-
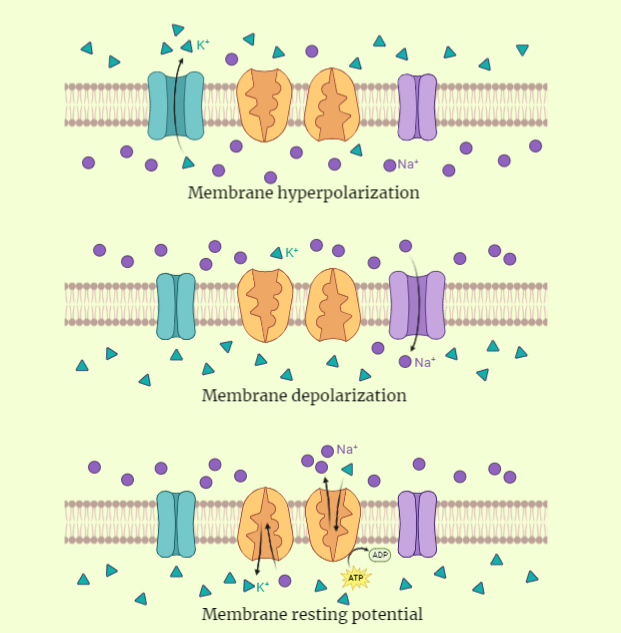
Membrane Potential
The membrane potential is a fundamental concept in cellular physiology, playing a crucial role in the proper functioning of cells. It refers to the electrical potential difference across a biological cell membrane, which is maintained by ion gradients. These gradients are created by the selective permeability of the membrane to ions such as sodium, potassium,…
-
Immune Response in Plants
Plants, just like animals, have a sophisticated immune system that protects them from pathogens. However, the plant immune response differs from that of animals, as it relies on physical and chemical barriers, as well as specific responses triggered by pathogen detection. The immune response in plants can be classified into basal defense, which is the…
-
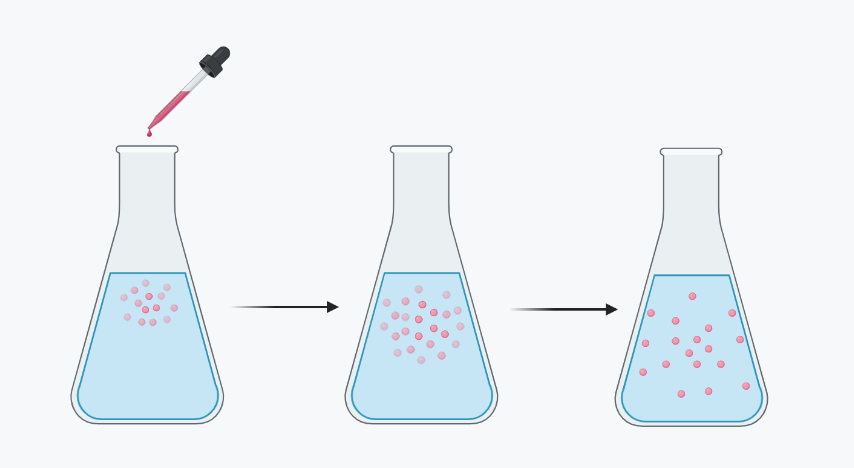
Osmosis Process
Explore the fascinating process of osmosis, where water moves across membranes to balance solute concentrations. Learn about its principles, factors influencing it, and examples of osmosis in plant roots, kidney function, and cellular dehydration. Gain insights into how osmosis plays a crucial role in maintaining water balance and cellular function in living organisms.
-
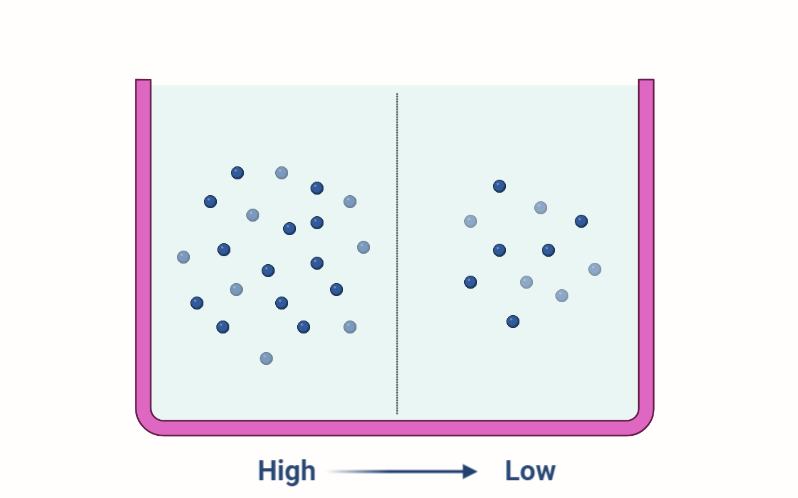
Diffusion
Explore the fascinating process of diffusion, where particles naturally move from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Delve into the principles, factors, and examples of diffusion to understand its significance in various scientific fields and everyday phenomena. Gain insights into how temperature, molecular size, and concentration gradients influence this fundamental process.
