-

Applications of Light Microscopy
Light microscopy has revolutionized the study of cellular structures and organization within the biological sciences. From simple cell identification and quality assessments to more advanced applications like protein dynamics and co-localization of proteins, this powerful tool plays a crucial role. Techniques such as phase contrast and fluorescence microscopy have significantly enhanced the visualization of specimens,…
-
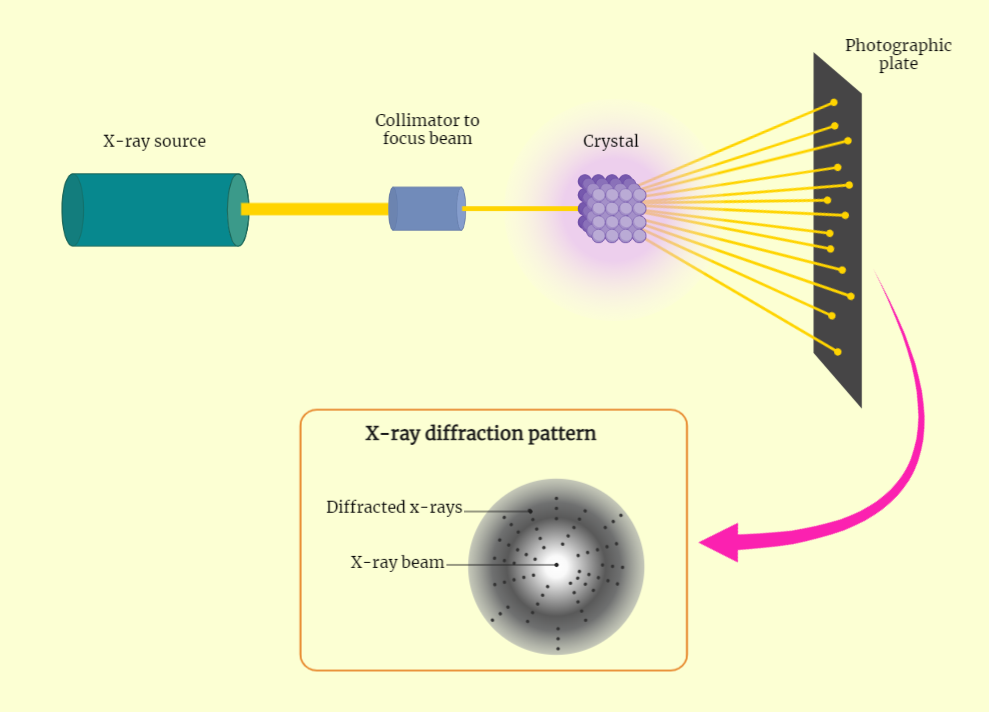
Conformation of Protein
Protein conformation plays a crucial role in the understanding of protein function, stability, and interactions with other molecules. Scientists have employed various methods to unravel the intricate three-dimensional structures of proteins. X-ray crystallography utilizes X-ray diffraction to precisely determine the atom locations in protein crystals, while NMR spectroscopy exploits the magnetic properties of atoms in…
-
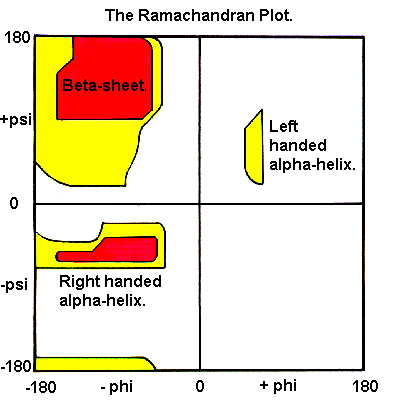
Applications of Ramachandran Plot
Discover the diverse applications of the Ramachandran plot in protein research. From predicting protein structures to identifying binding sites and analyzing mutations, this powerful tool aids in validating structures, comparing conformations, and uncovering novel protein structures. By utilizing the Ramachandran plot alongside other techniques, researchers can gain a comprehensive understanding of protein structure and flexibility.
-
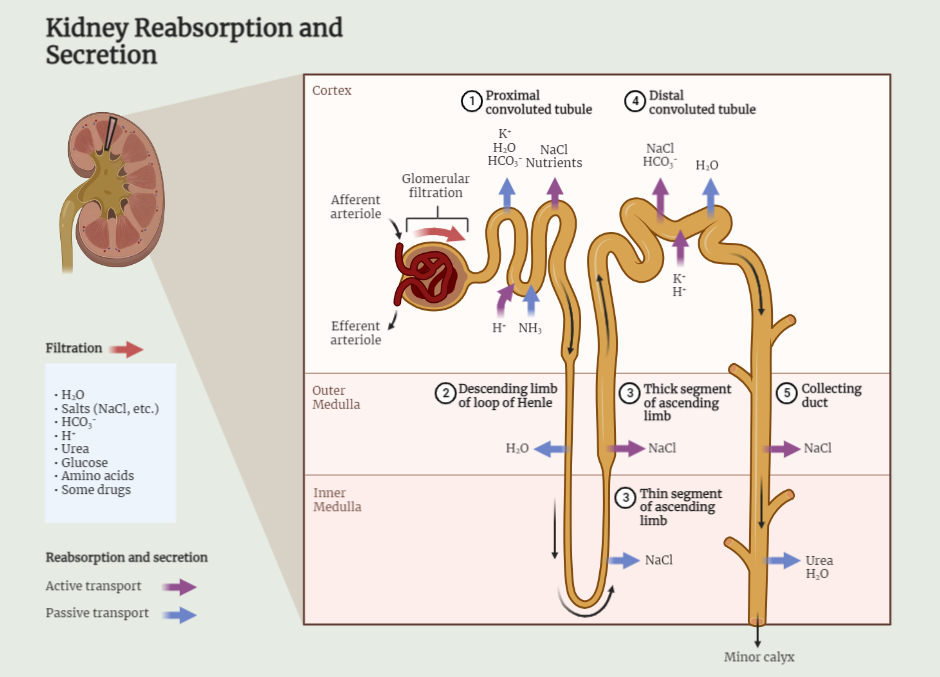
Mechanism of Urine Formation by the Kidney
Explore the intricate mechanism of urine formation by the kidney, involving filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Discover how the kidney maintains fluid and electrolyte balance while regulating the concentration and dilution of urine. Understand the role of hormones in this vital physiological process.
