Table of Contents
Introduction:
- RAPD is a PCR-based technique used in molecular biology to detect genetic variations in DNA.
- It is based on the amplification of random regions of DNA using primers of arbitrary sequence.
- The amplified products, called RAPD markers, can then be separated by size using gel electrophoresis and compared among different individuals or samples.
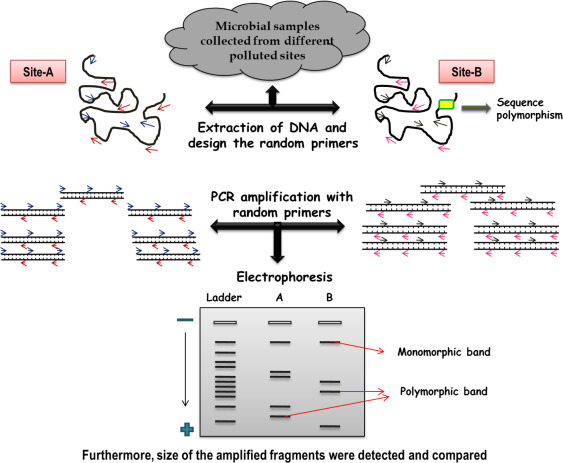
Principles of RAPD:
- The RAPD technique uses a pair of primers of arbitrary sequence, usually 10-mer (10 base pair long) primers, to amplify random regions of DNA.
- The primers are designed to be arbitrary, meaning that they do not have a specific sequence to match, but instead bind to any region of the genome.
- The amplified products, called RAPD markers, are unique to each individual or sample and can be used to differentiate between them.
Procedure:
RAPD analysis involves the following steps:
- Isolation of DNA from the sample of interest (e.g. blood, tissue, etc.)
- PCR amplification of random regions of DNA using arbitrary primers
- Separation of the amplified products by size using gel electrophoresis
- Visualization of the amplified products using ethidium bromide staining
- Comparison of the RAPD profiles among different individuals or samples.
Applications:
- RAPD is used in a variety of fields, including genetics, plant breeding, and forensic science.
- RAPD can be used to detect genetic variations among individuals or populations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or larger structural variations.
- RAPD can also be used to identify and classify organisms, such as bacteria or plants.
Limitations:
- RAPD is a relatively low resolution technique, as it amplifies random regions of DNA and may not detect all variations present.
- RAPD markers are not always reproducible, as the amplification of random regions may vary between reactions or experiments.
- RAPD markers are also not easily transferable across species, as the amplified regions are not conserved.
Conclusion:
- RAPD is a simple and rapid technique that can detect genetic variations in DNA, but it has low resolution and reproducibility.
- RAPD has been largely replaced by more sensitive and specific methods, such as PCR-based techniques (e.g. AFLP, ISSR) and DNA sequencing.
- However, RAPD still has its place in certain fields, such as plant breeding and forensic science, where its simplicity and rapidity are highly valued.