-
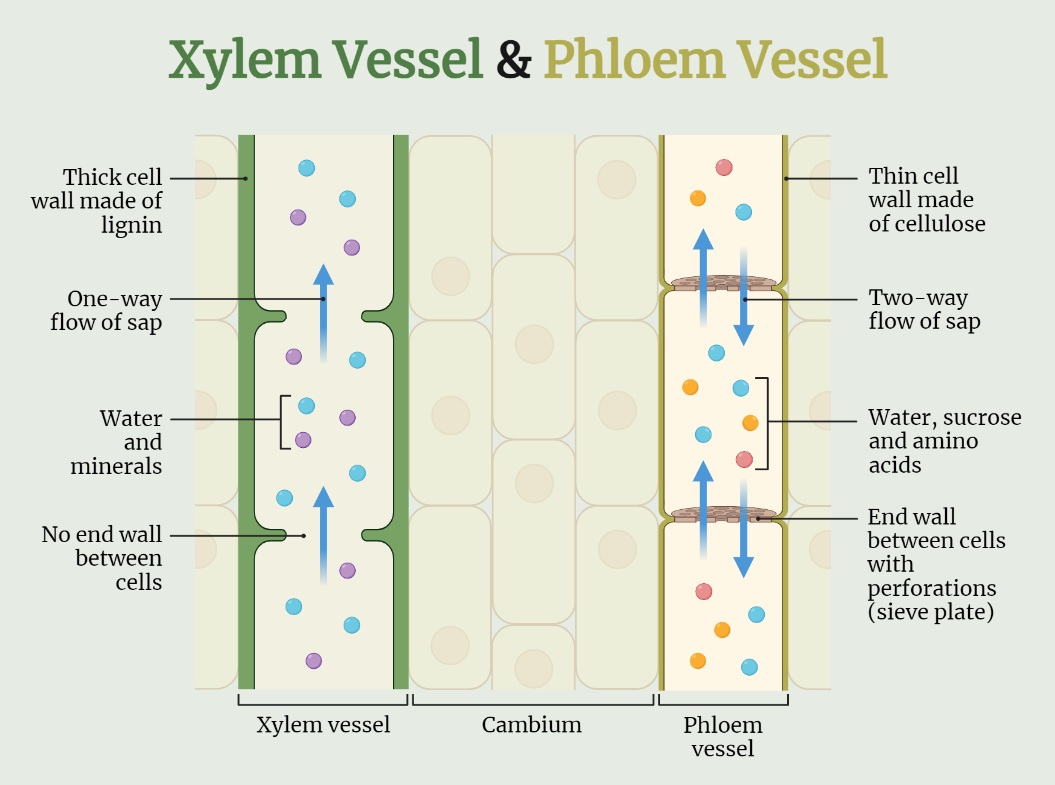
Means of Transport in Plants
Discover the fascinating means of transport in plants, as water, nutrients, and sugars are efficiently distributed through specialized structures like xylem and phloem. From transpiration and active transport to cytokinesis and endocytosis, explore the intricate mechanisms that ensure the plant’s survival and growth by delivering essential resources to various parts of the pla
-
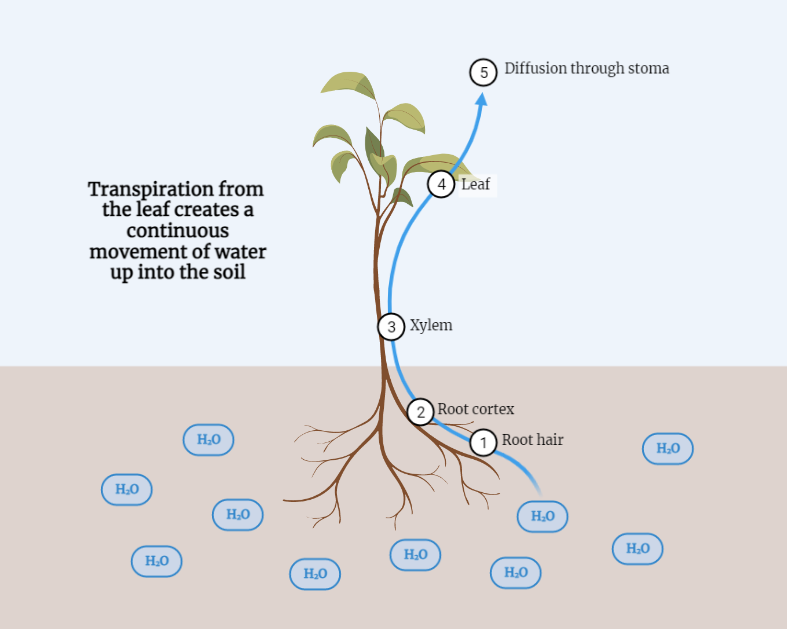
Transportation in Plants
Transportation in plants is a vital process that ensures the distribution of water, nutrients, and organic compounds throughout the plant’s various parts. Through transpiration, water is absorbed by the roots and transported upwards through the xylem vessels, driven by a combination of factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed. Meanwhile, translocation facilitates the movement…
-
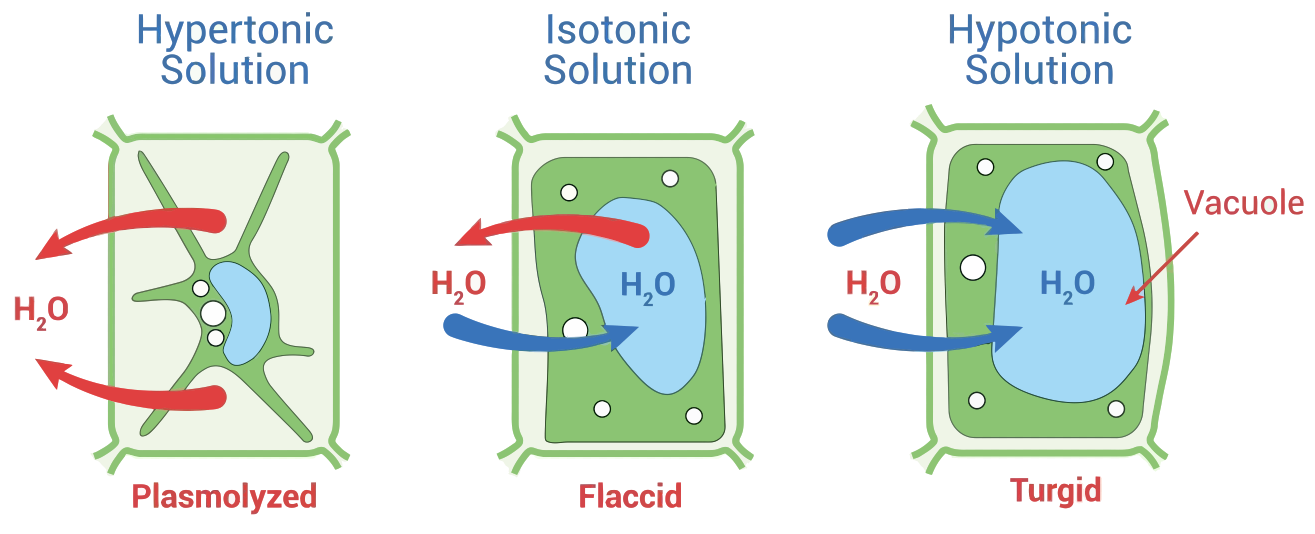
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process by which a plant cell shrinks away from its cell wall when placed in a hypertonic solution. This study note explains the process, types, examples, and the significance of plasmolysis in plant biology and agriculture. Explore the effects of water and solute stress on plants.
