-
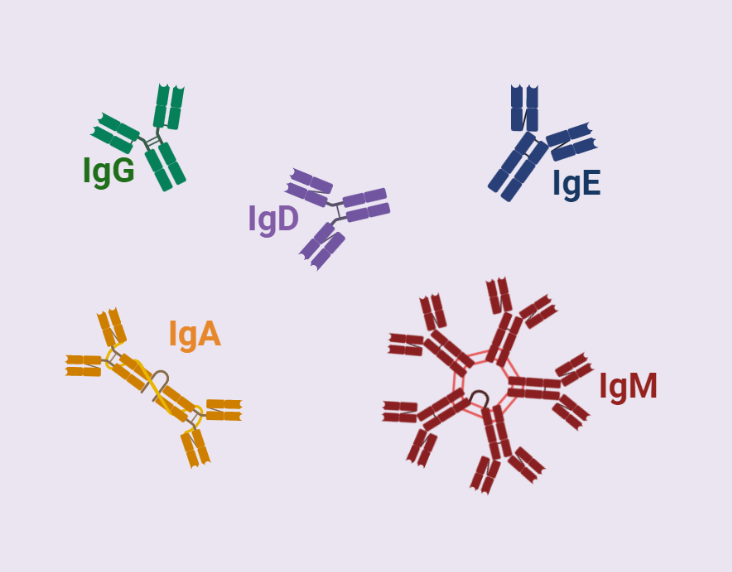
Types of Antibodies
This text provides an overview of the five main classes of antibodies and their distinct properties and functions. Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are proteins produced by B-lymphocytes that play a critical role in the immune response by specifically binding to antigens. The five classes of antibodies are IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE. IgG…
-
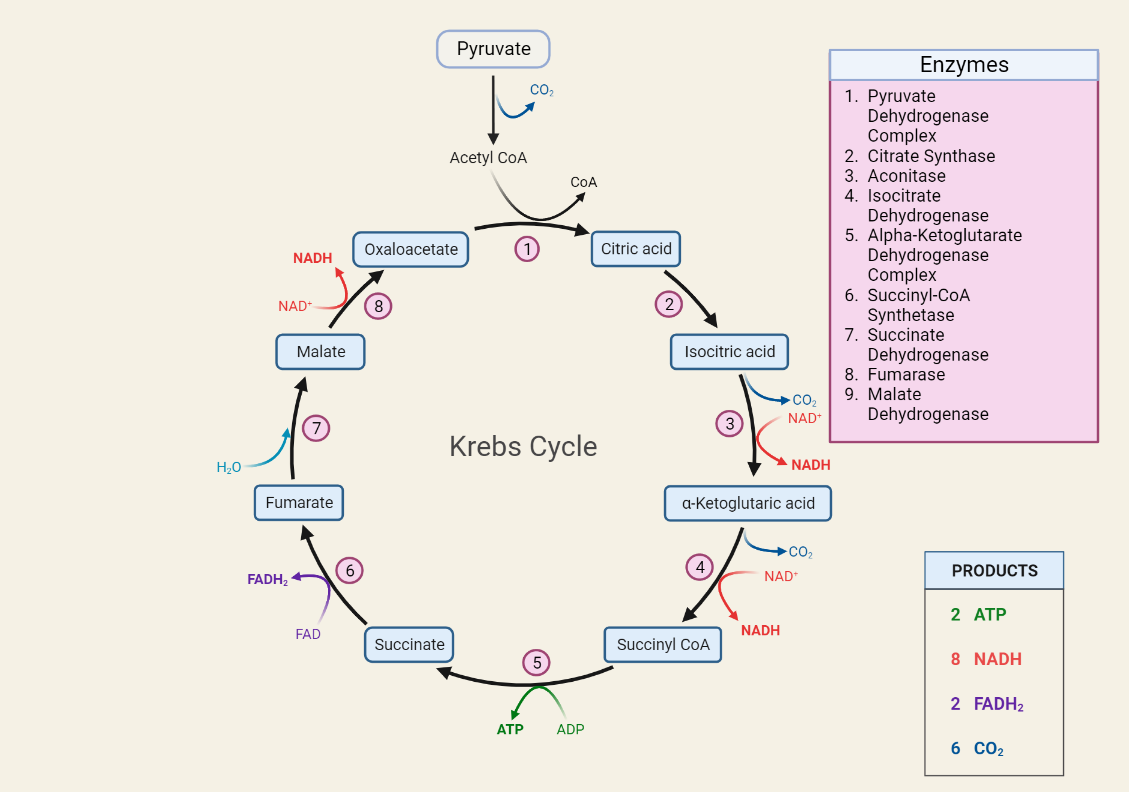
Krebs cycle
occur in the mitochondria of cells. It is a crucial process in cellular respiration, where it breaks down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy that the cell can use. In this article, we will explore the definition, equation, enzymes, and steps involved in the Krebs cycle, as well as its importance in cellular metabolism. Understanding…
