-
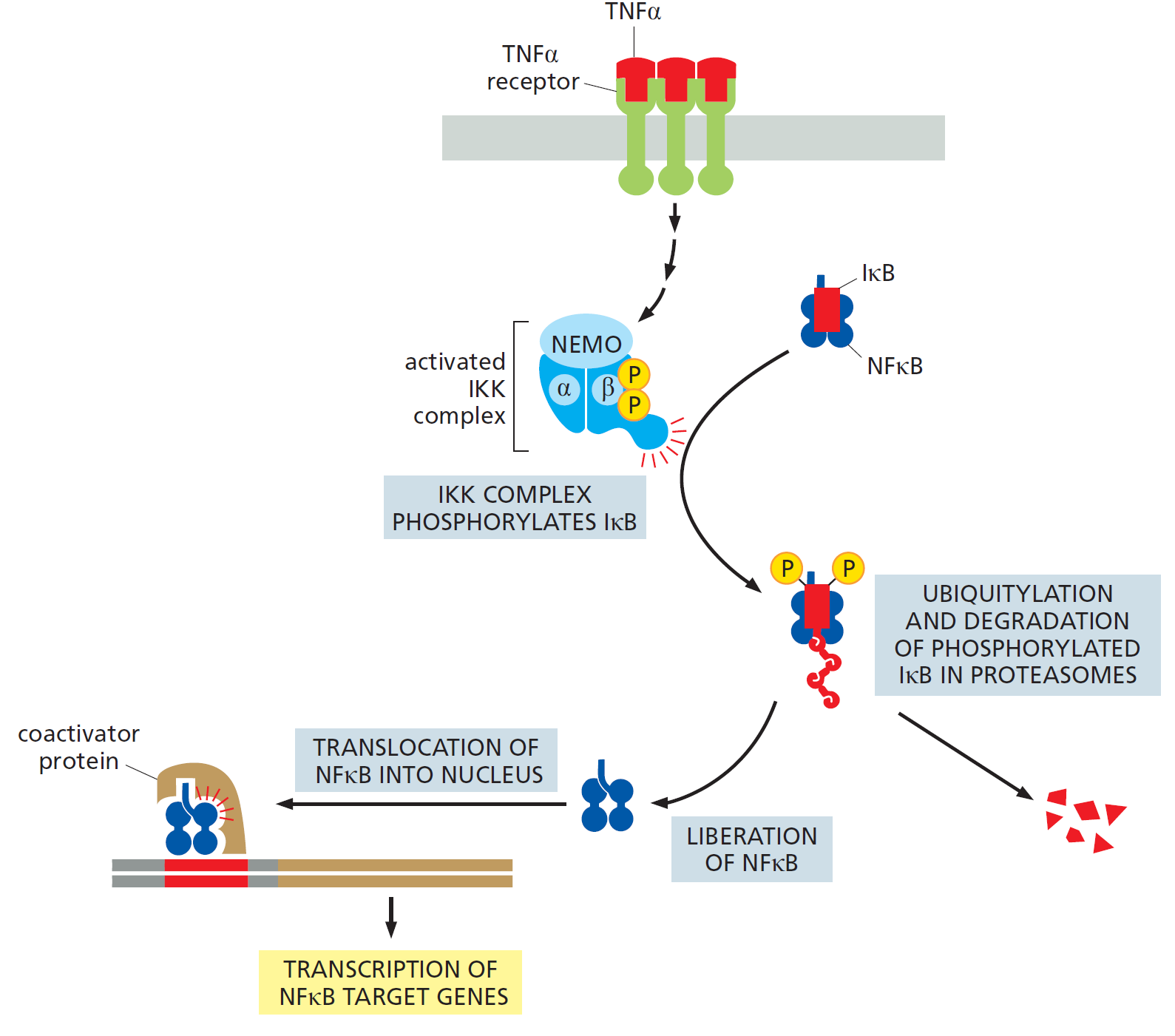
NFκB Signaling Pathway
NFκB Signaling Pathway Excerpt: The NFκB signaling pathway is a critical regulator of gene expression in response to stimuli like inflammation and infection. NFκB proteins, normally inactive due to IκB proteins, become activated upon signals such as TNFα. This leads to the degradation of IκB and the release of NFκB, which enters the nucleus to…
-
Objective Lenses of Microscopes
Discover the various types of objective lenses used in microscopes. Learn about achromatic, plan, apochromatic, and oil immersion lenses, their unique properties, and applications in microscopy. Choose the right lens for enhanced imaging and accurate observations.
