Table of Contents
I. Introduction
- Definition: Eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of an internal compartment called the nucleus, where DNA is stored.
- Characteristics: Compared to prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells are typically larger, have an elaborate cytoskeleton, and internal membranes that are involved in digestion and secretion.
II. Predatory Origins
- Plausible View: One theory is that eukaryotic cells originated as predators, living by capturing and eating other cells.
- Features: Such a way of life requires a large cell with a flexible plasma membrane, an elaborate cytoskeleton, and the sequestration of DNA in a nucleus to protect the genome.
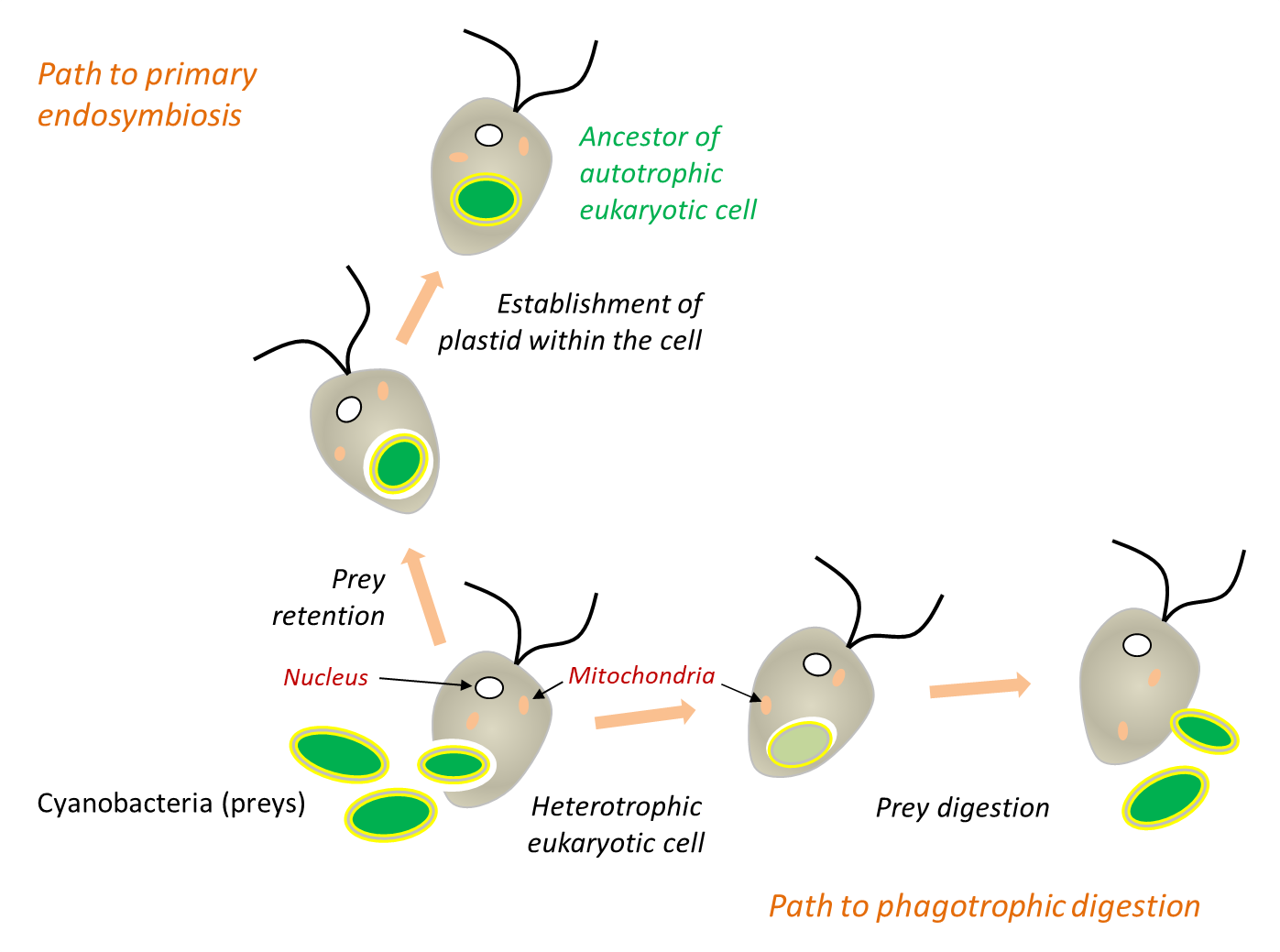
III. Evolution through Symbiosis
- Mitochondria: All eukaryotic cells contain (or at one time contained) mitochondria, which are small, membrane-bound bodies that harness energy from food molecules to produce ATP.
- Mitochondrial Origin: It is generally accepted that mitochondria originated from aerobic bacteria that were engulfed by an ancestral cell, forming a symbiotic relationship.
- Chloroplasts: Some eukaryotic cells, such as plants and algae, also contain chloroplasts, which perform photosynthesis and have their own genome.
- Chloroplast Origin: Chloroplasts likely originated from photosynthetic bacteria that were acquired by eukaryotic cells that already contained mitochondria.
IV. Different Ways of Life
- Plant Cells: Plant cells, which contain chloroplasts, have transitioned from hunting to farming, losing the ability to move rapidly and engulf other cells and creating a protective cell wall.
- Fungal Cells: Fungal cells, like animal cells, possess mitochondria but not chloroplasts and have a tough outer wall that limits their ability to move rapidly or engulf other cells.
- Animal Cells: Animal cells, including protozoa, have a flexible plasma membrane, the ability to change shape rapidly, and to engulf other cells by phagocytosis.
V. Conclusion
- Mystery: The evolution and sequence of the unique properties of eukaryotic cells is still a mystery.
- Advances: Advances in genomic analyses are helping to shed light on the origins of eukaryotic cells, including the establishment of symbiotic relationships between cells.