-
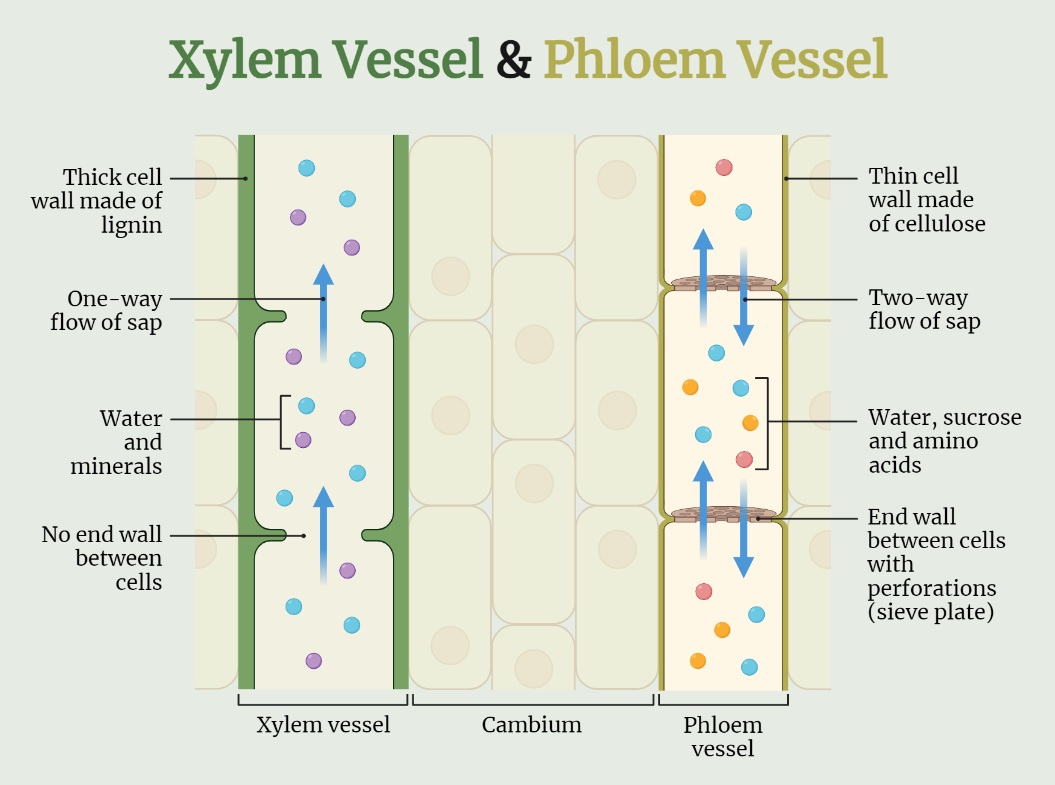
Means of Transport in Plants
Discover the fascinating means of transport in plants, as water, nutrients, and sugars are efficiently distributed through specialized structures like xylem and phloem. From transpiration and active transport to cytokinesis and endocytosis, explore the intricate mechanisms that ensure the plant’s survival and growth by delivering essential resources to various parts of the pla
-
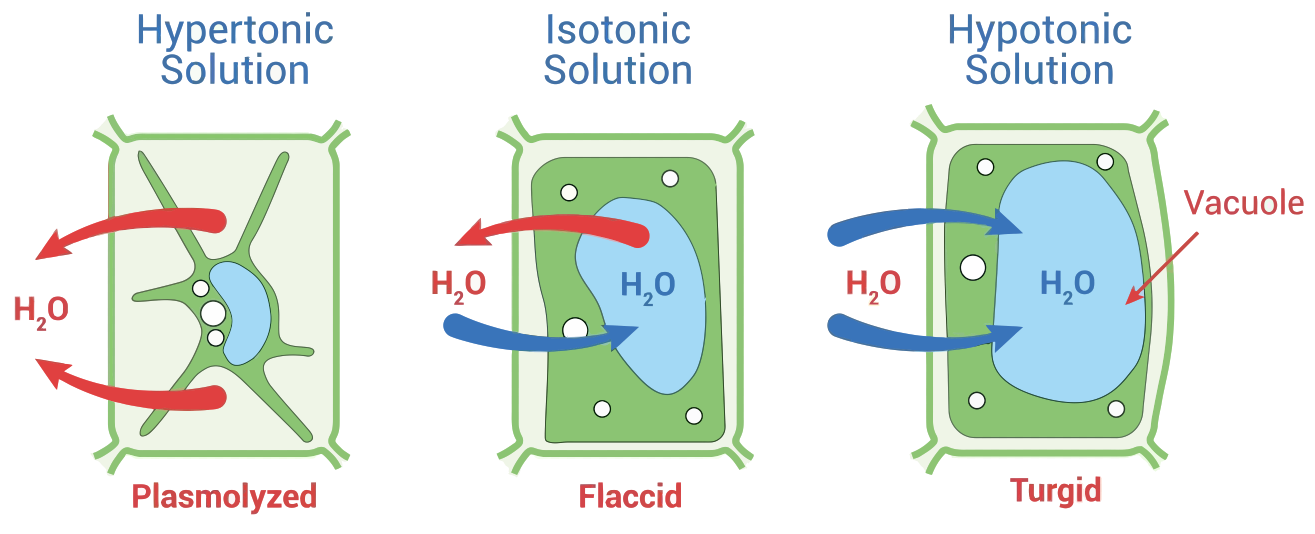
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process by which a plant cell shrinks away from its cell wall when placed in a hypertonic solution. This study note explains the process, types, examples, and the significance of plasmolysis in plant biology and agriculture. Explore the effects of water and solute stress on plants.
-
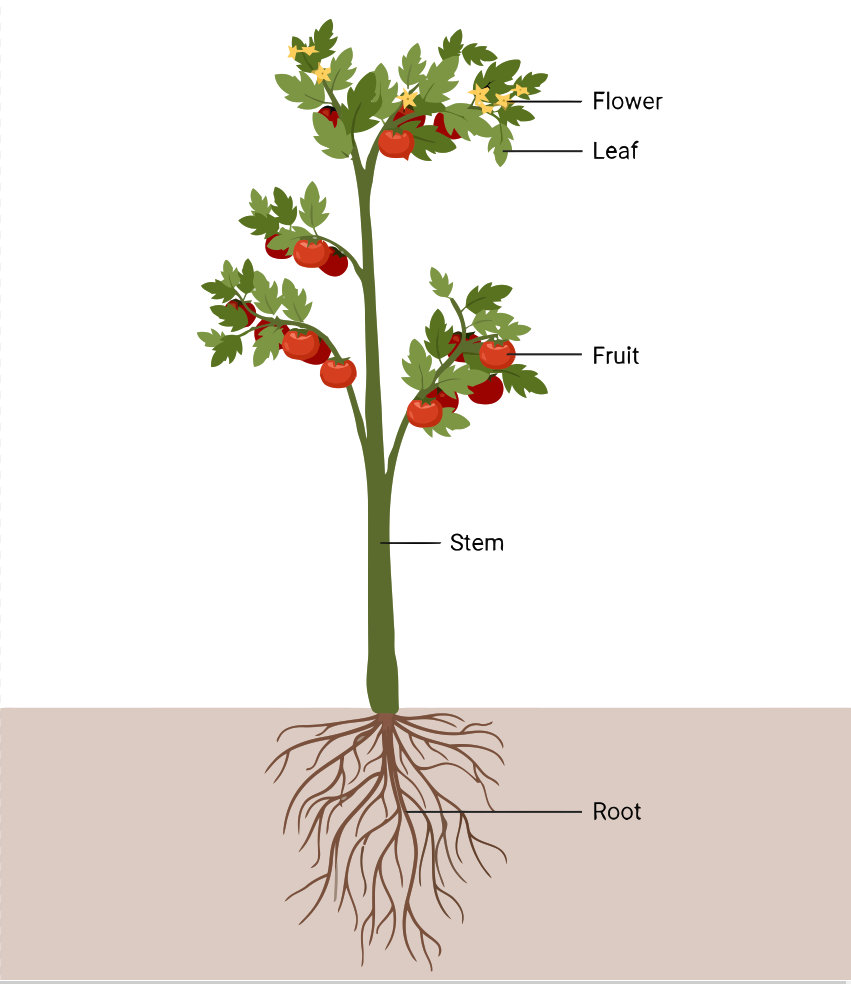