-
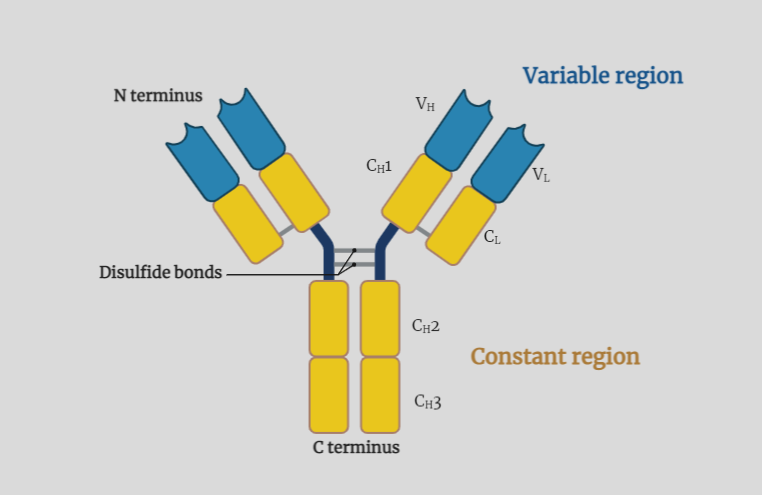
Structure of Antibodies
The text provides an overview of the structure of antibodies. It explains that antibodies are a class of proteins produced by B-lymphocytes that specifically bind to antigens. The basic structure of antibodies consists of four polypeptide chains – two heavy chains and two light chains. The variable domains of the heavy and light chains form…
-
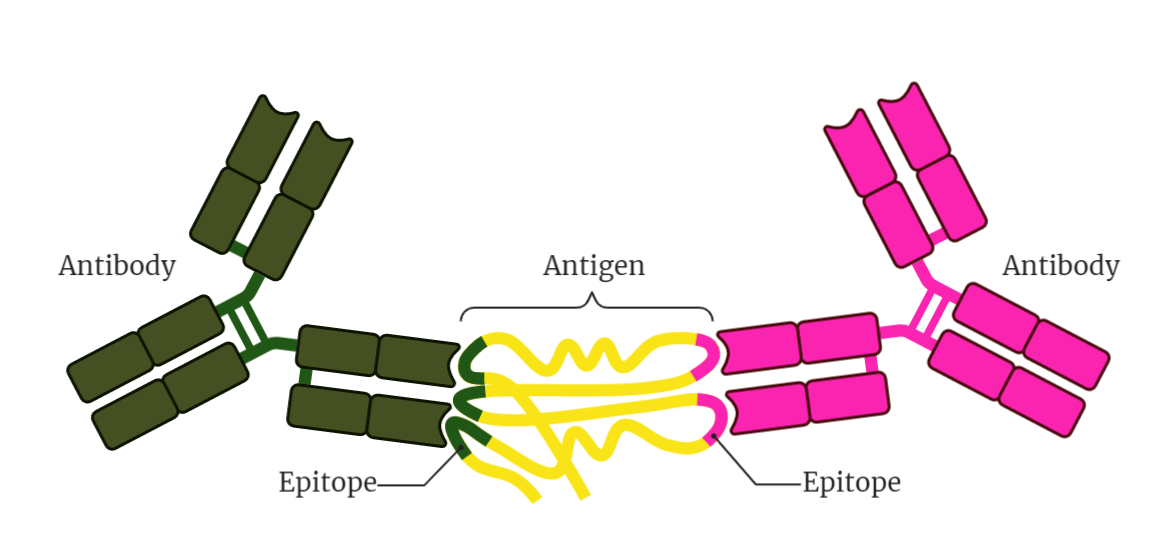
Antigen-Antibody Reaction
The text above provides an overview of antigen-antibody reactions, which play a crucial role in the immune response. It explains the specific binding of an antigen to an antibody through non-covalent bonds and the diversity of antibodies generated