-
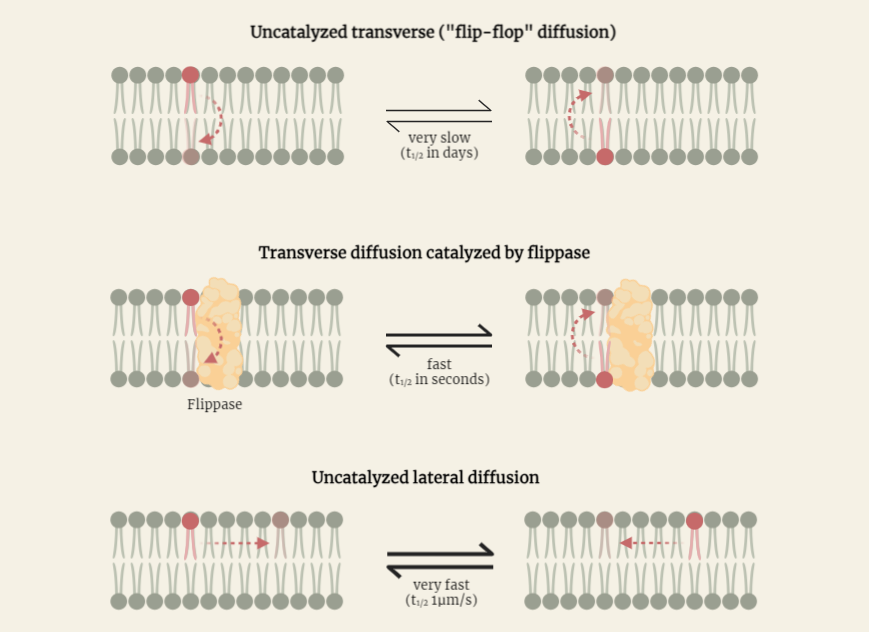
Phospholipid Movement
Phospholipids, essential components of cell membranes, play a pivotal role in maintaining membrane integrity. Explore the dynamic movements of phospholipids through lateral and transverse diffusion, as well as the crucial processes of fusion and fission. Gain insights into the intricate dynamics of cell membranes and their significance in cellular function.
-

Ramachandran Plot
Explore the Ramachandran plot, a vital tool in structural biology for analyzing protein conformation and folding. Understand the significance of phi and psi angles, interpret the plot, and its applications in protein structure prediction and refinement. Discover how the plot aids in unraveling protein folding pathways and assessing stability. Gain insights into protein engineering and…
-
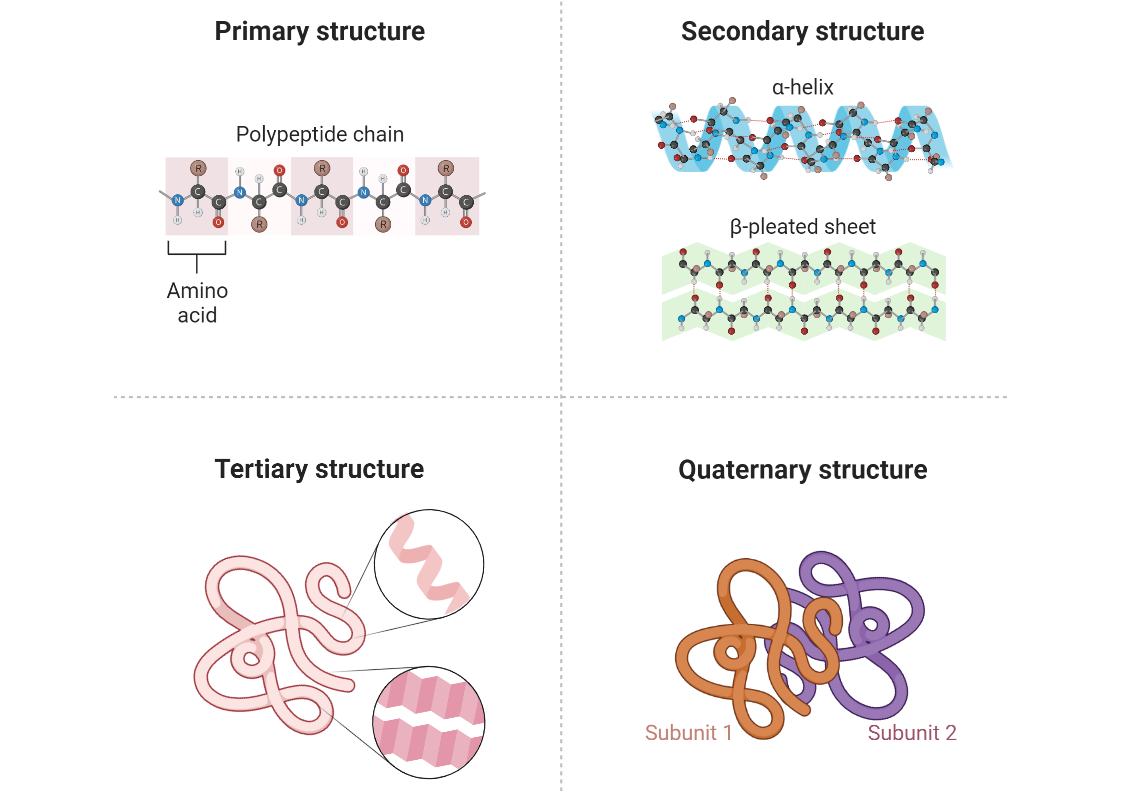
Protein Folding
Dive into the fascinating world of protein folding, where linear sequences of amino acids transform into intricate three-dimensional structures. Discover the driving forces behind protein folding, such as the hydrophobic effect and hydrogen bonding. Explore the stages of protein folding, from primary to tertiary structure, and unravel its applications in understanding protein function, designing drugs,…
-
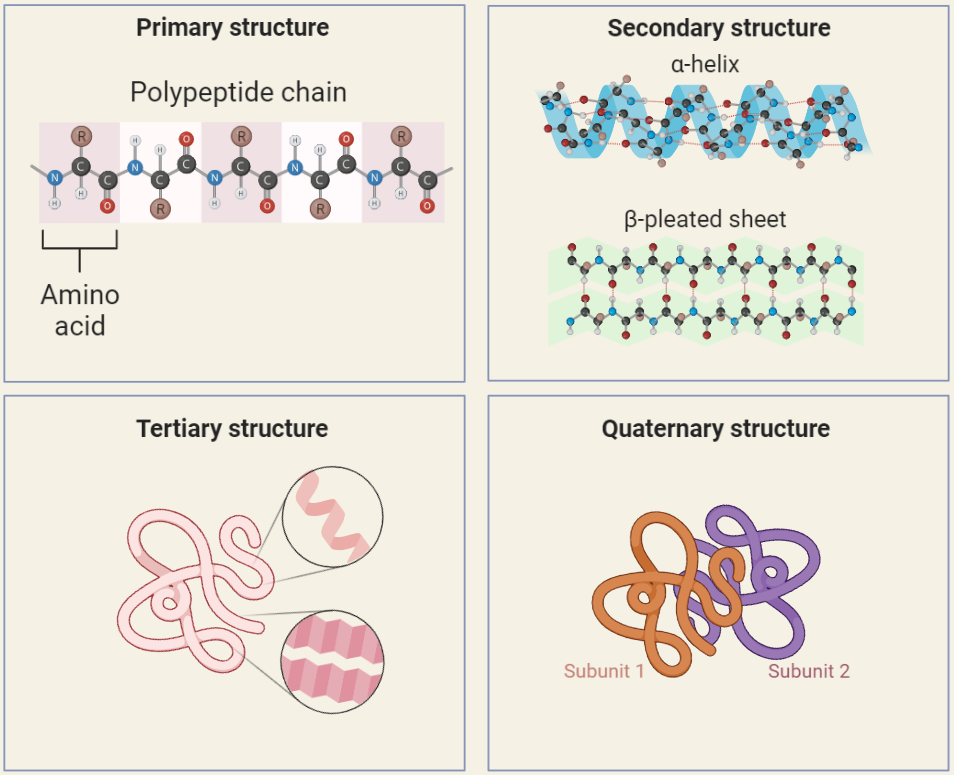
Secondary Structures of Proteins
Protein secondary structure, including alpha helix and beta sheet, plays a vital role in protein function and stability. Explore their characteristics, discover their importance in drug design and protein engineering, and learn about their applications in biotechnology.
