Table of Contents
Introduction
Ion exchange chromatography (IEC) is a type of liquid chromatography that separates molecules based on their charge. It is a widely used technique in biochemistry and analytical chemistry for the purification and isolation of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules.
Principles of Ion Exchange Chromatography
IEC utilizes a stationary phase, which is a solid matrix that is functionalized with ionizable groups, and a mobile phase, which is a liquid that flows through the matrix. The stationary phase is typically a solid support such as beads or a packed column. The ionizable groups on the stationary phase can be either positively or negatively charged, and they interact with the oppositely charged species in the mobile phase.
Separation Mechanism
The separation of molecules in IEC is based on the interaction between the ionizable groups on the stationary phase and the oppositely charged species in the mobile phase. When a molecule with a charge that is opposite to the charge of the ionizable group binds to the stationary phase, it is said to be adsorbed. The molecules that are not adsorbed will pass through the column and are referred to as eluted. The elution of molecules from the column can be achieved by altering the mobile phase, such as by changing the pH or the salt concentration, to disrupt the binding of the molecules to the stationary phase.
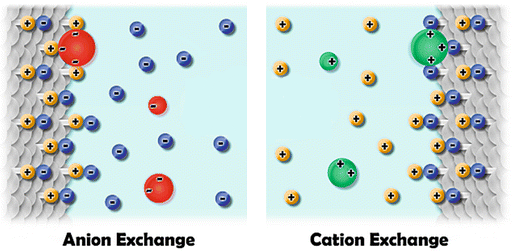
Types of Ion Exchange Chromatography
There are two main types of IEC: cation exchange chromatography and anion exchange chromatography.
Types of Ion Exchange Chromatography:
Cation Exchange Chromatography (CEC)
Cation exchange chromatography is a type of IEC that utilizes a stationary phase that is functionalized with negatively charged groups, such as carboxylic acids. In CEC, positively charged molecules in the mobile phase bind to the negatively charged groups on the stationary phase and are adsorbed. The elution of molecules from the column is achieved by altering the mobile phase, such as by increasing the salt concentration, to disrupt the binding of the molecules to the stationary phase. CEC is commonly used for the purification and isolation of positively charged biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.
Anion Exchange Chromatography (AEC)
Anion exchange chromatography is a type of IEC that utilizes a stationary phase that is functionalized with positively charged groups, such as amines. In AEC, negatively charged molecules in the mobile phase bind to the positively charged groups on the stationary phase and are adsorbed. The elution of molecules from the column is achieved by altering the mobile phase, such as by decreasing the pH or increasing the salt concentration, to disrupt the binding of the molecules to the stationary phase. AEC is commonly used for the purification and isolation of negatively charged biomolecules such as nucleic acids and small molecules.
Applications
- Purification and isolation of biomolecules: IEC is widely used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry for the purification and isolation of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules. The charge of these biomolecules can be used to selectively bind them to the stationary phase, allowing for efficient purification and isolation.
- Analysis of inorganic ions: IEC can also be used to separate and analyze inorganic ions such as metal ions, which can have a wide range of applications in fields such as environmental chemistry and geochemistry.
- Water purification: IEC can be used to remove contaminants from water by binding them to the stationary phase. This includes ions such as heavy metals and radioactive ions, as well as organic molecules such as dyes and pesticides.
- Food and beverage industry: IEC can be used in the food and beverage industry for the purification of food ingredients, such as sugars and amino acids, and the analysis of food additives.
- Pharmaceutical industry: IEC is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the purification of drugs and other compounds, as well as the analysis of impurities.
- Biotechnology: IEC is used in the biotechnology industry for the purification of enzymes and other biomolecules for use in industrial processes.
- Biomedical research: IEC is used in biomedical research for the purification of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids for use in assays and other experiments.
- Environmental analysis: IEC can be used to analyze environmental samples, such as soil and water, for the presence of contaminants and other ions of interest.