Morphology of Plant
The study of plant morphology is the study of the structure and form of plants. It encompasses the organization of plant tissues, the structure and function of roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, and the processes of photosynthesis and reproduction. Understanding plant morphology is essential for comprehending the interactions between plants and their environment, as well…
-
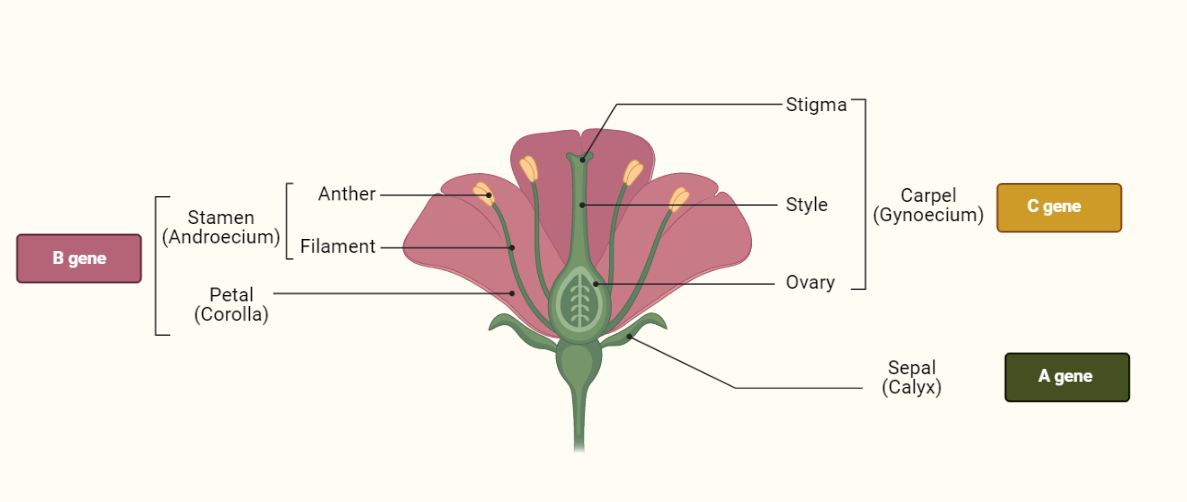
ABC Model of Flowering
The ABC model of flowering is a genetic and molecular framework that explains how plants transition from vegetative growth to reproductive development. The model proposes that three groups of genes, referred to as A, B, and C genes, work together to regulate this process. A genes are responsible for initiating the flowering process independently of…
-
C4 Plants