by the immune system. The mechanisms of action resulting from antigen-antibody reactions are also discussed, including neutralization,…
-
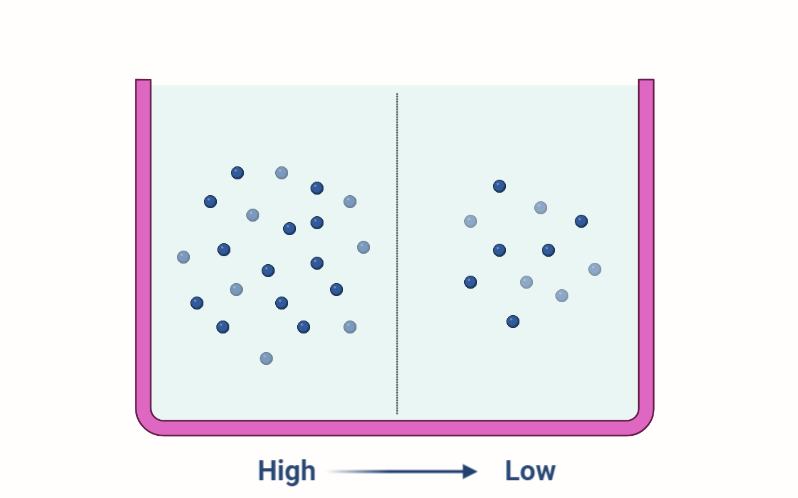
Osmosis
Osmosis is a process that occurs naturally in all living things, including plants and animals. It is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This movement of water molecules helps maintain the balance…
-
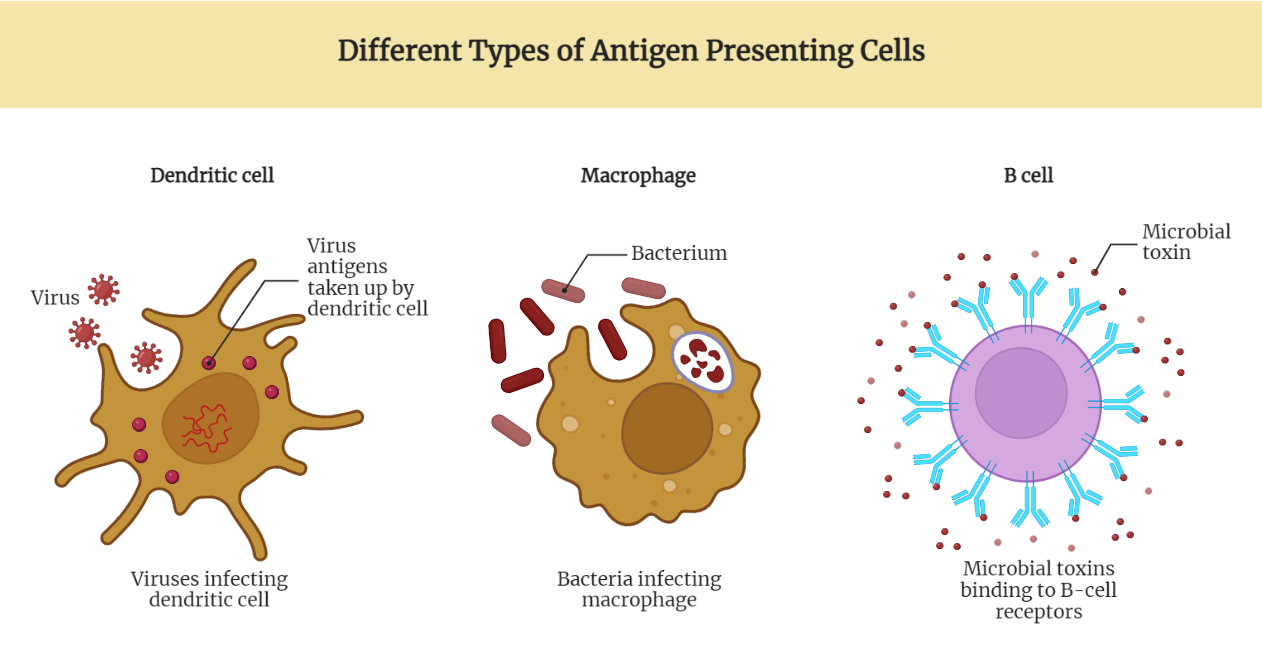
Antigen Presenting Cells
This text provides an overview of antigen presenting cells (APCs), including dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, and their crucial role in initiating the adaptive immune response. It also discusses the process of maturation of APCs, which enhances their efficiency in presenting antigens to T cells.
