Table of Contents
Introduction to Microtubular arrangement:
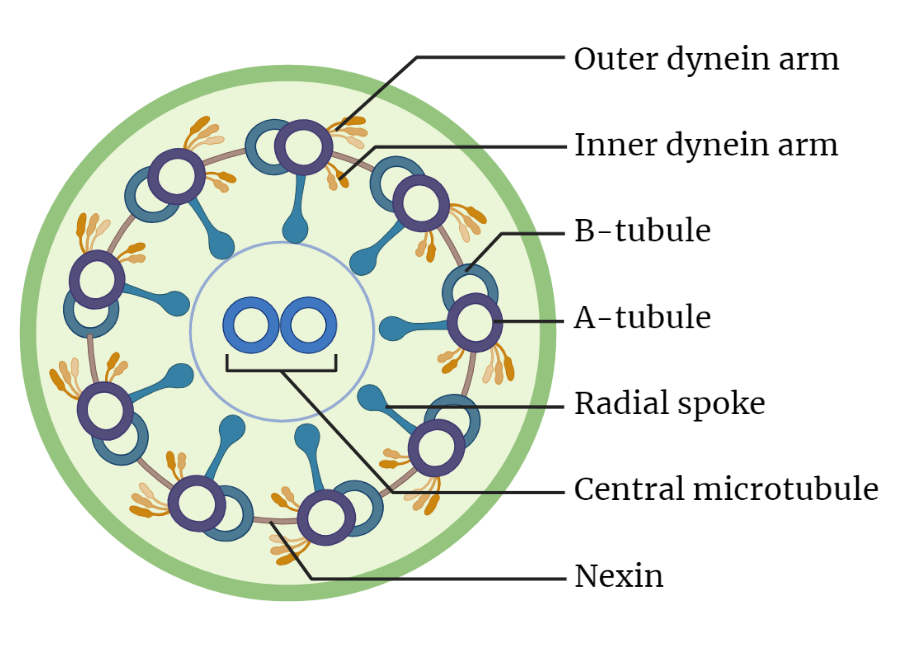
The 9+2 microtubular arrangement is a unique structure found in cilia and flagella, which are hair-like structures that protrude from the surface of cells and are used for movement. The 9+2 microtubular arrangement consists of 9 doublet microtubules surrounding a central pair of microtubules, hence the name 9+2.
Doublet Microtubules:
The 9 doublet microtubules are composed of two microtubules, one microtubule called A-tubule and the other called B-tubule, that are closely associated and are held together by a protein called nexin.
Central Pair Microtubules:
The central pair of microtubules, also known as the “9+0” microtubules, are located in the center of the cilium or flagellum and are responsible for the sliding movement of the doublet microtubules.
Dynein:
The sliding movement of the doublet microtubules is caused by the action of a motor protein called dynein. Dynein is located on the A-tubules of the doublet microtubules and uses ATP as an energy source to generate movement.
Radial spokes:
Connect the central pair microtubules to the doublet microtubules.
Function:
The 9+2 microtubular arrangement is responsible for the coordinated movement of cilia and flagella. The sliding movement of the doublet microtubules generates a wavelike motion that propels the cilia or flagella forward. This coordinated movement is crucial for functions such as cell movement, fluid movement in the respiratory and reproductive tracts, and the movement of sperm.
Cilia:
They are short and numerous, they are involved in movement of fluids and mucus on the cell surface.
Flagella:
They are long and few, they are responsible for the movement of cells such as sperm.
Conclusion
The 9+2 microtubular arrangement is a unique structure found in cilia and flagella, which are hair-like structures that protrude from the surface of cells and are used for movement. This structure is composed of 9 doublet microtubules surrounding a central pair of microtubules, and is responsible for the coordinated movement of cilia and flagella. Dysfunction of the 9+2 microtubular arrangement can lead to ciliopathies, a group of genetic disorders affecting the cilia and flagella.