-
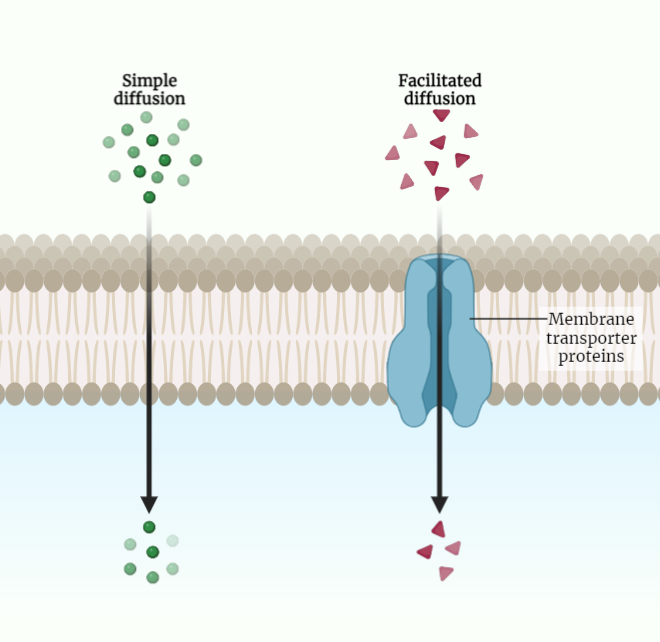
Passive Transport
Passive transport refers to the movement of substances across cell membranes without the use of energy. This study note explores key concepts such as diffusion, osmosis, the role of the cell membrane, concentration gradients, and how passive transport contributes to maintaining cellular homeostasis. Understanding these mechanisms is vital in comprehending the fundamental processes of substance…
-
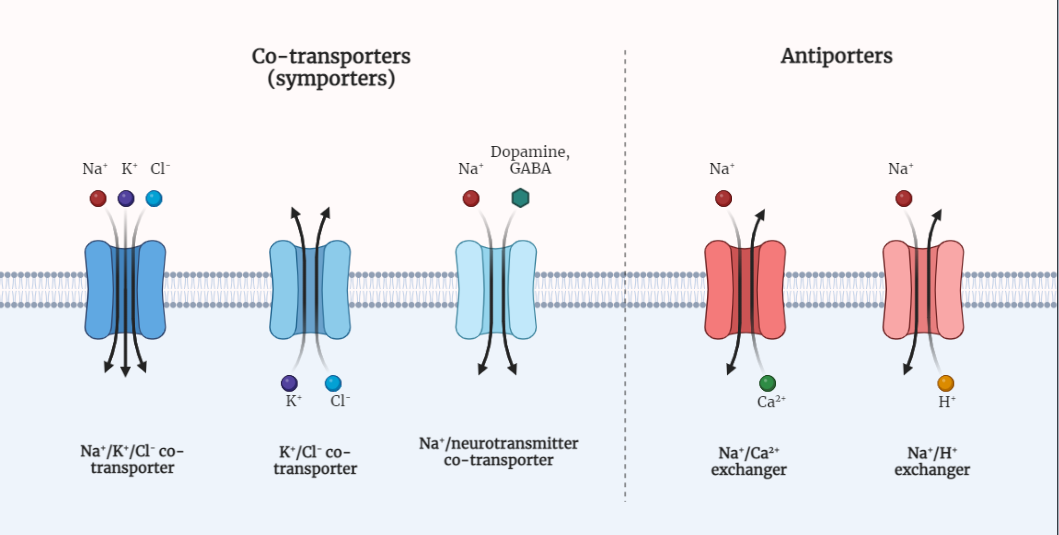
Active Transport
Active transport is a fundamental process in cellular biology that enables the movement of molecules across cell membranes against their concentration gradient. It requires the expenditure of energy, typically derived from ATP. This article explores the different types of active transport, including primary and secondary active transport, as well as cotransport. It highlights the significance…
-
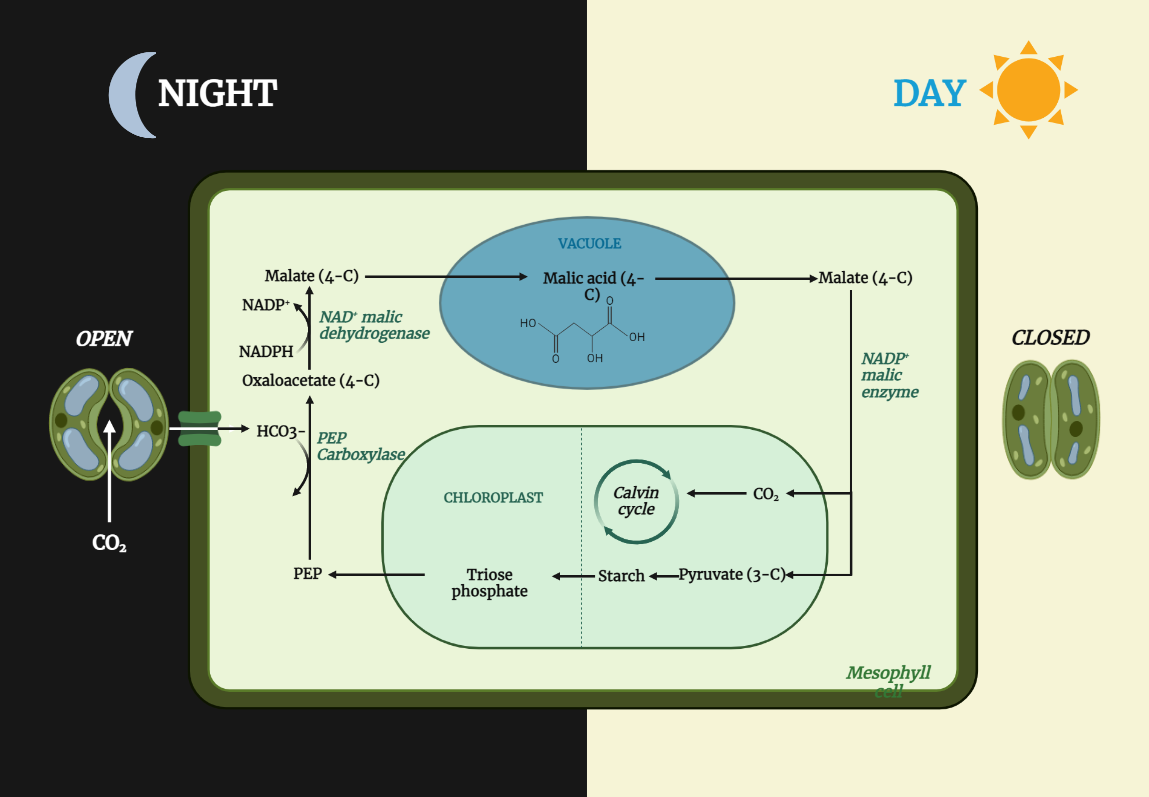
CAM plants
CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) plants have evolved a specialized carbon fixation pathway that allows them to carry out photosynthesis while minimizing water loss, making them well adapted to arid and semi-arid environments. Their ability to store water in their leaves, stems, and roots, along with their thick, waxy leaves and shallow root system, helps them…
-
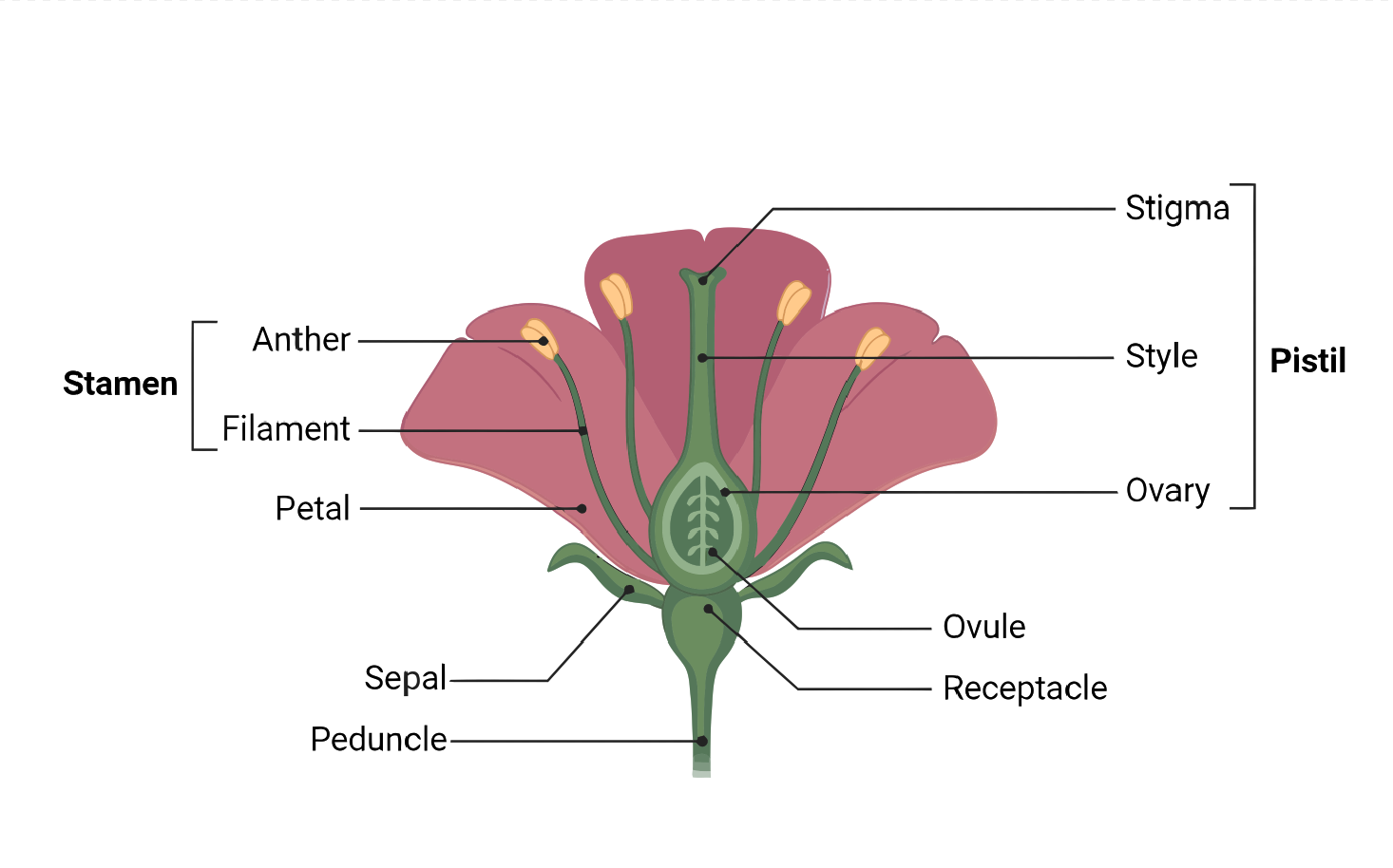
The Flower
Understanding the anatomy of a flower is essential to comprehend the mechanism of plant reproduction and pollination. A flower consists of several parts, including sepals, petals, stamens, pistil, and nectary, arranged in a specific pattern. The arrangement of petals in a flower’s corolla is known as aestivation and can be of various types, such as…
-
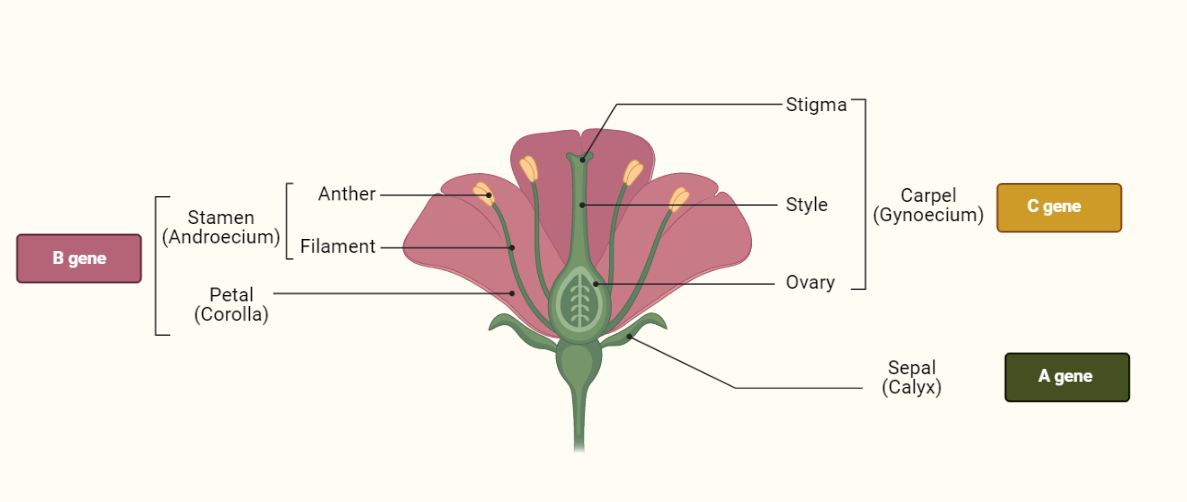
ABC Model of Flowering
The ABC model of flowering is a genetic and molecular framework that explains how plants transition from vegetative growth to reproductive development. The model proposes that three groups of genes, referred to as A, B, and C genes, work together to regulate this process. A genes are responsible for initiating the flowering process independently of…