-

Spectroscopy and Beer-Lambert’s Law
Spectroscopy, a fascinating scientific technique, delves into the captivating interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation. By analyzing how substances interact with light at different wavelengths, spectroscopy provides crucial insights into the composition, structure, and behavior of materials. One of the fundamental principles in spectroscopy is the Beer-Lambert’s Law, a cornerstone in quantitative analysis. This law…
-
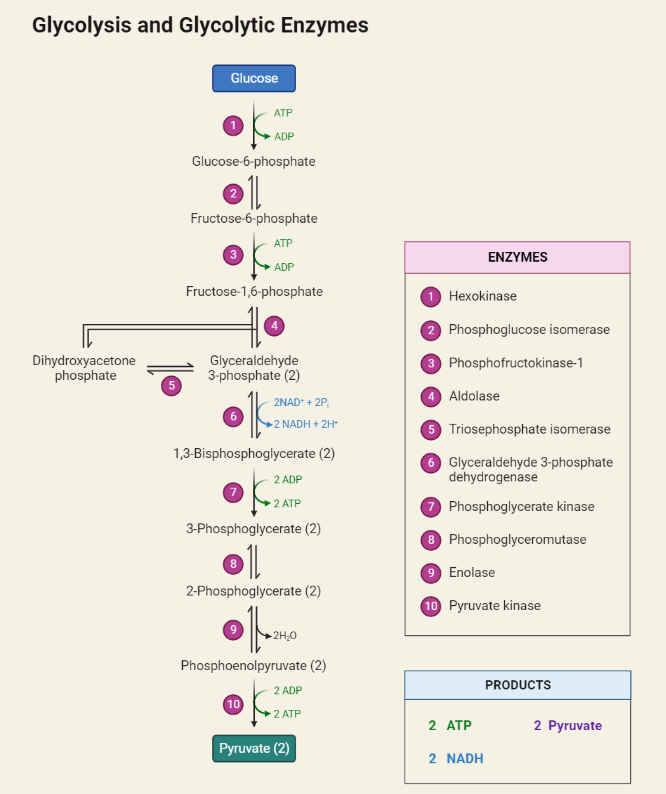
Steps of Glycolysis
The text provides a comprehensive overview of glycolysis, a crucial metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, ATP, and NADH. It explores the process, enzymes involved, and its significance in cellular energy production. Glycolysis’s versatility, occurring in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, makes it fundamental for cell survival and energy generation in various organisms, from…
-

Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic process that occurs in almost all living organisms. It is a critical pathway that provides energy for cells by breaking down glucose to produce ATP. This article will discuss the definition, equation, enzymes, and steps involved in glycolysis. What is Glycolysis? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate,…
-
CT Scan Technique
CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a widely used medical imaging technique that produces detailed, cross-sectional images of the body using x-rays and computer technology. The technique uses x-ray detectors, reconstruction algorithms and dose management techniques to minimize the radiation dose to the patient while producing high-quality images. Specialized CT scans such as CT angiography, CT…
-
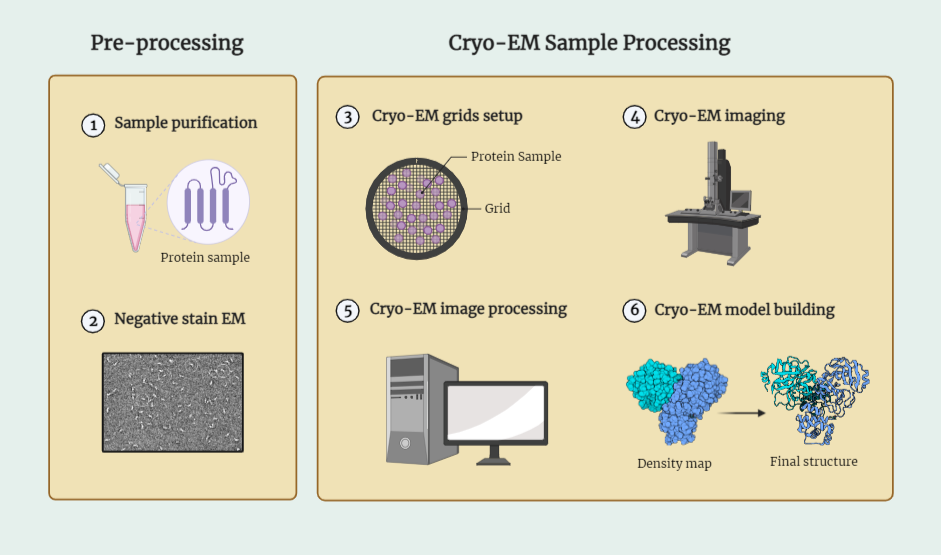
