Table of Contents
I. Introduction
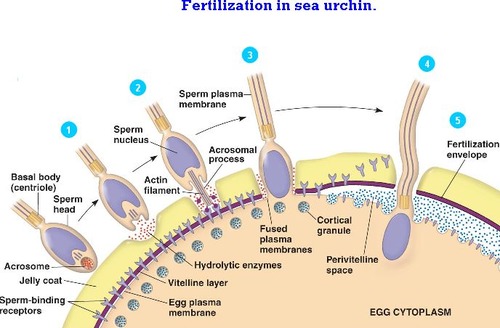
- Sperm-egg fusion is the process of the fusion of the sperm cell membrane with the egg cell membrane
- This process can be facilitated by specific “fusogenic” proteins and is an active process
- In the normal case, only one sperm enters the egg, leading to monospermy
II. Fusion of Sperm and Egg Cell Membranes
- The fusion of sperm and egg cell membranes is caused by the polymerization of actin, a protein found in both gametes
- In sea urchins, bindin plays a role as a fusogenic protein and causes the sperm and egg membranes to fuse
III. Monospermy
- The entrance of only one sperm leads to the formation of the diploid nucleus of the fertilized egg (zygote)
- In most animals, only one sperm provides a haploid nucleus and centriole
IV. Polyspermy
- Polyspermy occurs when multiple sperm enter the egg
- This leads to disastrous consequences in most organisms, including triploid nuclei and abnormal cell division
V. Fast Block to Polyspermy
- The most straightforward way to prevent polyspermy is to prevent more than one sperm from entering the egg
- The fast block to polyspermy is achieved by an electric change in the egg cell membrane
- This change occurs immediately upon the entry of the first sperm and is caused by a small influx of sodium ions (Na+)
- The change in the electric potential of the egg cell membrane prevents more sperm from entering the egg
- This fast block to polyspermy can be prevented by artificially keeping the membrane potential of the egg positive
VI. Slow Block to Polyspermy
- The slow block to polyspermy is a secondary mechanism that helps prevent polyspermy in the egg.
- After the fast block to polyspermy has been activated, the cortical granules within the egg undergo exocytosis.
- The cortical granules contain enzymes that create a physical barrier between the egg and the surrounding water, preventing further sperm from entering the egg.
- This process takes place over a longer time frame than the fast block to polyspermy, typically taking several minutes to complete.
- The slow block to polyspermy provides a backup mechanism to ensure that polyspermy is prevented, even if the fast block fails.
VII. Conclusion
- The fusion of the sperm and egg cell membranes is a crucial step in fertilization and the formation of the diploid nucleus
- The fast block to polyspermy helps to prevent disastrous consequences by preventing multiple sperm from entering the egg.