Mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). They are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell due to their essential role in cellular respiration. In this article, we will explore the detailed structure and function of these organellies.
Table of Contents
Discovery of Mitochondria
Mitochondria are essential organelles found in almost all eukaryotic cells. They play a vital role in the energy production of cells, and their dysfunction is associated with numerous human diseases. In this article, we will explore the structure and function of this important organelle in detail. These were first discovered in the late 1800s by a German pathologist named Richard Altman. However, it was not until the 1940s that their role in cellular respiration was discovered by the biochemist Albert Lehninger.
Structure of Mitochondria
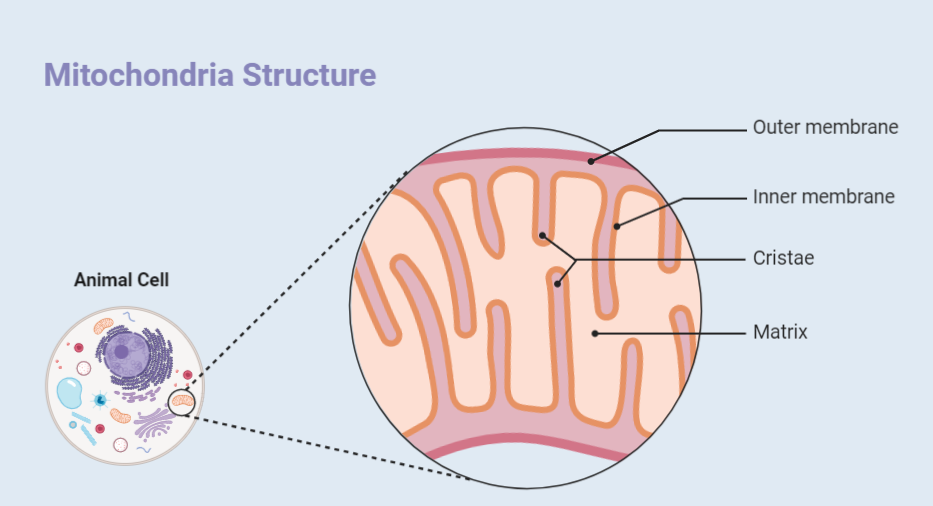
These organelles have a unique structure consisting of an outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix.
Outer Membrane
The outer membrane of mitochondria is a smooth, semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the organelle. It is made up of a lipid bilayer and contains various proteins, including porins that allow the passage of small molecules.
Intermembrane Space
The intermembrane space is the area between the outer and inner membranes of mitochondria. It is a fluid-filled space that contains numerous proteins involved in various cellular processes.
Inner Membrane
The inner membrane of mitochondria is highly folded and forms the cristae, which increase the surface area of the membrane. This membrane is also semi-permeable and contains several transport proteins that facilitate the movement of molecules into and out of the organelle.
Cristae
The cristae are the folded structures in the inner membrane of mitochondria that increase the surface area of the membrane. They are studded with various proteins that are involved in cellular respiration and ATP synthesis.
Matrix
The matrix is the innermost compartment of mitochondria that contains numerous enzymes involved in various metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, which generates ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
Function of Mitochondria
Mitochondria play a crucial role in cellular metabolism and energy production. Here are some of the essential functions of it:
ATP Production
Mitochondria are responsible for generating the majority of ATP produced by cells through cellular respiration. The TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation take place in the matrix and cristae, respectively, and produce ATP.
Cellular Metabolism
These organelles are involved in numerous metabolic pathways, including the TCA cycle, fatty acid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism. They also play a role in the biosynthesis of certain molecules, such as heme and steroids.
Apoptosis
Mitochondria also play a crucial role in programmed cell death, or apoptosis. They release various proteins, such as cytochrome c, which triggers the activation of caspases, enzymes that break down cellular components and lead to cell death.
Calcium Homeostasis
These are also involved in calcium homeostasis. They can take up calcium ions from the cytoplasm, helping to regulate intracellular calcium levels and prevent cellular damage.
Importance of Mitochondria
These organelles are essential for the proper functioning of cells and the overall health of an organism. Dysfunctional mitochondria are associated with numerous human diseases, including neurological disorders, metabolic disorders, and certain types of cancer.
Mitochondrial Diseases
Mitochondrial diseases are a group of genetic disorders that affect the function of mitochondria. They can range from mild to severe and can affect various organs and tissues in the body. Symptoms of mitochondrial diseases can include muscle weakness, fatigue, neurological symptoms, and developmental delays.

Conclusion
These are vital organelles found in eukaryotic cells that play a crucial role in energy production, cellular metabolism, apoptosis, and calcium homeostasis. Understanding the detailed structure and function of mitochondria is essential for understanding cellular processes and the development of treatments for mitochondrial diseases.