Cryo Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)
Cryo-EM is a cutting-edge imaging technique used for studying the structure of biological macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. By using a cryogenic electron microscope, researchers can capture high-resolution images of frozen, hydrated samples, preserving their native state and avoiding radiation damage. The sample preparation is a crucial step that involves rapid freezing of…
-

Proteins
Proteins are crucial biomolecules that perform a vast range of functions in living organisms, from providing mechanical support to catalyzing chemical reactions and protecting against pathogens. Composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, proteins come in various types, each with specific roles and characteristics. Structural proteins, such as collagen and elastin, provide support and…
-
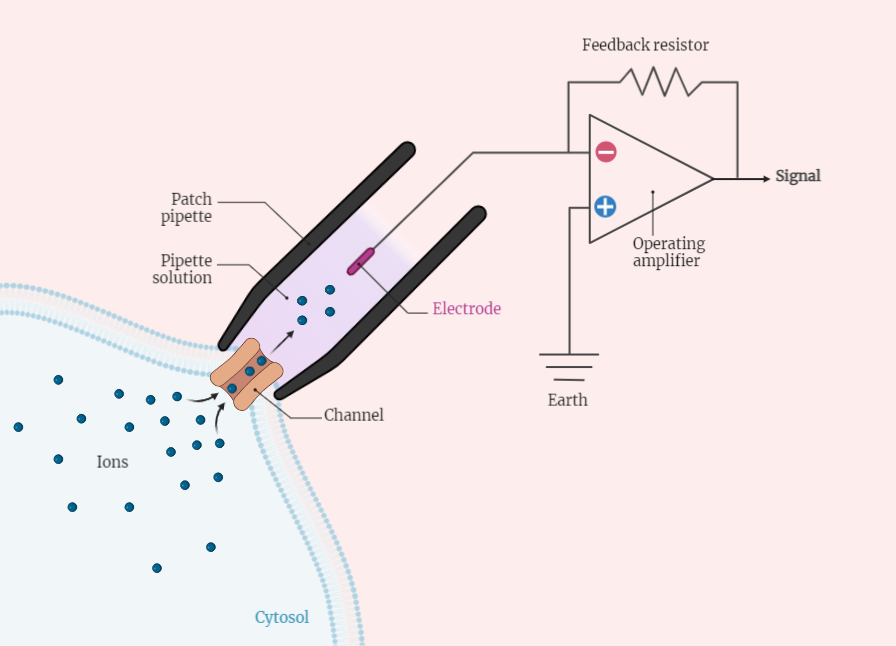
Patch Clamp Technique
The patch clamp technique is a widely used electrophysiological method for studying ion channels in cell membranes. This technique involves using a micropipette to form a gigaohm seal with a cell membrane, allowing for the manipulation of the electrical potential across the membrane. There are four main types of patch clamp, each with their own…
-

Carbohydrates
The text provides an overview of carbohydrates, which are a class of biomolecules composed of simple sugars linked together through glycosidic bonds. Carbohydrates play crucial roles in energy storage and transport, as well as in structural support and cell-cell recognition. The three main types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, each with specific functions…
-
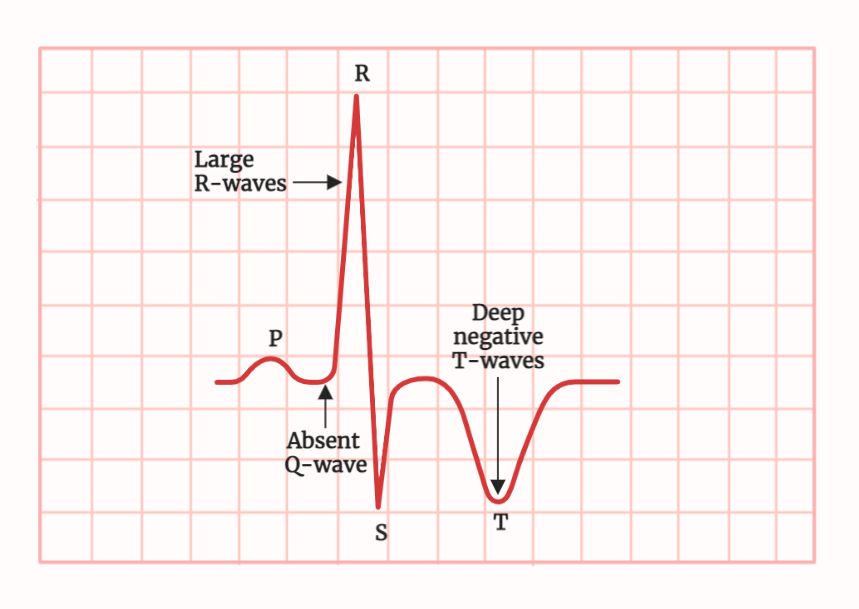
