Table of Contents
Definition:
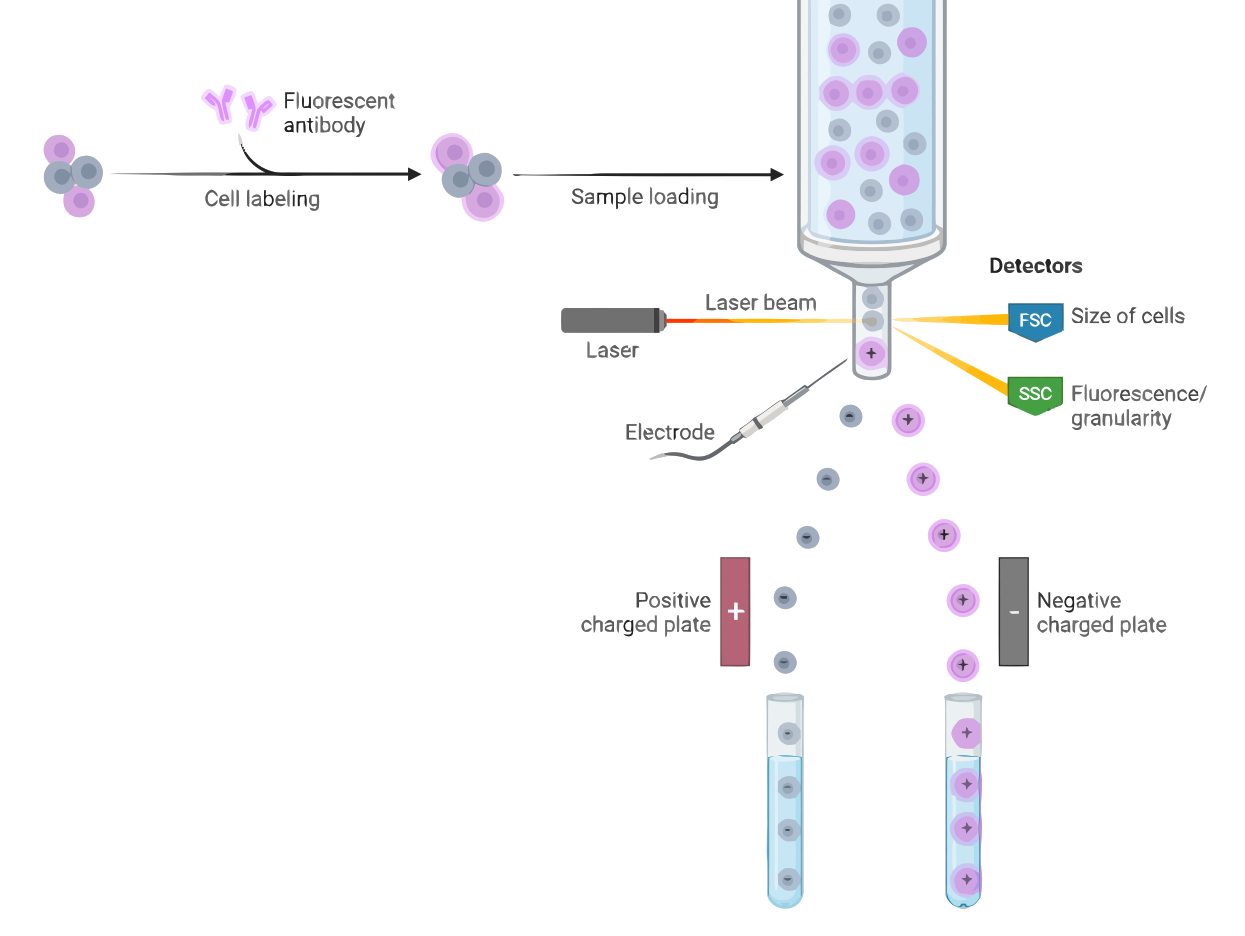
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) is a technique used to separate and purify cells or particles based on their fluorescence properties. It involves passing a suspension of cells or particles through a flow cytometer, which uses lasers and detectors to measure the fluorescence of each individual cell or particle. The cells or particles are then sorted based on their fluorescence properties using a mechanism such as an electric field or a nozzle.
Principle:
The principle of Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) is based on the ability of cells or particles to bind to fluorescently-labeled antibodies or other probes. These probes bind to specific cellular or particle markers, such as proteins or nucleic acids, and emit light when excited by a laser. By measuring the fluorescence of each individual cell or particle, it is possible to identify and sort cells or particles with specific markers.
Steps:
- Sample preparation: The cells or particles are prepared by suspending them in a buffer and adding the appropriate fluorescently-labeled probes.
- Sample injection: The prepared sample is injected into the flow cytometer.
- Analysis: The flow cytometer uses lasers and detectors to measure the fluorescence of each individual cell or particle.
- Sorting: The cells or particles are sorted based on their fluorescence properties using a mechanism such as an electric field or a nozzle.
Application:
- Immunology: FACS is commonly used to isolate and purify specific subpopulations of immune cells, such as T cells or B cells, for further analysis.
- Genetics: FACS can be used to sort and purify specific subpopulations of cells or particles based on their genetic markers, such as specific genes or chromosomal abnormalities.
- Cancer research: FACS can be used to sort and purify cancer cells for further analysis, such as gene expression profiling or drug susceptibility testing.
- Stem cell research: FACS can be used to isolate and purify specific subpopulations of stem cells for further analysis or transplantation.
- Other applications of FACS include protein purification, plant biology, and environmental monitoring.
Note: Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) is a powerful technique that allows researchers to study the properties of specific cell populations in great detail. However, it is important to keep in mind that FACS can only sort cells or particles based on the markers that are available to bind to the fluorescently-labeled probes and that are being analyzed. It does not sort based on the functional activity of cells or particles.