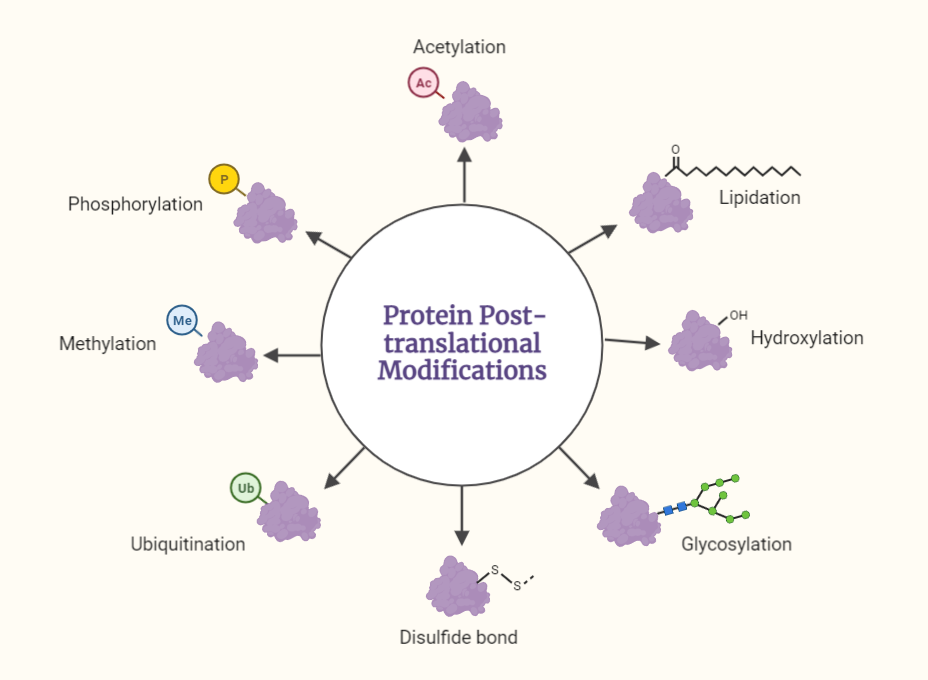
Post-translational processing refers to the series of modifications that occur to a protein after it has been synthesized by the ribosome. These modifications can include:
Table of Contents
Folding:
After being synthesized, a protein must fold into its correct three-dimensional structure in order to function properly. The process of folding is mediated by a variety of proteins called chaperones, which help the protein to fold into its correct shape.
Cleavage:
Some proteins are synthesized as larger precursor proteins that must be cleaved into smaller, functional proteins. Cleavage is mediated by enzymes called proteases, which cut the protein at specific locations.
Phosphorylation:
The addition of a phosphate group to a protein is called phosphorylation. Phosphorylation can change the activity, stability, or localization of a protein. It is mediated by enzymes called kinases, which transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the protein.
Acetylation:
The addition of an acetyl group to a protein is called acetylation. Acetylation can change the activity, stability, or localization of a protein. It is mediated by enzymes called acetyltransferases, which transfer an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to the protein.
Glycosylation:
The addition of a sugar group to a protein is called glycosylation. Glycosylation can change the activity, stability, or localization of a protein. It is mediated by enzymes called glycosyltransferases, which transfer a sugar group from a sugar donor to the protein.
Ubiquitination:
Ubiquitination is the process of adding a small protein called ubiquitin to a target protein. This modification targets the protein for degradation by the proteasome.
Methylation:
The addition of a methyl group to a protein is called methylation. Methylation can change the activity, stability, or localization of a protein. It is mediated by enzymes called methyltransferases, which transfer a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to the protein.

In summary, post-translational processing is a series of modifications that occur to a protein after it has been synthesized by the ribosome. These modifications can include folding, cleavage, phosphorylation, acetylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, and methylation. These modifications play an important role in the stability, activity, and localization of the protein.