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a widely used diagnostic tool for the evaluation of heart conditions. It is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart and displays it as waves on a graph. The ECG is used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac…
-

Structure of Protein
Proteins are essential macromolecules that play a crucial role in many biological processes. They are made up of amino acids, which are linked together through peptide bonds to form a linear chain. The sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its three-dimensional structure and, consequently, its function. In this study note, we will explore…
-
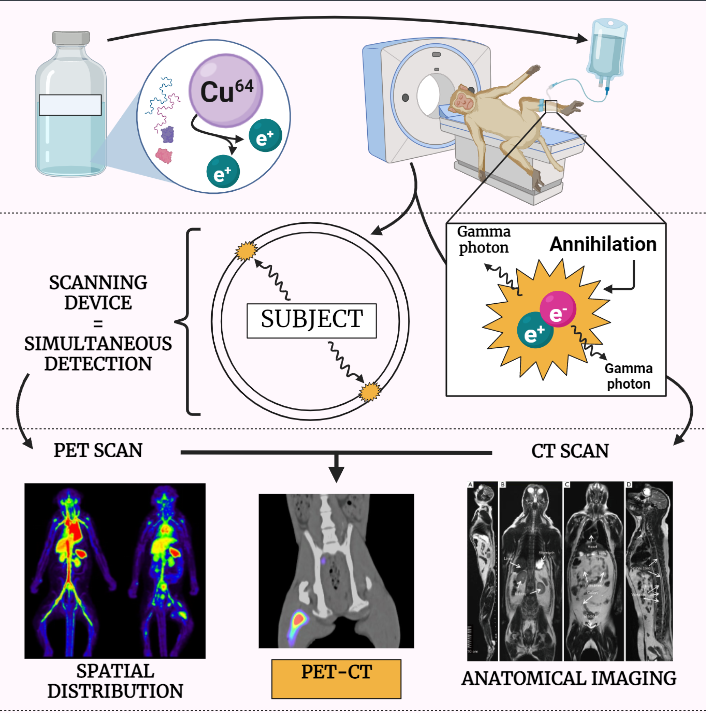
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
The article provides an in-depth study note on Positron Emission Tomography (PET), a non-invasive nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses small amounts of radioactive materials to produce images of the body’s biological processes. It explains the principles of the PET imaging technique, the use of radiotracers, its applications in detecting and diagnosing various diseases, and…
-
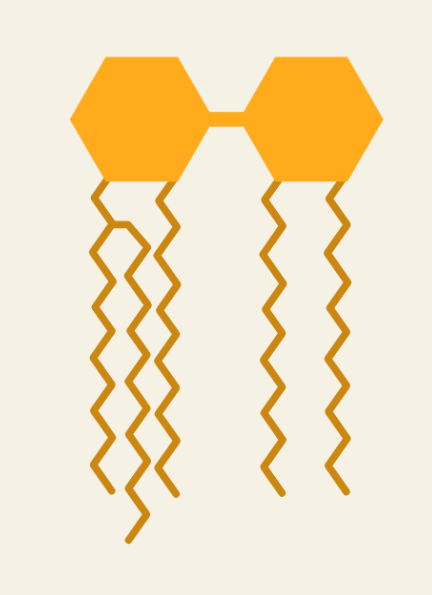

Lipids
Lipids are essential macromolecules that play a vital role in various biological processes. This guide explores the structure and function of lipids, their types, and their importance in energy storage, signaling, and cell membrane formation. We discuss the building blocks of lipids, including fatty acids and glycerol, and the types of lipids, including triglycerides, phospholipids,…
-
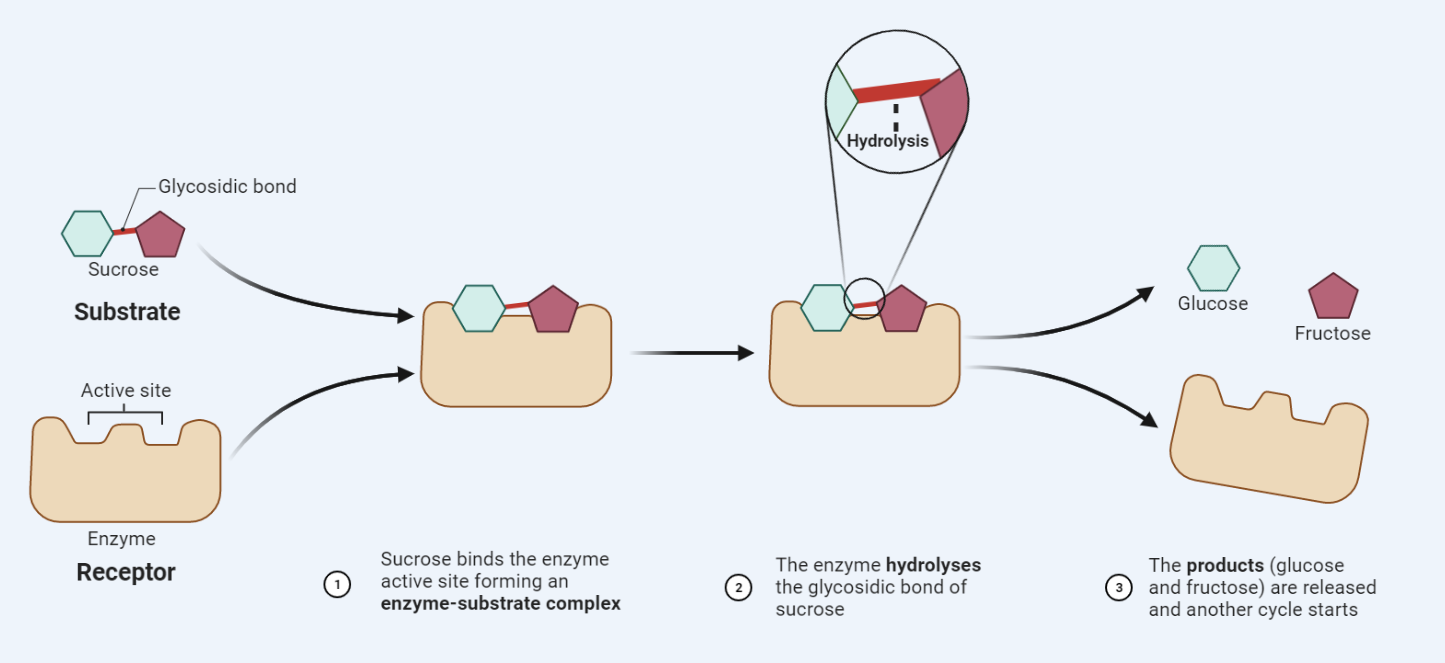
Enzyme-substrate interaction
Enzymes are crucial biomolecules that facilitate specific chemical reactions in living organisms. They do this by binding to specific molecules known as substrates, and this interaction is key to their function. Enzymes can only catalyze specific types of reactions, and this specificity is determined by the unique shape of their active site, which is in…