-
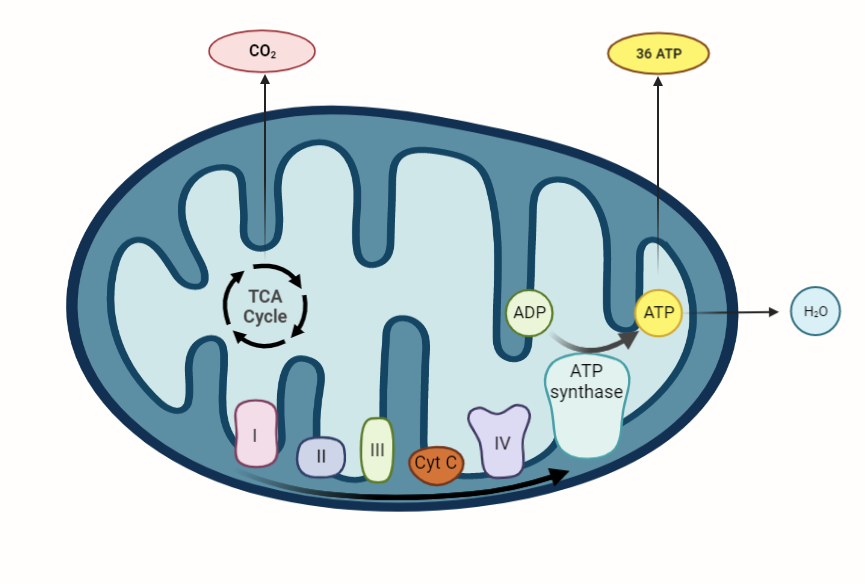
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
The chemiosmotic hypothesis proposed by Peter Mitchell in 1961 is a widely accepted model that explains how living organisms convert energy from electron transfer reactions into ATP synthesis. This hypothesis revolutionized our understanding of how cells generate ATP, the universal energy currency of living systems, and it is a fundamental principle of bioenergetics. The chemiosmotic…
-
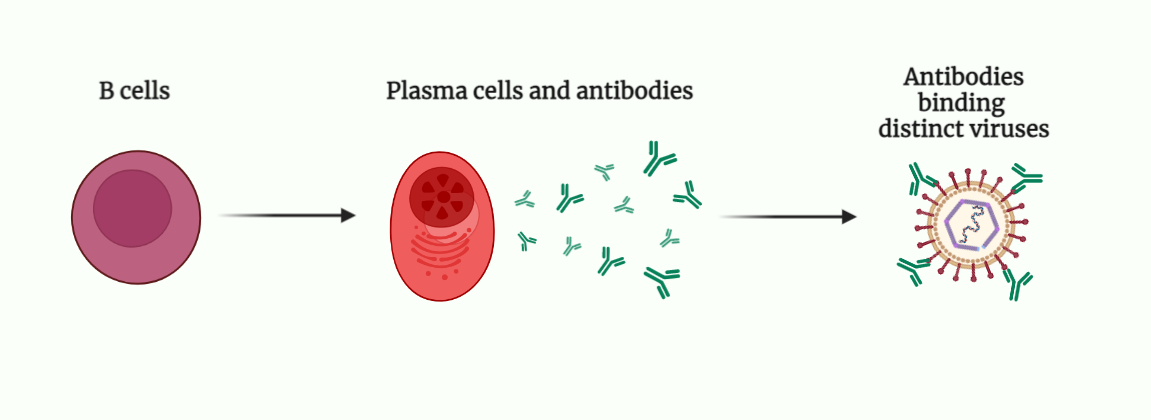
Humoral Immune Response
The humoral immune response, also known as antibody-mediated immunity, is one of the two branches of the adaptive immune response. It involves the production of antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), by B cells in response to an antigen. The purpose of the humoral immune response is to neutralize and remove antigens from the body.…
-
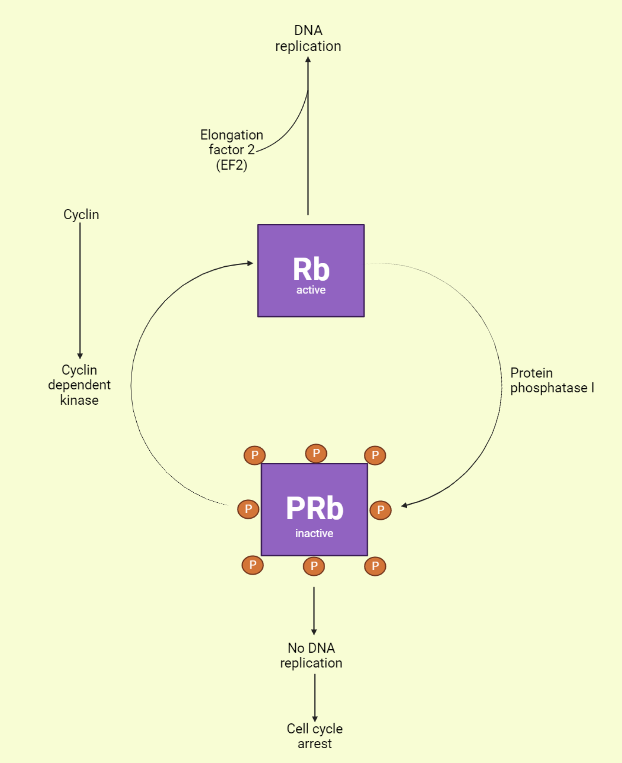
