Table of Contents
Introduction
- Resources partitioning is a process in which different species of organisms compete for the same limited resources in their shared environment.
- It is a key concept in community ecology that helps explain why different species can coexist within the same ecosystem.
- The process of resources partitioning refers to the way in which different species divide up the available resources in an ecosystem to minimize competition and reduce the risk of extinction.
Definition
- Resources partitioning can be defined as the process by which different species within an ecosystem allocate their usage of resources such as food, light, water, space, etc. to minimize competition and reduce the risk of extinction.
Types of Resources Partitioning
- Temporal Partitioning
- Temporal partitioning refers to the division of resources based on time.
- Different species may have different feeding patterns, which allow them to feed at different times of the day or in different seasons.
- For example, some species may feed during the day while others feed at night, which reduces competition for food.
- Spatial Partitioning
- Spatial partitioning refers to the division of resources based on space.
- Different species may occupy different regions of an ecosystem, which reduces competition for resources.
- For example, some species may occupy the forest floor while others occupy the forest canopy, which reduces competition for food and light.
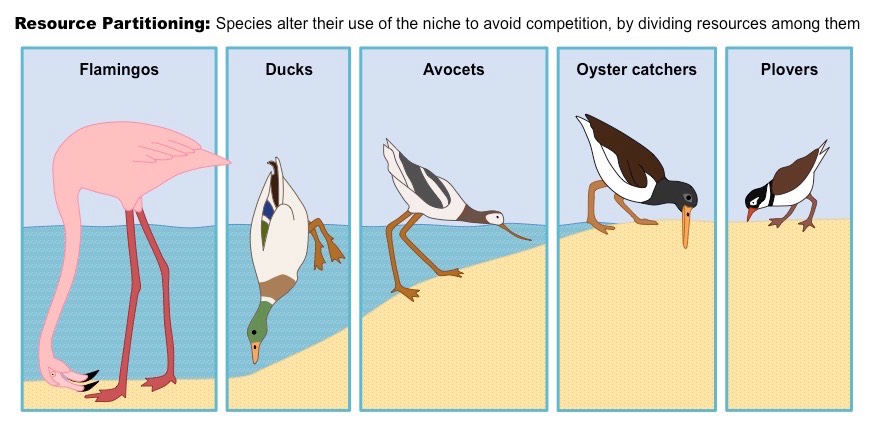
- Niche Partitioning
- Niche partitioning refers to the division of resources based on specific roles within an ecosystem.
- Each species has a unique niche, or role, within an ecosystem, which reduces competition for resources.
- For example, some species may feed on nectar while others feed on insects, which reduces competition for food.
Examples of Resources Partitioning
- African Grasslands
- African grasslands are a prime example of resources partitioning.
- Different species of grazers have evolved to feed on different parts of the grasses, which reduces competition for food.
- For example, zebras feed on the upper parts of the grass while wildebeests feed on the lower parts, which reduces competition for food.
- Tropical Rainforests
- Tropical rainforests are another example of resources partitioning.
- Different species of primates have evolved to feed on different parts of the trees, which reduces competition for food.
- For example, some species of primates feed on the leaves while others feed on the fruit, which reduces competition for food.
- Desert Ecosystems
- Desert ecosystems are also an example of resources partitioning.
- Different species of mammals have evolved to feed on different parts of the cacti, which reduces competition for food.
- For example, some species of mammals feed on the fruit while others feed on the flowers, which reduces competition for food.
Conclusion
- Resources partitioning is an important concept in community ecology that helps explain how different species can coexist within the same ecosystem.
- The process of resources partitioning refers to the way in which different species divide up the available resources in an ecosystem to minimize competition and reduce the risk of extinction.
- Different types of resources partitioning, including temporal, spatial, and niche partitioning, help to explain how different species allocate their usage of resources to minimize competition and reduce the risk of extinction.