-
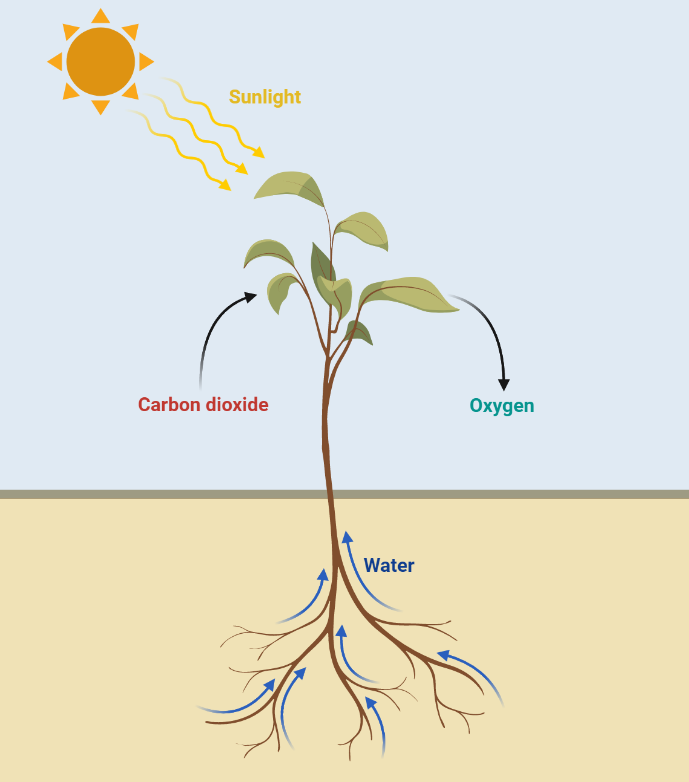
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that occurs in green plants and other photosynthetic organisms. It is the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose and other organic compounds. This energy is then used to fuel the metabolic processes of the organism. Photosynthesis is vital to the survival…
-

Osmosis
Osmosis is a process that occurs naturally in all living things, including plants and animals. It is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This movement of water molecules helps maintain the balance…
-
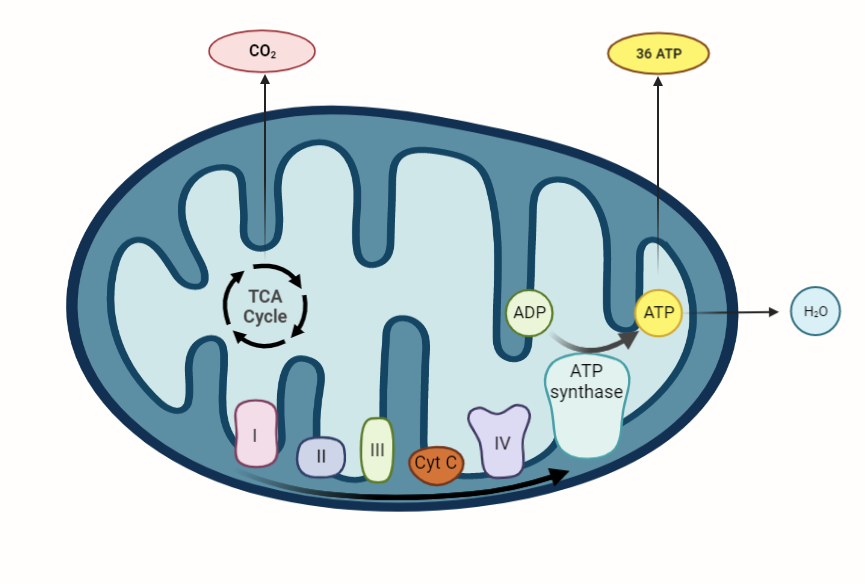
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
The chemiosmotic hypothesis proposed by Peter Mitchell in 1961 is a widely accepted model that explains how living organisms convert energy from electron transfer reactions into ATP synthesis. This hypothesis revolutionized our understanding of how cells generate ATP, the universal energy currency of living systems, and it is a fundamental principle of bioenergetics. The chemiosmotic…
-

CAM Pathway