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare type of cancer that affects the retina of the eye and is caused by mutations in the retinoblastoma (RB) gene. The RB gene plays a critical role in the regulation of cell growth and division, acting as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the activity of other proteins that are important for…
-
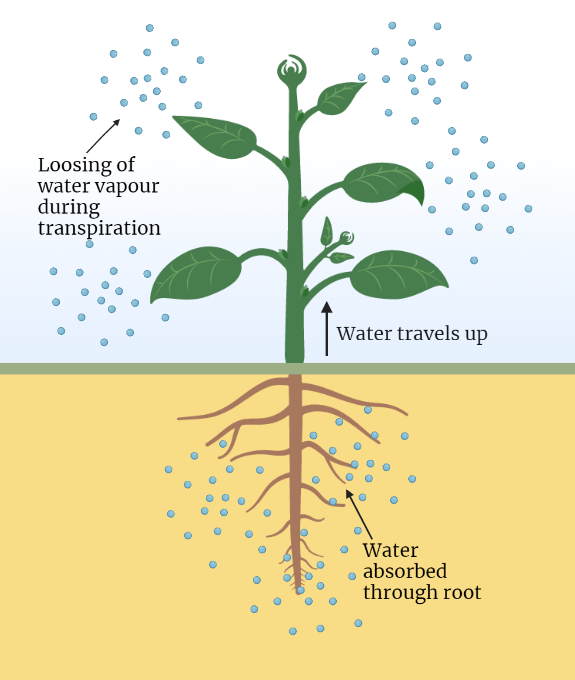
Water Potential
Water potential is a fundamental concept in the study of plant physiology and is also important in the understanding of the movement of water in living organisms. It is a measure of the potential energy of water in a system and is affected by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and solute concentration. Water potential has…
-
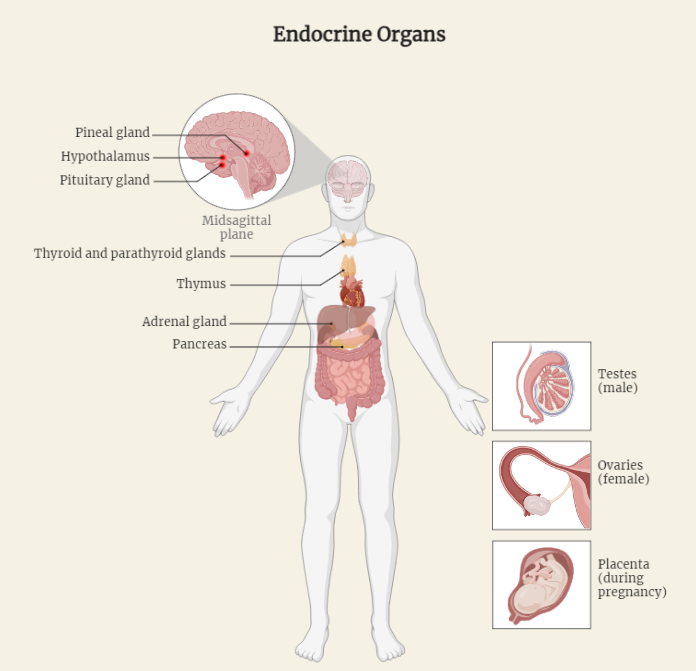
Endocrine Organs of the Human Body
The endocrine system is a complex network of organs in the human body that produces and regulates hormones. These endocrine organs, including the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and others, play crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis, metabolism, reproduction, and overall health. Understanding the functions and interactions of these organs is essential for comprehending the…
-
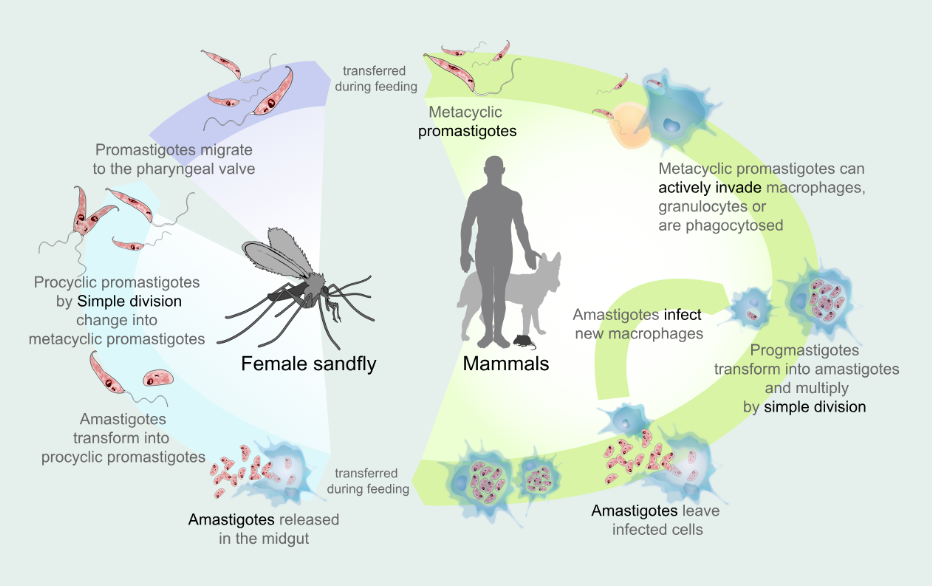
Leishmania donovani
Leishmania donovani is a parasitic protozoan responsible for visceral leishmaniasis, a severe and deadly disease. Explore its morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations in this comprehensive study. Understanding this parasite is crucial for effective treatment and prevention strategies.
-
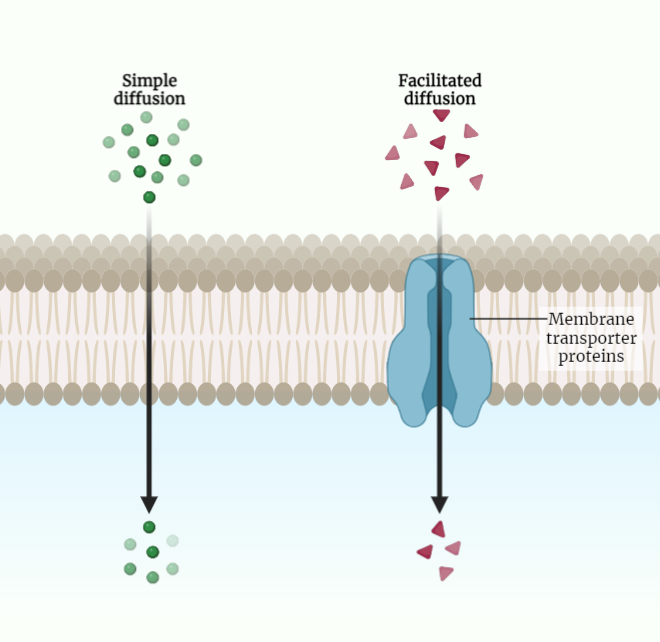
Facilitated Diffusion
Discover the intricacies of facilitated diffusion, a vital mechanism that allows specific molecules to cross cell membranes with the help of specialized proteins. Explore the principles, proteins involved, and examples of this selective transport process. Gain insights into how facilitated diffusion contributes to cellular homeostasis and essential molecule transport.