-
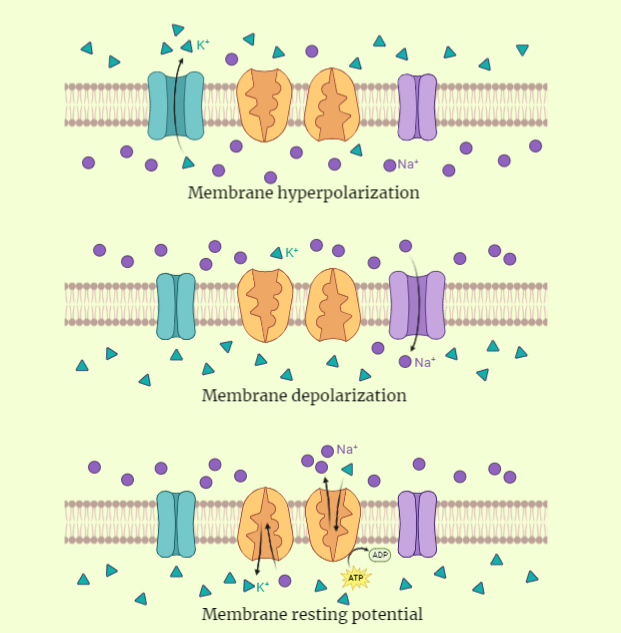
Membrane Potential
The membrane potential is a fundamental concept in cellular physiology, playing a crucial role in the proper functioning of cells. It refers to the electrical potential difference across a biological cell membrane, which is maintained by ion gradients. These gradients are created by the selective permeability of the membrane to ions such as sodium, potassium,…
-
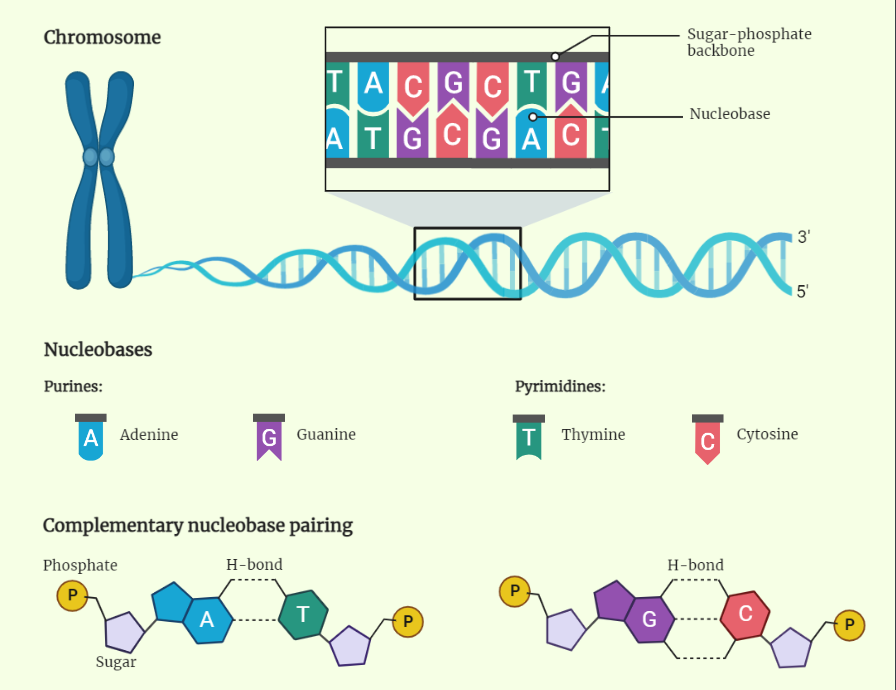
DNA and its types
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material that carries instructions for all living organisms. It comes in various types, including the double helix, single-stranded DNA, and RNA. DNA can have different conformations and can be supercoiled. Understanding these types is essential for DNA sequencing, genetic engineering, drug development, and forensic science.