-
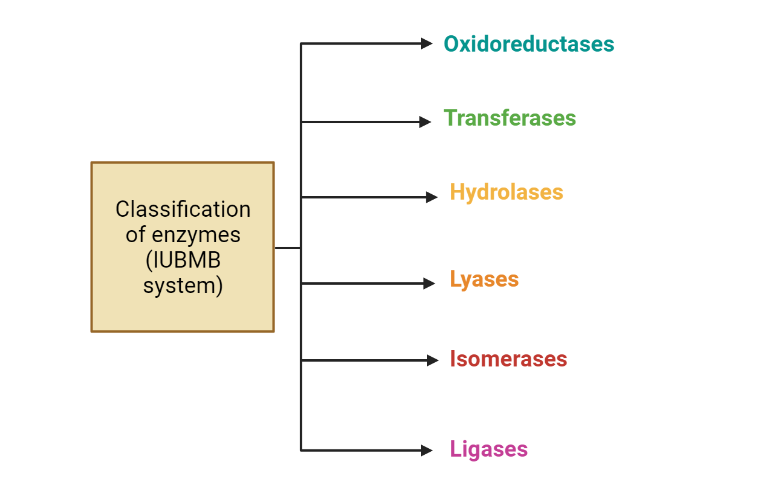
Enzymes : classification
Enzymes are incredibly important biomolecules that play a crucial role in the proper functioning of living organisms. They catalyze specific chemical reactions, making it possible for various biological processes such as metabolism, DNA replication, and cell signaling to occur efficiently. The structure of enzymes is complex, with different levels of organization, including the primary, secondary,…
-
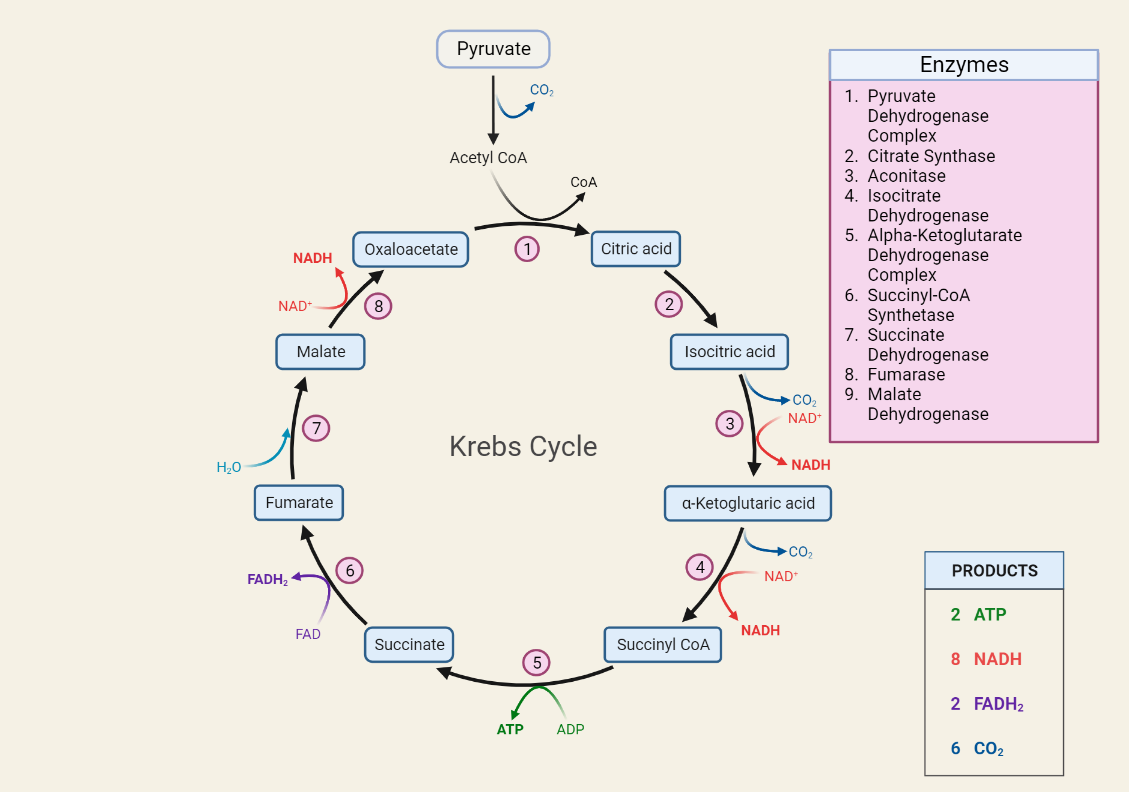
Krebs cycle
occur in the mitochondria of cells. It is a crucial process in cellular respiration, where it breaks down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy that the cell can use. In this article, we will explore the definition, equation, enzymes, and steps involved in the Krebs cycle, as well as its importance in cellular metabolism. Understanding…
-
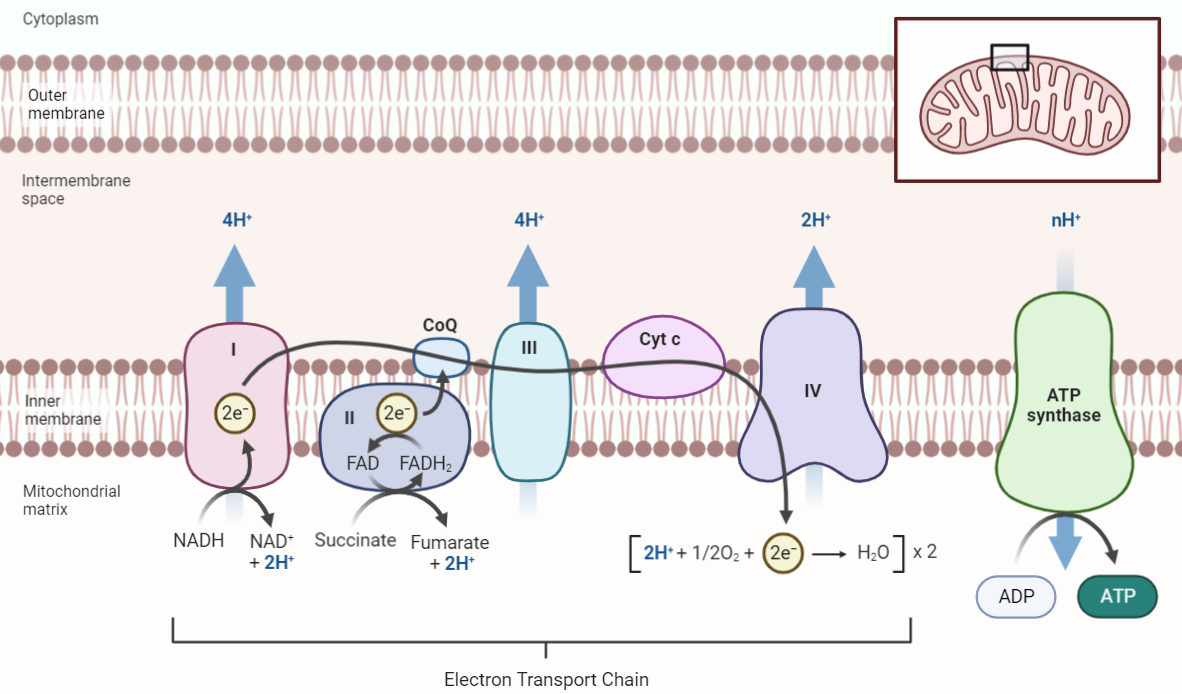
Electron Transport Chain: The Powerhouse of Cellular Respiration
Introduction: Structure of the Electron Transport Chain Complexes of ETC: The ETC is made up of four protein complexes: Complex I, Complex II, Complex III, and Complex IV. Each complex has a specific function in the ETC, and the electron transfer between complexes is tightly regulated. Complex I (NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase): Complex I is the first…
-
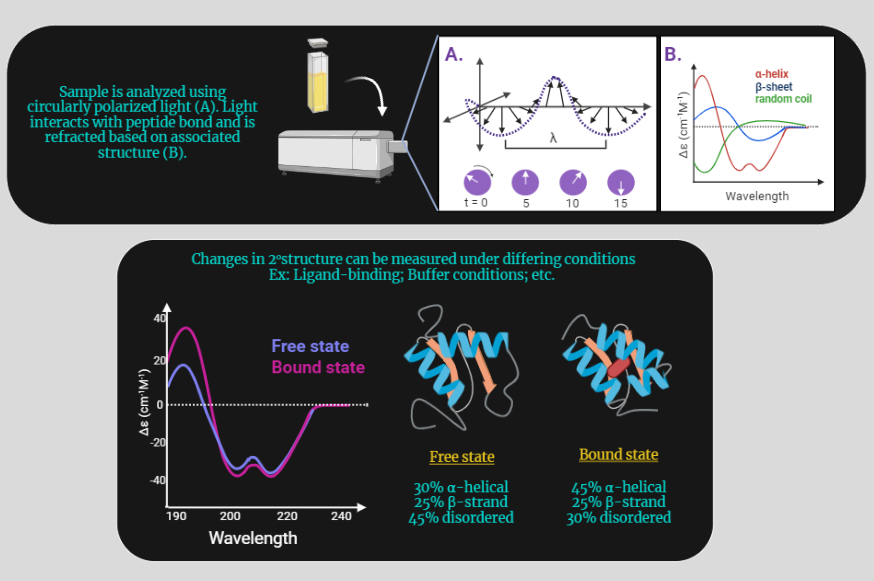
Circular Dichroism (CD) Technique
Circular dichroism (CD) is a powerful spectroscopic technique used to study the structure and properties of chiral molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. It is based on the differential absorption of left and right circularly polarized light by chiral molecules, which can provide information on their secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. In this…
