Table of Contents
Introduction to RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism):
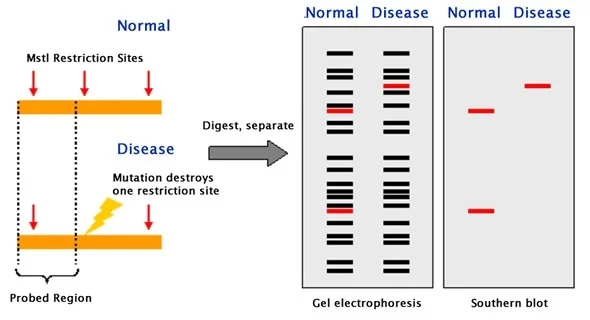
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) is a method used in molecular biology to detect variations in DNA sequences. It is based on the ability of certain enzymes, called restriction enzymes, to cut DNA at specific sequences, called recognition sites. The resulting fragments, called restriction fragments, can then be separated by size using gel electrophoresis, and compared among different individuals or samples.
Principles of RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism):
- Restriction enzymes are endonucleases that recognize and cut specific sequences of nucleotides in double-stranded DNA.
- These sequences, called recognition sites, vary in length and sequence among different restriction enzymes.
- The cutting of DNA by restriction enzymes creates specific patterns of fragments, called restriction maps.
Procedure:
- RFLP analysis involves the following steps:
- Isolation of DNA from the sample of interest (e.g. blood, tissue, etc.)
- Digestion of the DNA with one or more restriction enzymes to generate restriction fragments
- Separation of the restriction fragments by size using gel electrophoresis
- Transfer of the separated fragments to a nylon or nitrocellulose membrane (Southern blotting)
- Hybridization of a labeled probe (e.g. radioactive or fluorescent) to the restriction fragments on the membrane
- Detection and analysis of the hybridized fragments
Applications:
- RFLP is used in a variety of fields, including genetics, forensic science, and medical diagnostics.
- It can be used to detect genetic variations among individuals or populations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or larger structural variations.
- This can also be used to identify the presence of specific pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria.
Limitations:
- RFLP has been largely replaced by more sensitive and specific methods, such as PCR-based techniques (e.g. RFLP-PCR, PCR-RFLP) and DNA sequencing.
- This process also has limited resolution, as it can only detect variations that result in differences in fragment size.
- It is also labour intensive, time consuming, and require large amount of DNA.
Conclusion:
- RFLP is a powerful method that can detect variations in DNA sequences, but it has been largely replaced by newer technologies.
- However, RFLP still has its place in certain fields, such as forensic science and medical diagnostics, where its simplicity and reliability are still highly valued.