Table of Contents
Introduction
Isolating pure RNA is a fundamental step in molecular biology research. Whether you’re investigating gene expression patterns or preparing RNA for downstream analyses, obtaining intact and high-quality RNA is essential. There are two primary RNA extraction techniques: total RNA isolation and mRNA isolation.
Total RNA Isolation
Total RNA isolation is commonly used when pure RNA is required for experiments. These techniques are less laborious and time-consuming than mRNA isolation. The choice of method depends on the nature of the RNA needed and the specific application.
Techniques for Total RNA Isolation
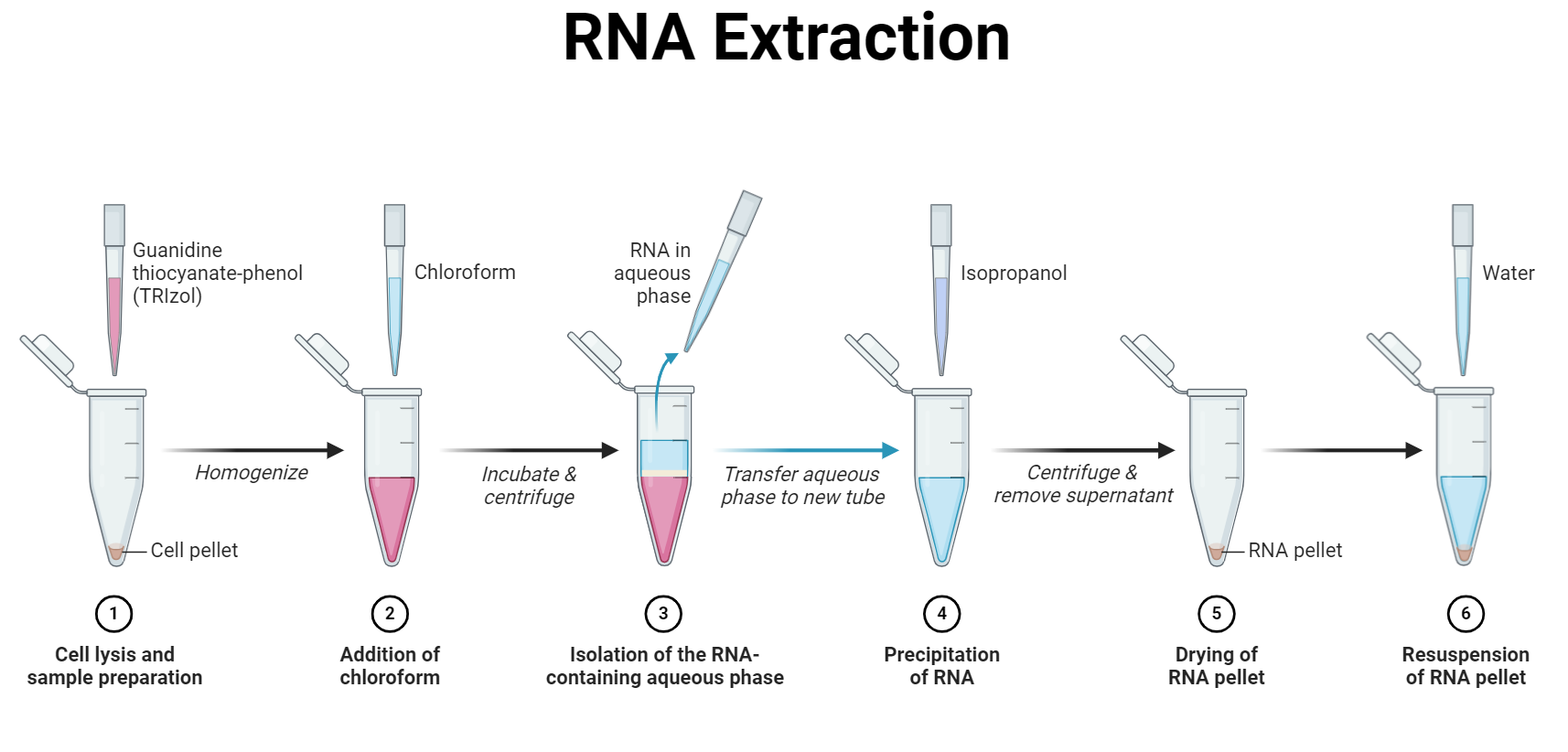
- Phenol-Chloroform Extraction:
- Principle:
- Differential solubility of RNA, DNA, and proteins in phenol and chloroform.
- Phenol denatures proteins, chloroform separates phases, and RNA remains in the aqueous phase.
- Procedure:
- Lysate preparation.
- Phenol-chloroform extraction.
- Ethanol precipitation for RNA concentration.
- Advantages:
- Effective for large-scale RNA extraction.
- Removes most contaminants.
- Suitable for various sample types.
- Principle:
- Spin Column Purification:
- Principle:
- Silica-based columns with selective binding properties.
- RNA binds to the column, contaminants are washed away.
- Procedure:
- Lysate loaded onto the column.
- Contaminants washed out.
- RNA eluted.
- Advantages:
- Fast and convenient.
- High-quality RNA.
- Scalable for small to moderate sample sizes.
- Principle:
- Magnetic Bead-Based Methods:
- Principle:
- Magnetic beads coated with RNA-binding molecules capture RNA.
- Beads separated using a magnetic field.
- Procedure:
- Lysate mixed with magnetic beads.
- Beads capture RNA.
- Beads collected using a magnet.
- RNA eluted.
- Advantages:
- Automation-friendly.
- High yield and purity.
- Compatible with various sample types.
- Principle:

Conclusion
Select the appropriate RNA isolation method based on sample characteristics, contaminant types, target RNA length, abundance, scale of sample processing, and downstream analyses.
References:
- Surzycki, S. (2000). Basic Techniques in Molecular Biology. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
- NEB RNA Extraction and Purification