C4 plants have evolved a unique mechanism for carbon fixation that allows them to efficiently produce glucose in hot and dry environments. This mechanism, known as the C4 pathway, involves the spatial separation of carbon dioxide fixation and the Calvin cycle. The C4 pathway provides several ecological advantages to plants, including increased water use efficiency…
-
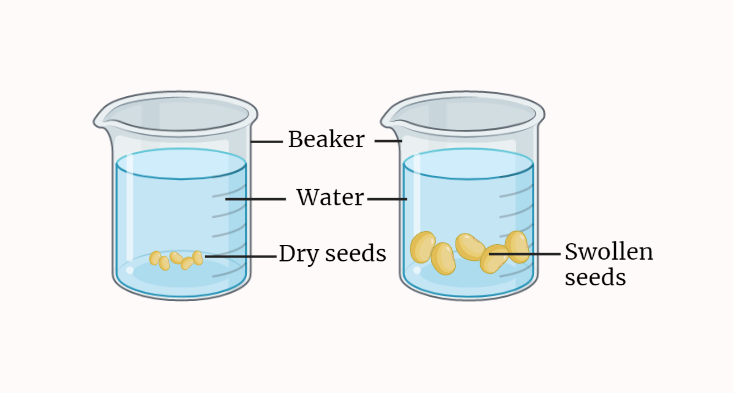
Imbibition
Imbibition is a fascinating process observed in both plants and materials science. It involves the absorption of liquid by solids, resulting in interesting phenomena such as seed germination, polymer swelling, and capillary action. Understanding imbibition provides insights into various natural and synthetic systems, contributing to advancements in agriculture, materials engineering, and more.
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