The CAM pathway is a unique mechanism for carbon fixation in plants that allows them to carry out photosynthesis in arid environments with minimal water loss. By fixing carbon dioxide at night and storing it as malic acid, CAM plants are able to use it during the day to carry out photosynthesis without losing water.…
-
C4 Plants
C4 plants have evolved a unique mechanism for carbon fixation that allows them to efficiently produce glucose in hot and dry environments. This mechanism, known as the C4 pathway, involves the spatial separation of carbon dioxide fixation and the Calvin cycle. The C4 pathway provides several ecological advantages to plants, including increased water use efficiency…
-
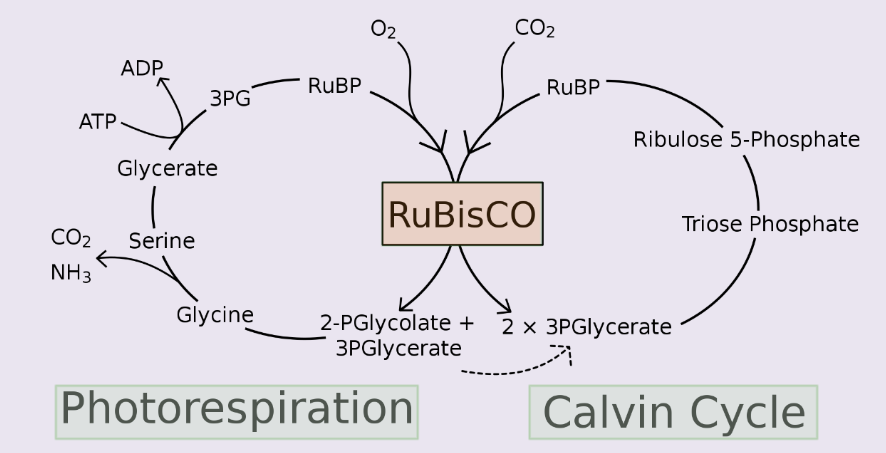
Photorespiration
Photorespiration is a complex process that takes place in plants when the concentration of CO2 inside the leaves decreases. This process reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis and ultimately leads to decreased plant growth and yield. In this chapter, we provide an in-depth overview of photorespiration, its biochemistry, regulation, and its impact on plant growth and…
-
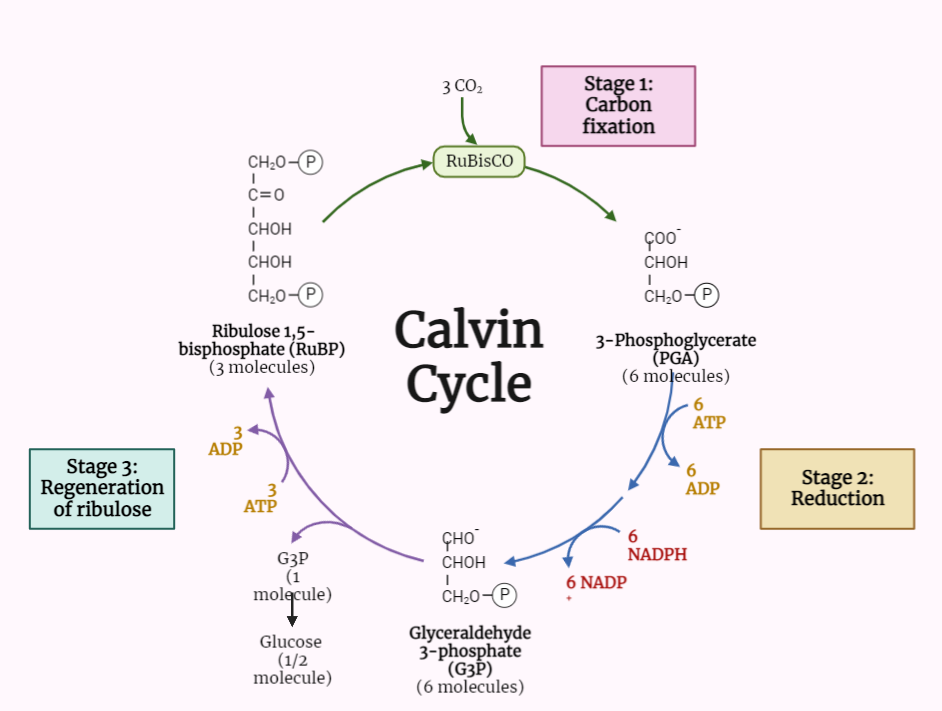
