Table of Contents
Introduction:
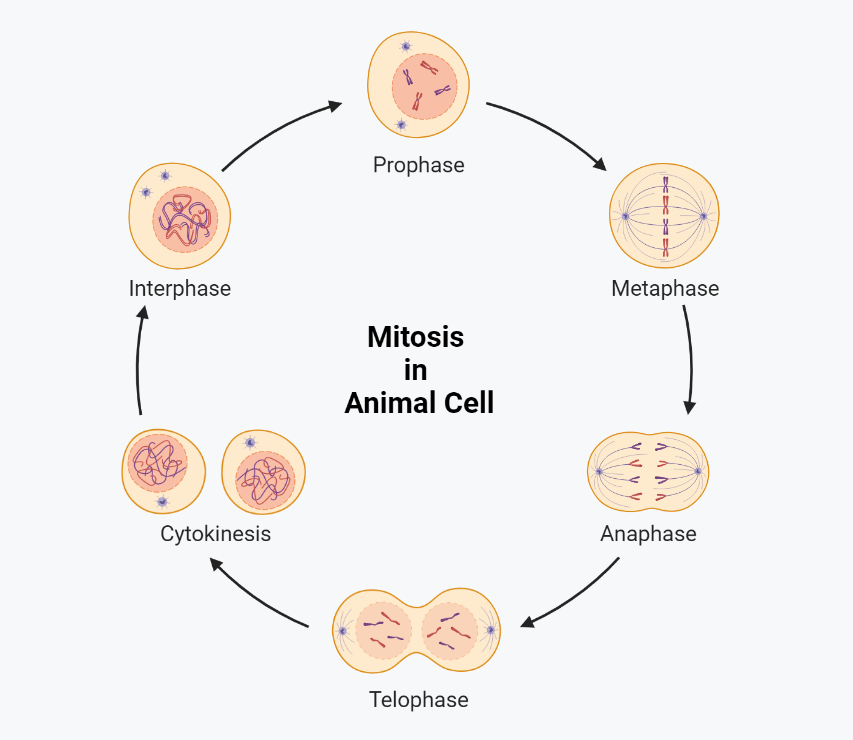
Mitosis is the process of cell division in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The purpose of mitosis is to produce genetically identical cells for growth and repair of the organism. Mitosis is divided into four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase:
In prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. The nuclear envelope breaks down, and the spindle apparatus forms. The spindle apparatus is made up of microtubules that will later help to pull the chromosomes apart during cell division.
Metaphase:
In metaphase, the chromosomes align at the center of the cell, called the metaphase plate, and are attached to the spindle fibers. The spindle fibers are pulled tight, pulling the chromosomes to the center of the cell and aligning them at the metaphase plate. This is the stage where the cell checks for any errors in chromosome alignment, and if any errors are found, the cell will not proceed to the next stage until they are corrected.
Anaphase:
In anaphase, the chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindle fibers, resulting in the separation of sister chromatids. The sister chromatids are identical copies of each other and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell, called the poles.
Telophase:
In telophase, the chromosomes reach the opposite ends of the cell and new nuclear envelopes form around each set of chromosomes. The spindle apparatus breaks down, and the cell begins to physically divide through a process called cytokinesis.

Cytokinesis:
Cytokinesis is the final stage of mitosis, where the cell physically divides into two daughter cells. In animal cells, a contractile ring made up of actin and myosin fibers forms around the center of the cell. These fibers pull the cell membrane in and divide the cell into two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms between the two daughter cells and eventually develops into a cell wall. And it physically separates the two cells.

Conclusion:
Mitosis is the process of cell division in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The purpose of mitosis is to produce genetically identical cells for growth and repair of the organism. Mitosis is divided into four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Proper mitosis is crucial for the correct replication and segregation of DNA, and the maintenance of the integrity of chromosomes.