Table of Contents
Introduction:
- Telomeres are specialized structures found at the end of chromosomes that play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of genetic material.
- Telomeres act as a protective cap that prevent loss of important genetic information during cell division.
- Replication of telomeres is a complex process that ensures the preservation of telomere length and stability.
Functions of Telomeres:
- Protection of genetic information: Telomeres protect the ends of chromosomes from degradation and fusion, which can cause genetic instability and disease.
- Regulation of cell division: Telomeres regulate the number of times a cell can divide and help prevent the loss of important genetic information during replication.
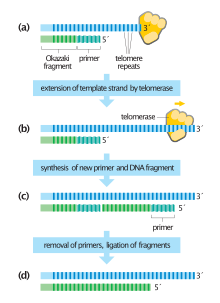
Telomere Replication:
- Telomere replication is a complex process that requires the coordinated action of several proteins and enzymes.
- The telomere replication process can be divided into two main stages: extension and replication.
Extension:
- Extension refers to the process of adding nucleotides to the end of the telomere.
- This is accomplished by the action of telomerase, an enzyme that adds DNA sequences to the end of telomeres.
- Telomerase is active in germ cells, stem cells, and some cancer cells, allowing them to maintain the length of their telomeres and continue to divide.
Replication:
- Replication refers to the process of copying the telomere DNA sequence during cell division.
- This is accomplished by the replication machinery, which replicates the DNA molecule along its entire length.
- However, the replication machinery is unable to fully replicate the end of the telomere, resulting in a gradual shortening of telomeres with each cell division.
Factors Influencing Telomere Replication:
- Telomere length: Longer telomeres are more stable and are less likely to cause genetic instability.
- Telomerase activity: Telomerase activity is essential for maintaining telomere length and stability, and its activity is regulated by several factors including cell type, stress, and aging.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to stress and oxidative damage can accelerate telomere shortening and cause genetic instability.
Conclusion:
- Telomere replication is a critical process that ensures the preservation of telomere length and stability, and is essential for the maintenance of genetic information and cell division.
- Understanding the factors that influence telomere replication is important for understanding the underlying causes of genetic instability, disease, and aging.