Table of Contents
Introduction to Taenia solium:
Taenia solium, also known as the pork tapeworm, is a parasitic cestode (tapeworm) that causes taeniasis and cysticercosis in humans. Taeniasis is an infection of the intestinal tract, while cysticercosis is a systemic infection caused by the larvae of the parasite. In this study note, we will discuss the morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical disease of T. solium.
Morphology of Taenia solium:
- T. solium is a segmented tapeworm that can grow up to several meters in length.
- The adult tapeworm resides in the small intestine of the human host and is composed of several segments called proglottids.
- Each proglottid contains both male and female reproductive organs, allowing the tapeworm to reproduce asexually.
- The scolex (head) of the tapeworm is equipped with four suckers and a double row of hooks that allow it to attach to the intestinal wall.
Life Cycle of Taenia solium:
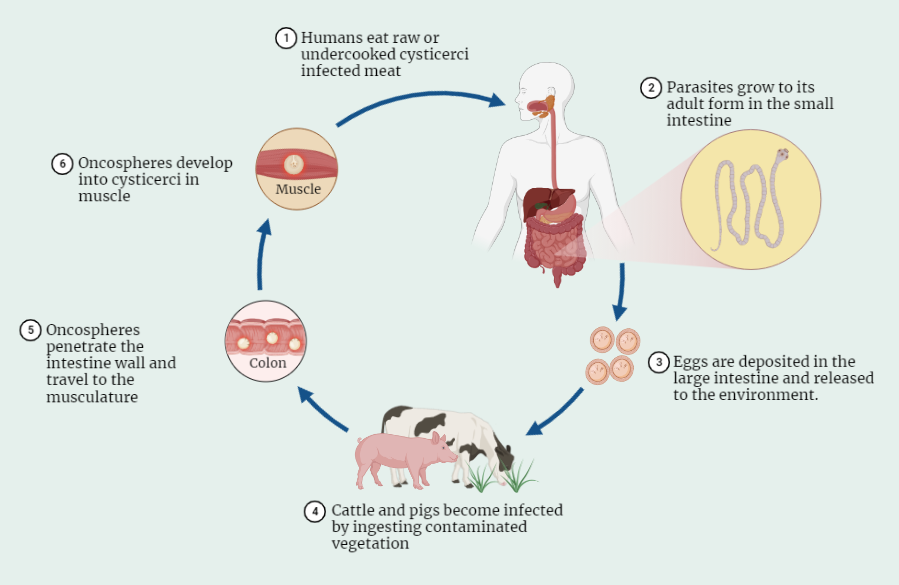
T. solium has a complex life cycle that involves both the human host and the intermediate host, usually pigs. The life cycle can be divided into three main stages: the oncosphere, the cysticercus, and the adult tapeworm.
Oncosphere Stage:
- The oncosphere stage begins when adult tapeworms in the human host release eggs into the feces.
- These eggs are ingested by pigs, where they hatch and develop into oncospheres.
- The oncospheres penetrate the intestinal wall and migrate to various tissues, where they develop into cysticerci.
Cysticercus Stage:
- The cysticercus stage begins when the oncospheres develop into cysticerci, which are fluid-filled cysts containing a fully developed larva.
- The cysticerci can be found in various organs and tissues, including the brain, muscles, and subcutaneous tissue.
Adult Tapeworm Stage:
- The adult tapeworm stage begins when humans ingest the cysticerci, usually by consuming undercooked pork.
- The cysticerci reach the small intestine and attach to the intestinal wall, where they develop into adult tapeworms.
- The adult tapeworms can live for several years and continue to produce eggs, perpetuating the cycle.
Pathogenesis:
- Taeniasis is caused by the presence of adult tapeworms in the intestine, which can lead to abdominal discomfort, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies.
- Cysticercosis is caused by the presence of cysticerci in various organs and tissues, which can lead to a wide range of symptoms depending on the location of the cysts.
- In the brain, cysticerci can cause seizures and neurological deficits. In muscles, they can cause pain and weakness.
Clinical Disease:
- Taeniasis is usually asymptomatic, but can lead to abdominal discomfort, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies.
- Cysticercosis can cause a wide range of symptoms depending on the location of the cysts.
- In the brain, cysticercosis can cause seizures, headaches, and neurological deficits.
- In muscles, cysticercosis can cause pain and weakness.
- In the retina of the eye, cysticercosis can cause vision loss.
- Cysticercosis can also lead to chronic disability, social stigma, and economic loss.
In conclusion, Taenia solium is a parasitic tapeworm that causes taeniasis and cysticercosis in humans. Understanding its morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical disease is crucial for the development of effective treatments and strategies for controlling and preventing the spread of this parasitic infection.