Calvin-Benson Cycle
The Calvin-Benson cycle is a fundamental process in photosynthesis, the metabolic pathway by which autotrophs, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This cycle takes place in the chloroplasts of these organisms and is responsible for fixing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into…
-
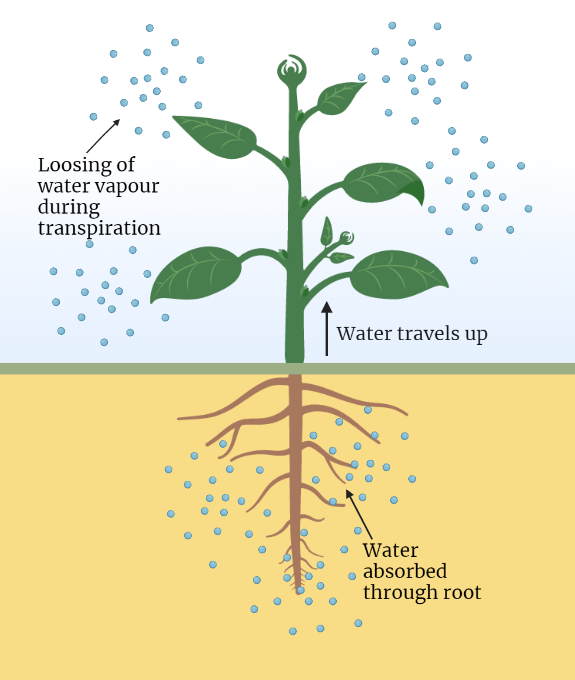
Water Potential
Water potential is a fundamental concept in the study of plant physiology and is also important in the understanding of the movement of water in living organisms. It is a measure of the potential energy of water in a system and is affected by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and solute concentration. Water potential has…
-

Light Signaling in Plants
The article discusses the importance of light signaling in plants and its role in regulating various physiological and developmental processes. It covers topics such as phototropism, photomorphogenesis, photoperiodism, and the light-dependent and independent reactions of photosynthesis. The article provides a brief overview of each topic, explaining their significance in plant growth and survival.
