Table of Contents
Introduction to Human Nervous System
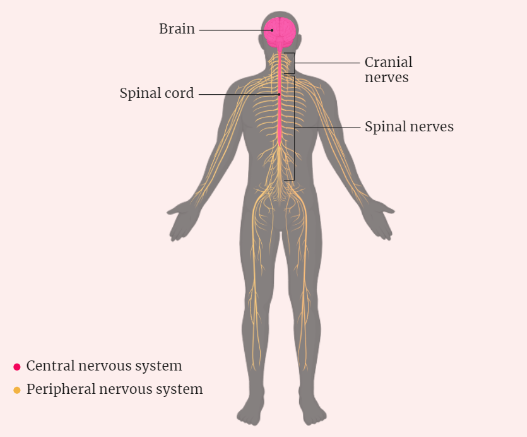
The human nervous system is a complex network of specialized cells and structures that coordinate communication and control throughout the body. Divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), it plays a pivotal role in regulating bodily functions, processing sensory information, and enabling conscious thought.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord. The brain, housed within the skull, consists of various regions responsible for different functions: the cerebrum controls voluntary actions and cognitive functions, the cerebellum coordinates motor movements, the brainstem regulates essential functions like breathing and heart rate, and the diencephalon manages processes like sleep and hormone secretion.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The PNS extends from the CNS to the rest of the body and includes sensory and motor neurons. It is further categorized into the somatic nervous system, governing voluntary actions, and the autonomic nervous system, controlling involuntary functions. The latter is subdivided into the sympathetic (fight-or-flight response) and parasympathetic (rest and digest) systems.
Neurons and Neural Communication
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system, transmitting electrical signals called action potentials. A neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites (receiving signals), and an axon (sending signals). Synapses, specialized junctions between neurons, enable communication through neurotransmitters.
Neural Signaling
Neural signaling involves transmission of information via action potentials. Resting potential, the neuron’s stable state, becomes depolarized when stimulated, generating an action potential. This electrical signal travels along the axon, triggering neurotransmitter release at the synapse.
Sensory and Motor Systems
Sensory neurons gather information from sensory receptors (e.g., touch, sight, hearing) and transmit it to the CNS. Motor neurons receive instructions from the CNS and elicit appropriate responses in muscles or glands.
Brain Function and Complexity
The brain’s intricate structure underlies its diverse functions. Cerebral hemispheres control distinct tasks, with the left hemisphere specializing in language and logic, while the right hemisphere excels in creativity and spatial awareness.
Nervous System Disorders
Disruptions in the nervous system lead to various disorders. Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s result in cognitive and motor impairments. Nervous system injuries, such as spinal cord damage, may lead to paralysis.
Plasticity and Adaptation
Neural plasticity allows the nervous system to adapt and change in response to experiences. Learning and memory involve strengthening or weakening synapses through repeated stimulation or neglect.
Current Research and Future Prospects
Advances in neuroscience continue to unravel the complexities of the human nervous system. Research spans neuroimaging techniques, studying brain connectivity, and developing treatments for neurological disorders.
Conclusion
The human nervous system orchestrates communication, control, and cognition. Its intricate components, from neurons to brain regions, facilitate sensory perception, motor responses, and conscious thought. Uncovering its functions and mechanisms contributes to a deeper understanding of human behavior, health, and potential therapeutic interventions.