-
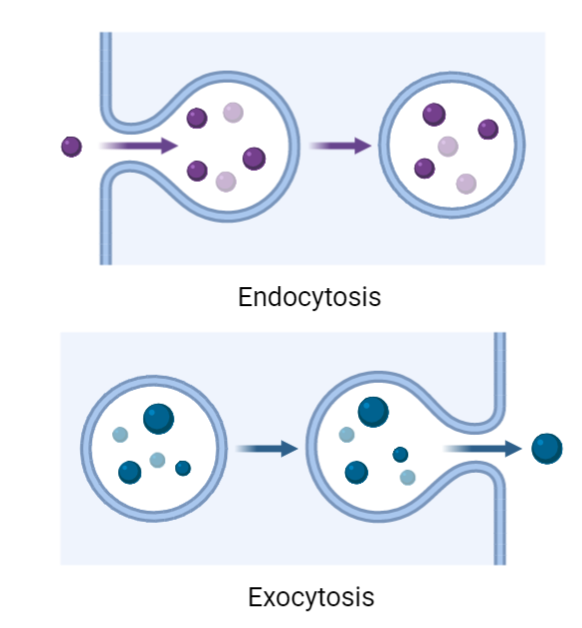
Vesicular Transport
Vesicular transport is a fundamental process that enables the movement of molecules, organelles, and macromolecules within cells. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, facilitating intercellular communication, and carrying out essential physiological functions. This comprehensive study note provides an in-depth exploration of vesicular transport, including its mechanisms, types, regulation, and significance in cellular…
-
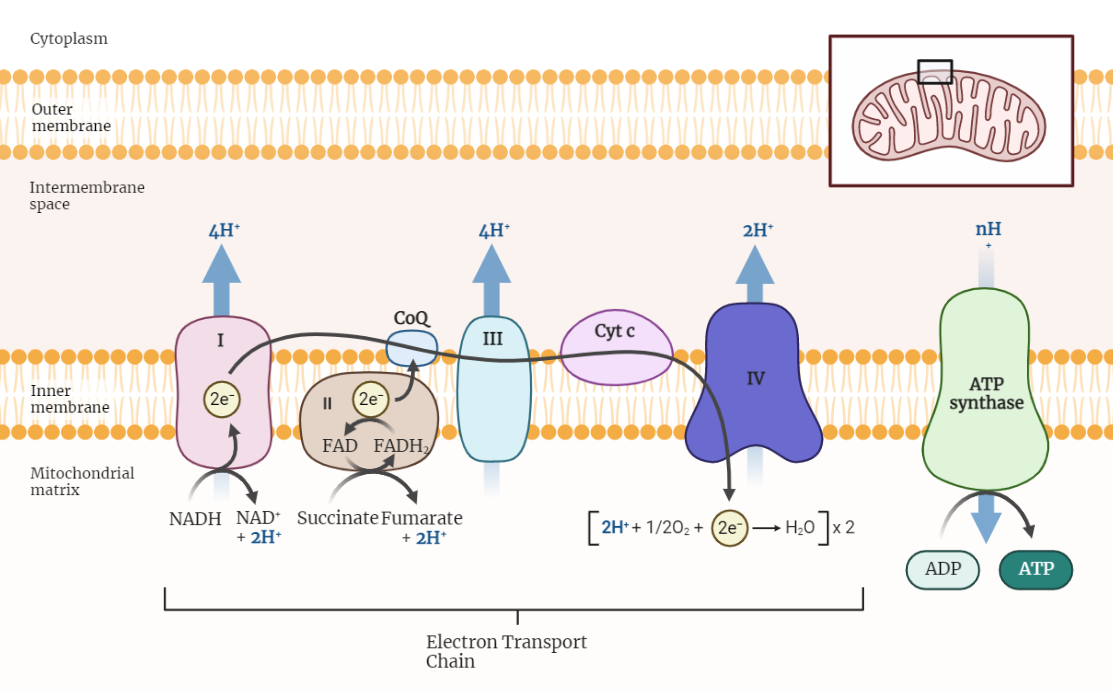
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a fundamental process in cellular energy production. It involves the synthesis of ATP through the electron transport chain (ETC) and chemiosmosis. The ETC, consisting of protein complexes, facilitates the flow of electrons and generates a proton gradient. This proton gradient is harnessed by ATP synthase to produce ATP. The efficiency of oxidative…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