-
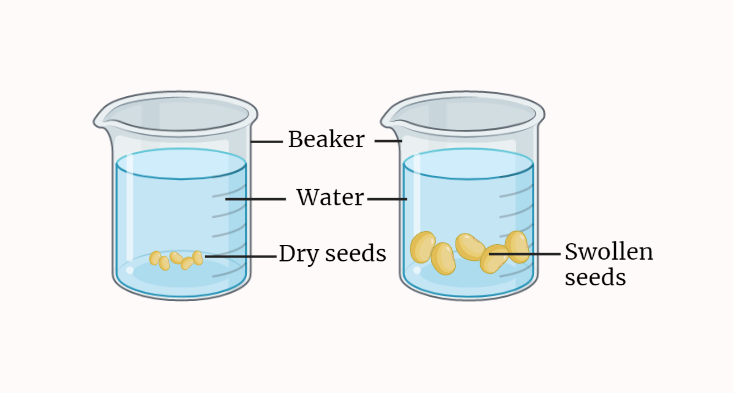
Imbibition
Imbibition is a fascinating process observed in both plants and materials science. It involves the absorption of liquid by solids, resulting in interesting phenomena such as seed germination, polymer swelling, and capillary action. Understanding imbibition provides insights into various natural and synthetic systems, contributing to advancements in agriculture, materials engineering, and more.
-

Transpiration
In this chapter, we delve into the fascinating world of transpiration in plants. We explore the intricate mechanism behind this process, including the role of stomata and the water cycle. Discover how plants adapt to various environmental factors and examine the contrasting strategies of xerophytes and hydrophytes. Gain insight into the ecological impact of transpiration…
-

Facilitated Diffusion
Discover the intricacies of facilitated diffusion, a vital mechanism that allows specific molecules to cross cell membranes with the help of specialized proteins. Explore the principles, proteins involved, and examples of this selective transport process. Gain insights into how facilitated diffusion contributes to cellular homeostasis and essential molecule transport.
-
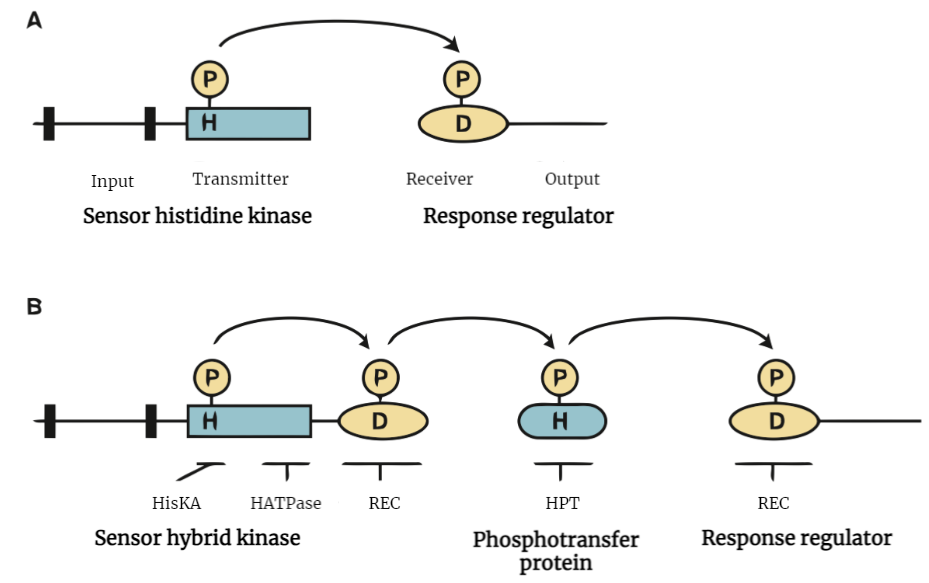
Two-Component Systems in Plants
Two-component systems in plants are vital signaling mechanisms that play a fundamental role in plant biology. Comprising histidine kinases (HKs) and response regulators (RRs), these systems facilitate signal perception and transmission within plant cells, orchestrating various biological processes. One noteworthy example is the ethylene signaling pathway, where the ethylene receptor acts as a histidine kinase,…
-
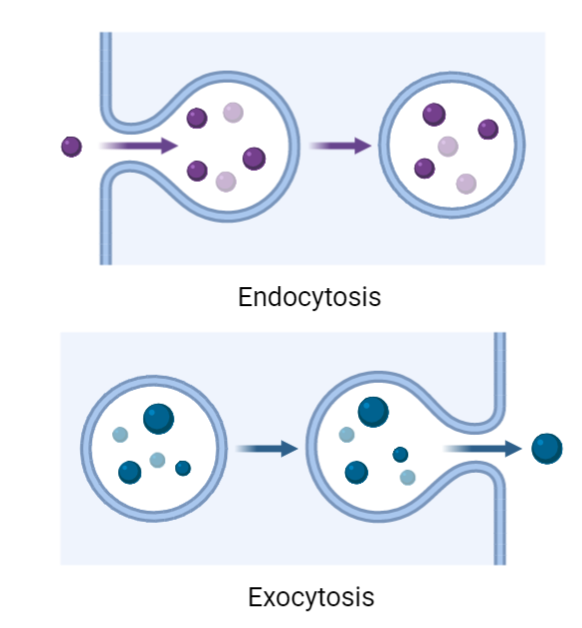
Vesicular Transport
Vesicular transport is a fundamental process that enables the movement of molecules, organelles, and macromolecules within cells. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, facilitating intercellular communication, and carrying out essential physiological functions. This comprehensive study note provides an in-depth exploration of vesicular transport, including its mechanisms, types, regulation, and significance in cellular…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