-
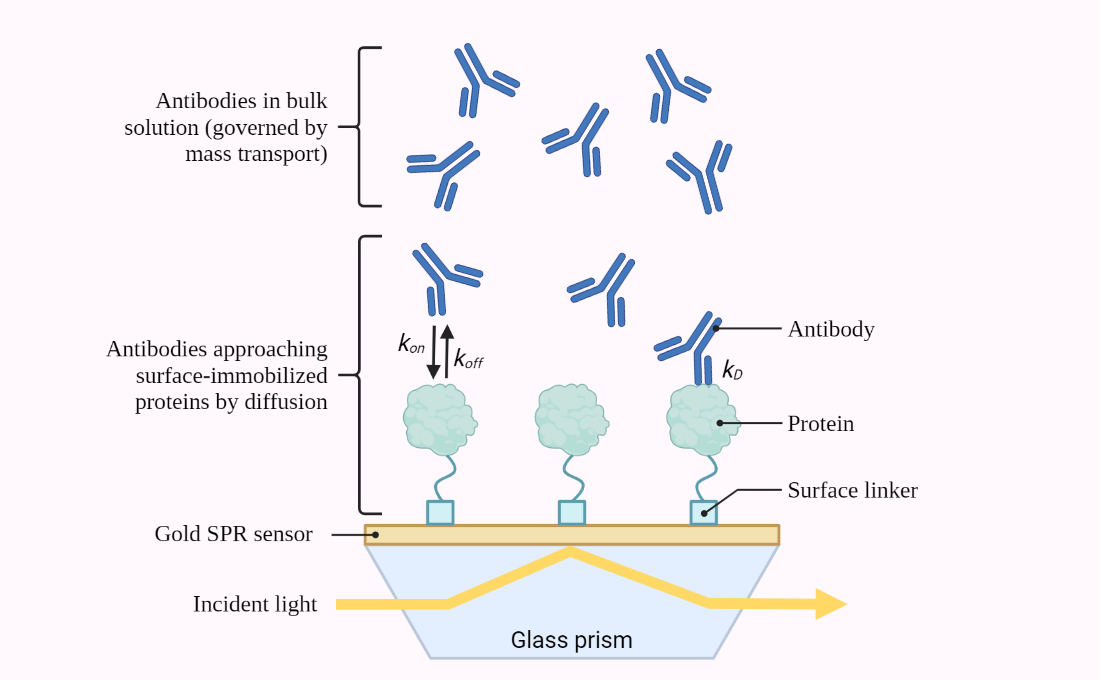
SURFACE PLASMON RESONANCE (SPR)
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) is a powerful label-free technique used for real-time monitoring of biomolecular interactions. This article provides a comprehensive study of the SPR technique, covering its principles, instrumentation, applications, factors affecting the SPR response, advantages and limitations, future directions, and more. With 15 headings and FAQs, this article is a valuable resource for…
-
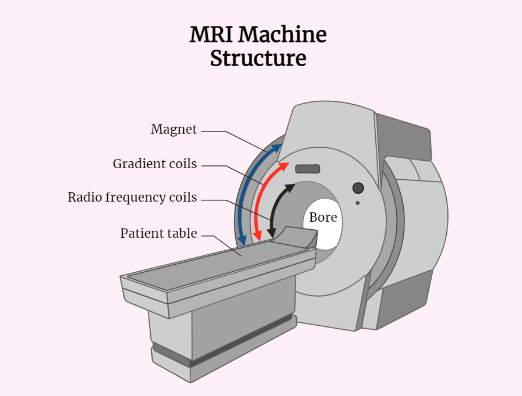
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that creates detailed images of the internal structures of the body using magnetic fields and radio waves. MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that provides high-quality images of soft tissues, organs, and bones without exposing patients to harmful radiation. The basic principle of MRI is to…
-
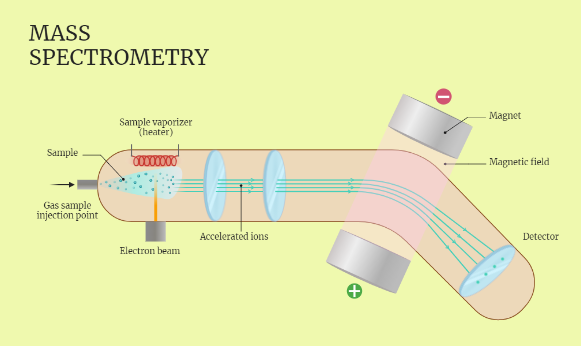
Mass Spectrometry (MS) Technique
The article discusses the principles, techniques, and applications of Mass Spectrometry (MS) from a biophysics perspective. It explains how MS is used to study the structure, dynamics, and interactions of biomolecules and how it can be applied to a wide range of biomolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and small molecules. The article also discusses…
-
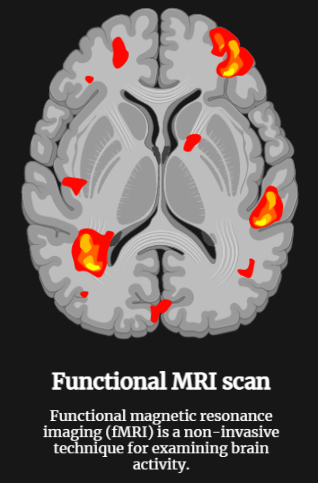
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is a powerful medical imaging technique used to study brain function. It measures changes in blood flow in the brain using MRI technology, which can be used to infer changes in neural activity. fMRI is commonly used in neuroscience, psychology, and psychiatry to investigate a wide range of questions related…
-
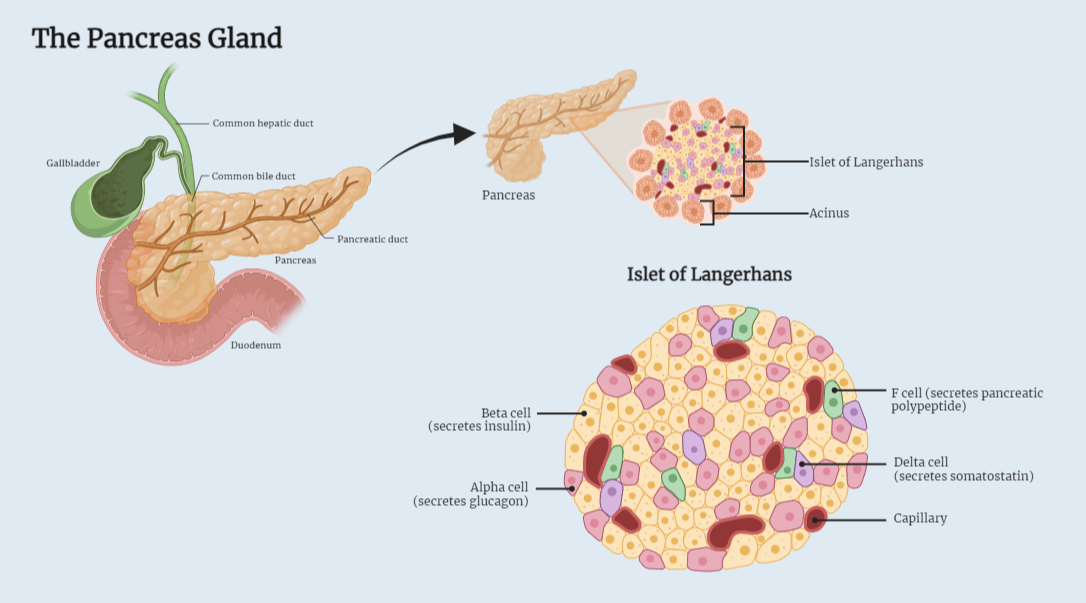
The pancreas gland
