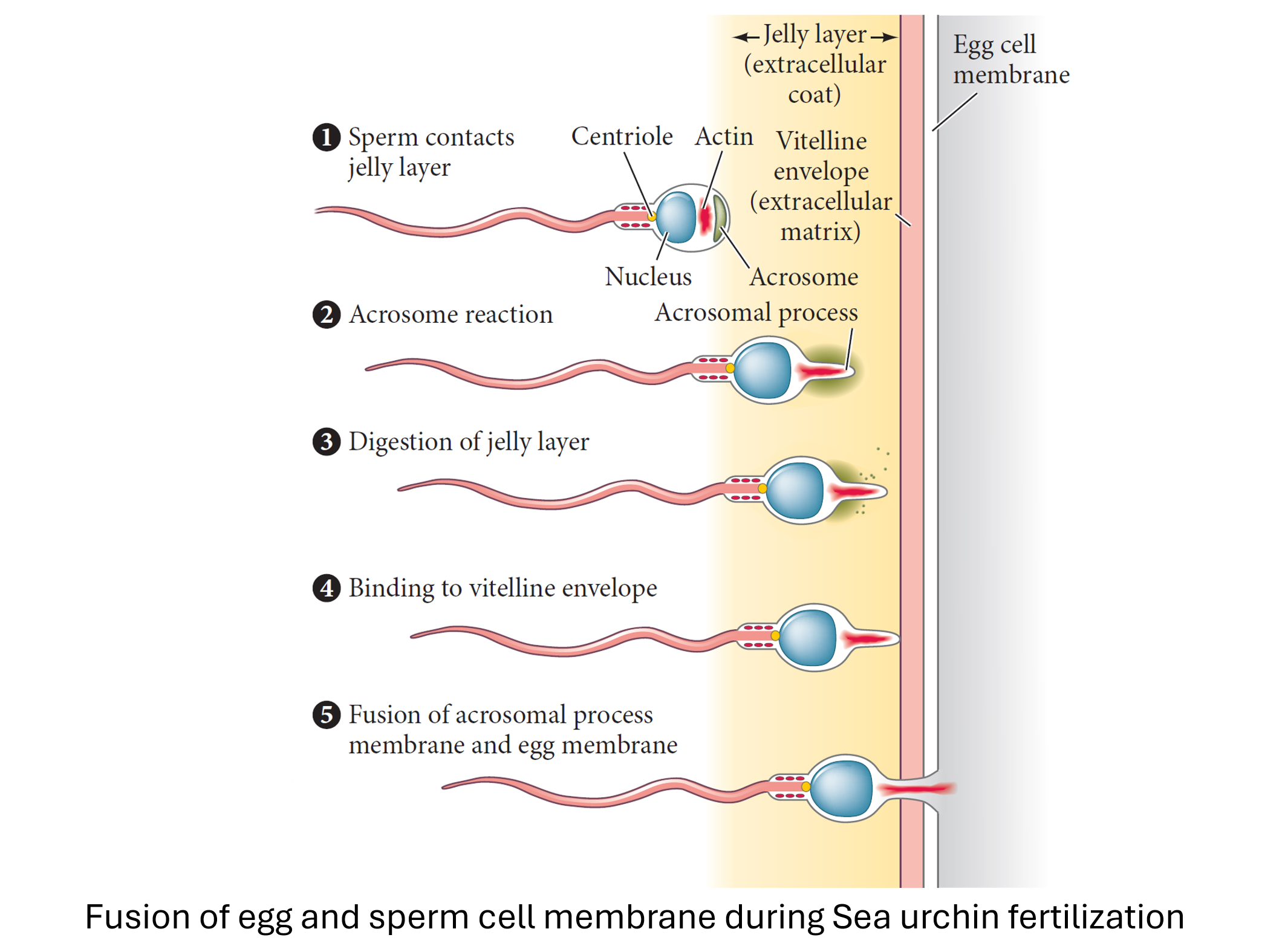
- Acrosome Reaction
- Definition: The release of digestive enzymes from the acrosome (a cap-like structure on the sperm head) when the sperm comes into contact with the egg’s zona pellucida.
- Purpose: These enzymes help the sperm penetrate the zona pellucida, the protective glycoprotein layer surrounding the egg.
- Penetration of the Zona Pellucida
- Process: The sperm uses the enzymes released during the acrosome reaction to digest a path through the zona pellucida.
- Outcome: The sperm reaches the perivitelline space, the area between the zona pellucida and the egg membrane.
- Sperm-Egg Binding
- Mechanism: Specific proteins on the sperm surface bind to receptors on the egg membrane.
- Significance: This binding is species-specific, ensuring that only sperm from the same species can fertilize the egg.
- Fusion of Sperm and Egg Membranes
- Process: The membranes of the sperm and egg fuse, allowing the sperm nucleus and other organelles to enter the egg cytoplasm.
- Result: The egg completes its second meiotic division, and the male and female pronuclei form.
- Formation of the Zygote
- Pronuclear Fusion: The male and female pronuclei move towards each other and fuse, combining their genetic material.
- Outcome: A diploid zygote is formed, containing a complete set of chromosomes.
Post-Fertilization Events
- Cortical Reaction
- Definition: A reaction that occurs immediately after sperm entry, where cortical granules in the egg release their contents into the perivitelline space.
- Purpose: This reaction prevents polyspermy, ensuring that only one sperm fertilizes the egg.
- Activation of the Egg
- Process: The egg undergoes metabolic and structural changes, initiating embryonic development.
- Key Changes: Increased protein synthesis, DNA replication, and the beginning of cell division.
Importance of Fertilization
- Genetic Diversity: Combines genetic material from two parents, increasing genetic variation in the offspring.
- Species Continuity: Ensures the continuation of species through sexual reproduction.
- Development Initiation: Triggers the processes that lead to the development of a new organism.
Conclusion
Fertilization is a complex and highly regulated process that ensures the successful union of sperm and egg, leading to the formation of a new organism. Understanding the steps and mechanisms involved provides insight into the fundamental aspects of reproductive biology.