Table of Contents
Introduction:
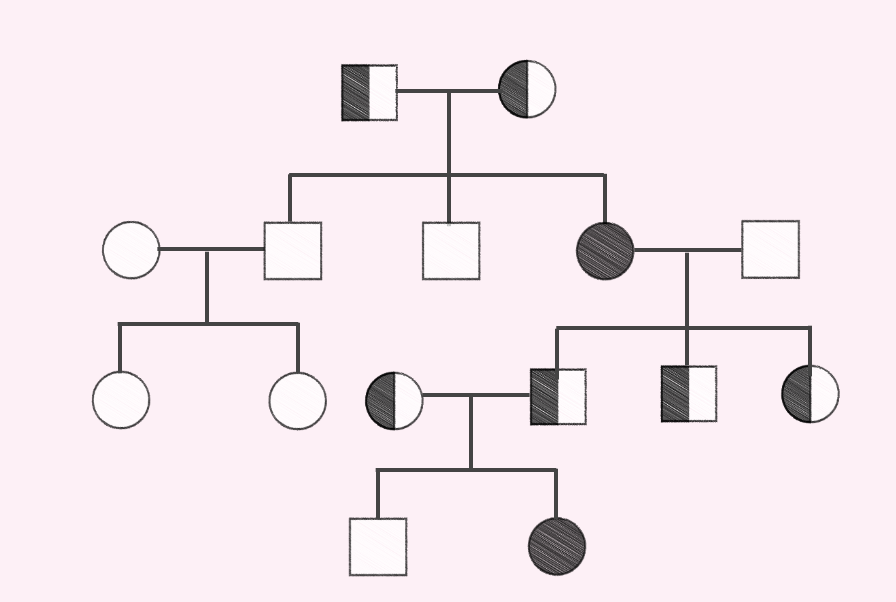
Pedigree analysis is a method used in genetics to study the inheritance patterns of specific traits or disorders within a family. It involves constructing a diagram, or pedigree, that represents the family tree and the presence or absence of the trait or disorder in each individual. Pedigree analysis can help determine whether a trait or disorder is inherited in a dominant or recessive manner, and can also provide information about the likelihood of the trait or disorder being passed on to future generations.
Methods:
- The first step in pedigree analysis is to gather information about the family, including the medical history of each individual and their relationship to other members of the family.
- The information is then used to construct a pedigree, which is a diagram that represents the family tree and the presence or absence of the trait or disorder in each individual.
- The symbols used in a pedigree can vary, but common symbols include circles for females, squares for males, and half-shaded symbols for individuals who are carriers of a disorder but do not display symptoms.
- Once the pedigree is constructed, it can be analyzed to determine the mode of inheritance of the trait or disorder.
Dominant Inheritance:
- A trait or disorder that is inherited in a dominant manner is represented in a pedigree by the presence of the trait or disorder in each generation, with the affected individuals having at least one affected parent.
- A trait or disorder that is inherited in a dominant manner has a high probability of being passed on to future generations, as each affected individual has a 50% chance of passing the trait or disorder on to their offspring.
Recessive Inheritance:
- A trait or disorder that is inherited in a recessive manner is represented in a pedigree by the presence of the trait or disorder in every other generation, with affected individuals having unaffected parents.
- A trait or disorder that is inherited in a recessive manner has a lower probability of being passed on to future generations, as each carrier of the disorder has a 25% chance of passing it on to their offspring.

X-linked Inheritance:
- X-linked disorders are inherited via the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes in humans.
- X-linked disorders are characterized by the fact that they affect mostly males, because males have only one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes.
- X-linked disorders are inherited in a dominant or recessive manner, depending on the specific disorder.
- X-linked recessive disorders are represented in a pedigree by the presence of the disorder only in males, and often in a vertical pattern with the affected males having unaffected mothers.


Y-linked Inheritance:
- Y-linked disorders are inherited via the Y chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes in humans.
- Y-linked disorders are characterized by the fact that they affect only males, because the Y chromosome is present only in males.
- Y-linked disorders are inherited in a dominant or recessive manner, depending on the specific disorder.
- Y-linked disorders are represented in a pedigree by the presence of the disorder only in males, and often in a horizontal pattern with the affected males having unaffected fathers.
Conclusion:
- Pedigree analysis is a powerful tool for studying the inheritance patterns of specific traits or disorders within a family. It can help determine whether a trait or disorder is inherited in a dominant or recessive manner, and can also provide information about the likelihood of the trait or disorder being passed on to future generations. Pedigree analysis can also help identify potential carriers of a disorder, and can be used to determine the risk of future generations developing the disorder.
- In addition, pedigree analysis can be used to identify the specific genetic mutations or variations that are associated with a particular disorder, and can aid in the development of genetic testing and counseling for individuals and families affected by the disorder.
- However, it is important to note that pedigree analysis is not always able to provide a definitive diagnosis, and may need to be combined with other genetic testing methods such as genetic sequencing or linkage analysis to fully understand the inheritance patterns of a disorder.
- Overall, pedigree analysis is a valuable tool in genetics, that can help us understand the complex nature of the inheritance of certain traits, disorders and diseases. It can also help us understand the genetic makeup of a certain family, which can have important implications for medical diagnosis, treatment and genetic counseling.