The pancreas, situated behind the stomach in the upper abdomen, plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism regulation. It produces insulin and glucagon, which control blood sugar levels. Dysfunction of the pancreas can lead to conditions like diabetes mellitus and pancreatitis, necessitating accurate diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the pancreas’ significance helps comprehend its impact on…
-

Beer-Lambert Law and Spectrophotometry
Discover the principles of the Beer-Lambert Law and its application in spectrophotometry. Explore how this law relates the concentration of a solute to absorbance, and its significance in quantitative analysis, chemical kinetics, environmental monitoring, pharmaceutical analysis, and biochemical assays. Unlock the power of spectrophotometry in understanding chemical substances and their characteristics.
-
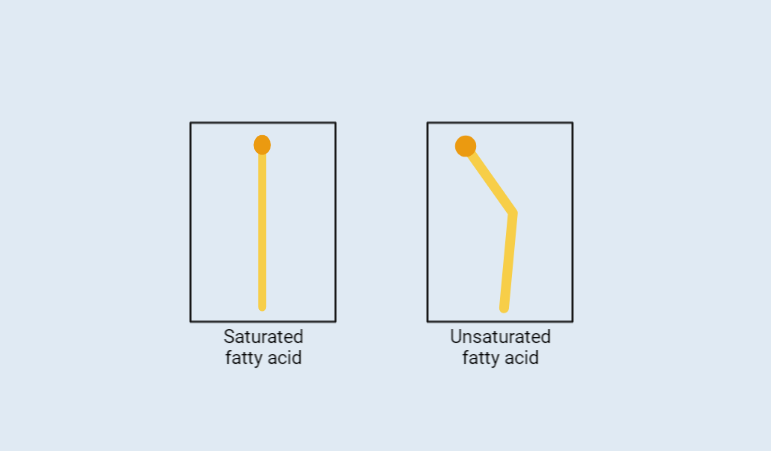

Saturated vs Unsaturated Fatty Acids
This excerpt compares saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, highlighting their differences in physical state, melting point, double bonds, stability, and their effects on cholesterol, heart diseases, diabetes, obesity, cancer, and other health risks. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed dietary choices and maintaining overall well-being.
-
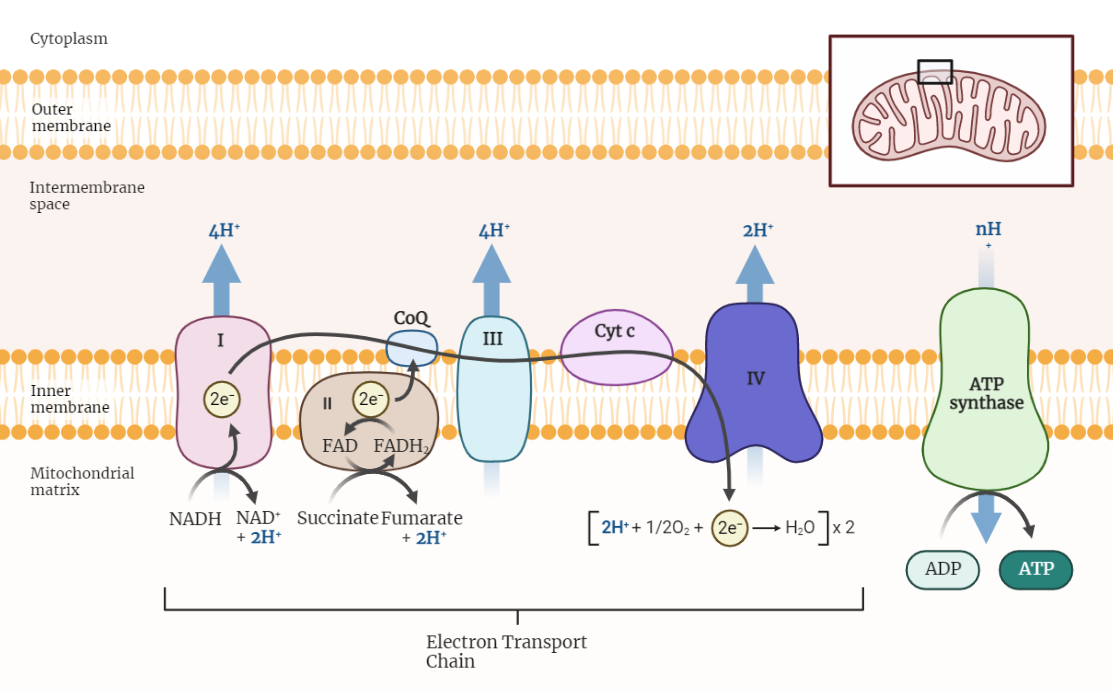
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a fundamental process in cellular energy production. It involves the synthesis of ATP through the electron transport chain (ETC) and chemiosmosis. The ETC, consisting of protein complexes, facilitates the flow of electrons and generates a proton gradient. This proton gradient is harnessed by ATP synthase to produce ATP. The efficiency of oxidative…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




