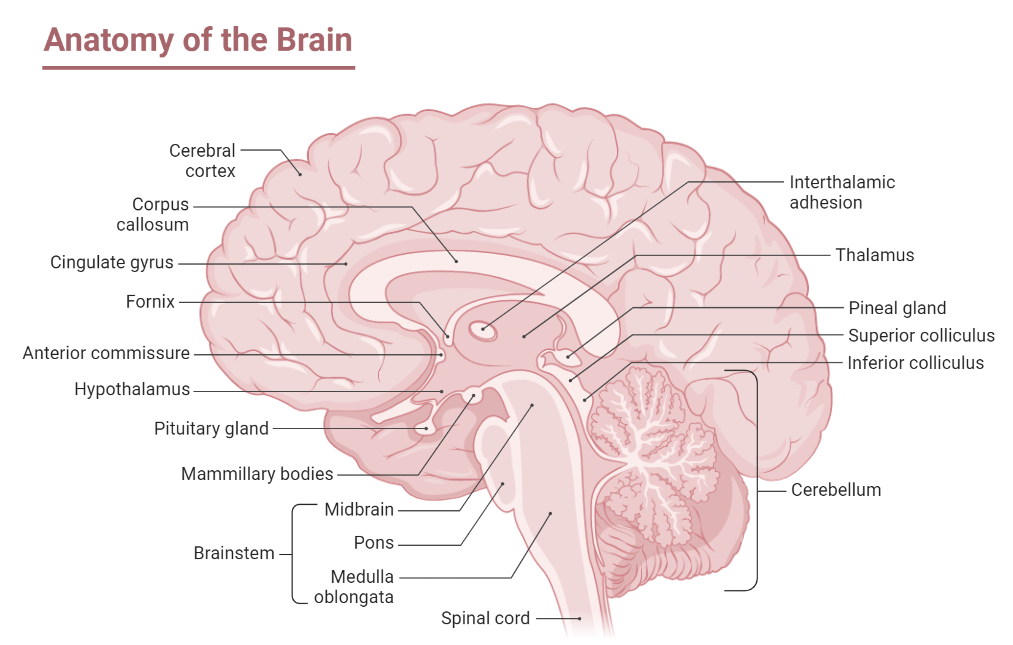
The brain is the most sophisticated organ in the human body, directing and coordinating all of the body’s operations. It is divided into three sections: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain.
Table of Contents
Forebrain
- The forebrain is the largest and most complicated portion of the brain.
- It includes the cerebral cortex, which is in charge of higher cognitive skills like reasoning, memory, and decision-making.
- The cerebral cortex is divided into four major lobes: the frontal lobes, the parietal lobes, the temporal lobes, and the occipital lobes.
- The frontal lobes are in charge of planning, problem solving, and decision making.
- The parietal lobes are in charge of processing sensory information such as touch, warmth, and pain.
- Memory, language, and hearing are all handled by the temporal lobes.
- Vision is controlled by the occipital lobes.
Thalamus and hypothalamus
- The thalamus and hypothalamus, which serve as relay stations for sensory information, are also part of the forebrain.
- The thalamus receives and passes sensory information from the body to the relevant parts of the cerebral cortex.
- The hypothalamus is in charge of maintaining homeostasis in the body, as well as controlling hunger, thirst, and body temperature.
Midbrain
- The midbrain is placed between the forebrain and the hindbrain.
- It regulates movement, vision, and hearing.
- The tectum, which is located in the midbrain, is in charge of conveying visual and auditory information to the cerebral cortex.
- It also contains the substantia nigra, which is crucial for movement regulation and is impaired in Parkinson’s disease.
Cerebellum
- The cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata make up the hindbrain, which is positioned near the base of the skull.
- The cerebellum is in charge of coordinating muscle action and balance.
- The pons is involved in sleep and arousal, as well as transferring information between the cerebellum and the cerebral cortex.
- The medulla oblongata regulates vital activities such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
To summarise, the brain is a highly complex and detailed organ, with diverse areas and structures specialised for different functions. The division of the brain into forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain compartments aids in the organisation and comprehension of the brain’s numerous tasks. Each of these regions comprises particular structures that conduct various roles ranging from transmitting and processing sensory information to coordinating movement and regulating key physiological functions.