-
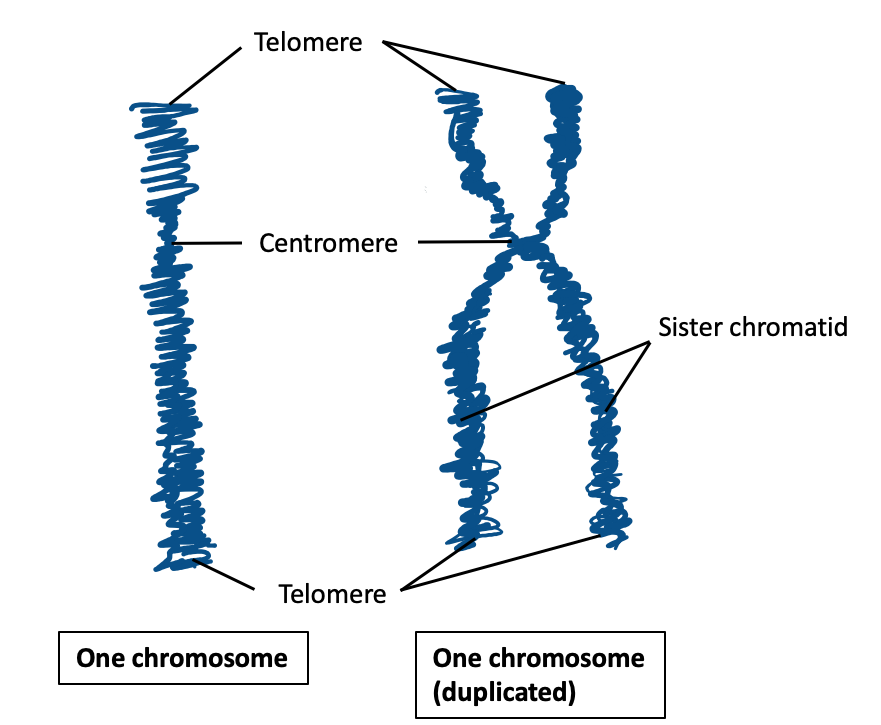
Chromosome : Function
Delve into the intricate realm of chromosomes and their specialized nucleotide sequences, which are fundamental to essential cellular processes like DNA replication and chromosome segregation. The cell cycle, where these genetic elements take center stage, involves replication during interphase, forming sister chromatids, and their condensation into visible mitotic chromosomes. Three guardian sequences orchestrate this process:…
-
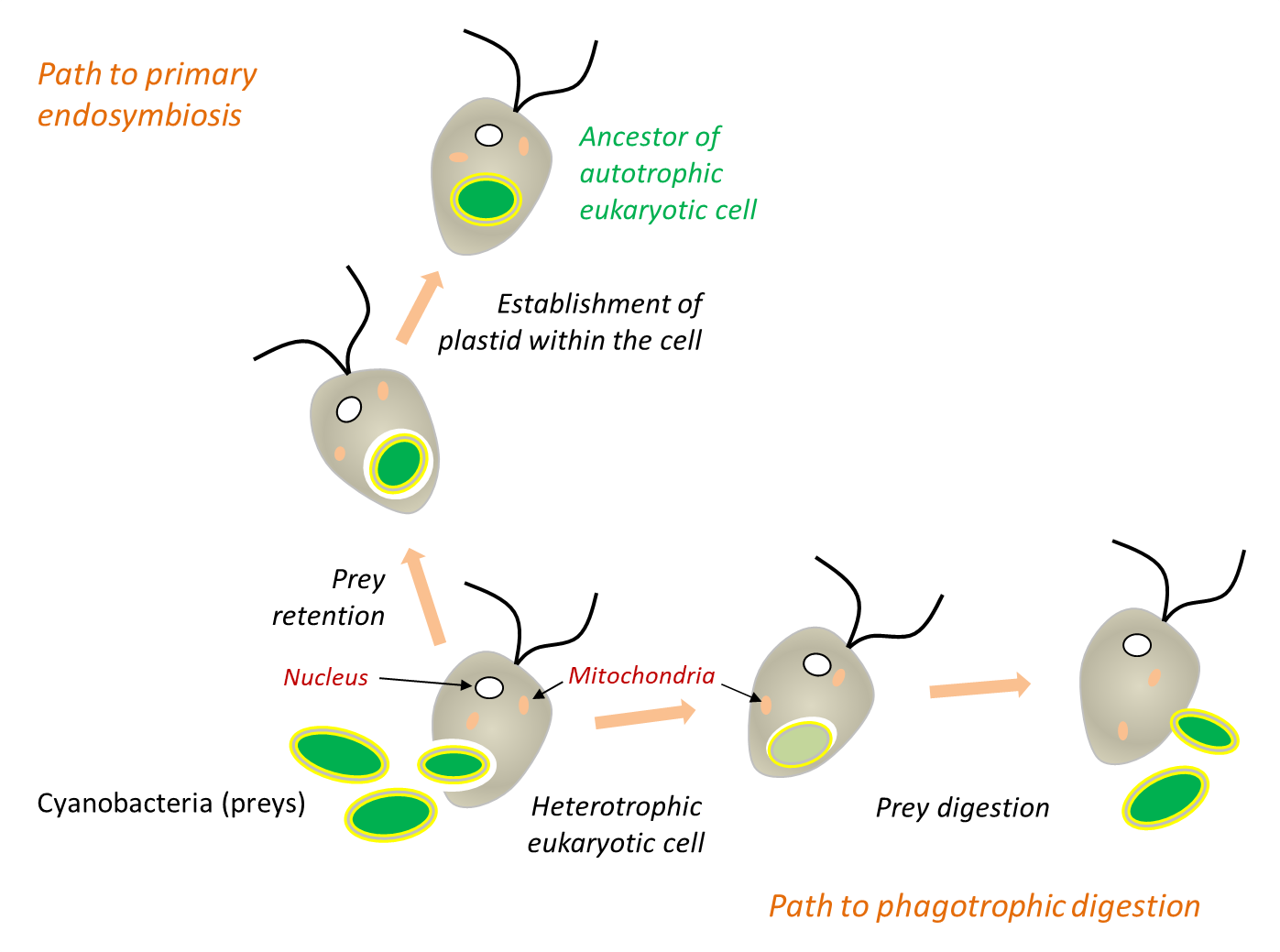
Origin of Eukaryotic Cells
I. Introduction II. Predatory Origins III. Evolution through Symbiosis IV. Different Ways of Life V. Conclusion
-
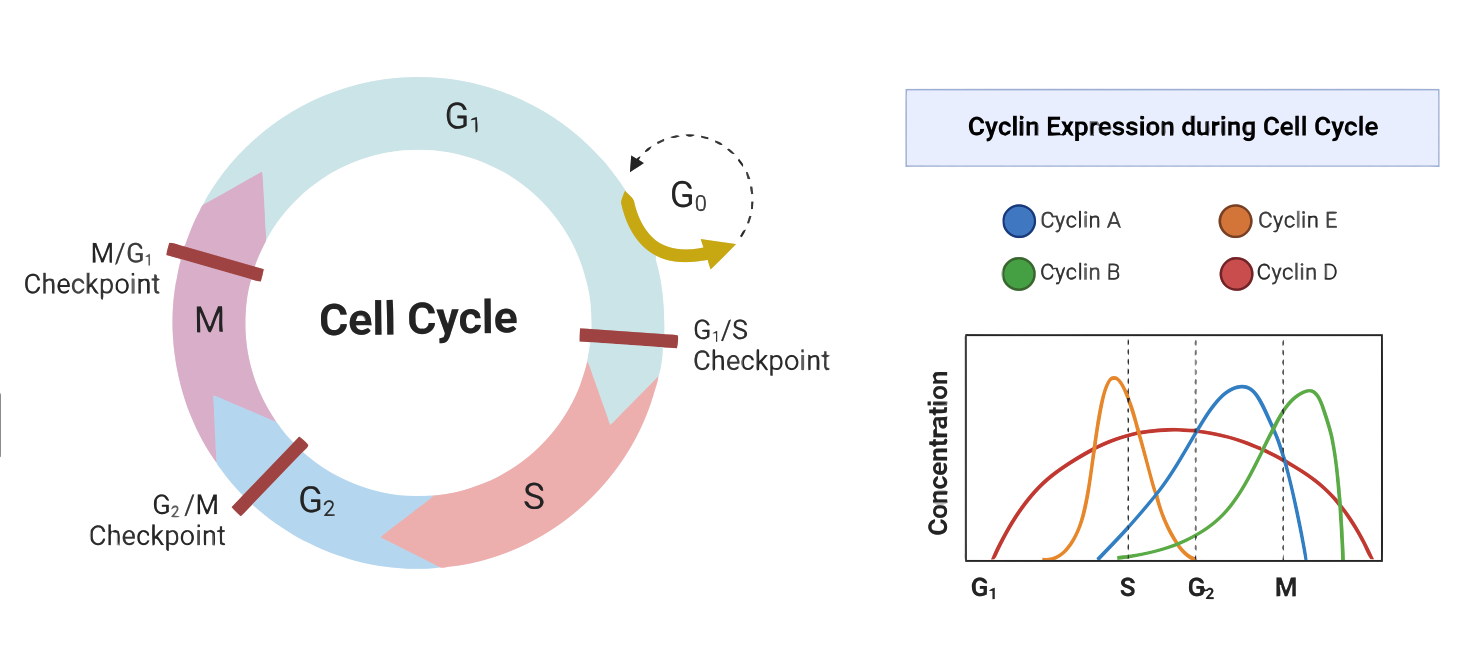
The Cell Cycle and Its Regulation
The cell cycle is a series of events that occur as a cell grows and divides into two daughter cells. It can be divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic phase. Interphase can be further divided into three stages: G1, S, and G2. During interphase, the cell grows and carries out necessary biosynthetic…
-
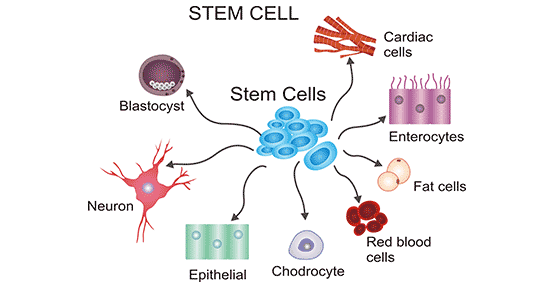
Stem Cell
Introduction: Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types. Stem cells play a crucial role in the development and regeneration of tissues and organs, and they have the potential to be used in a range of medical applications, including the treatment of various diseases and injuries.…
-
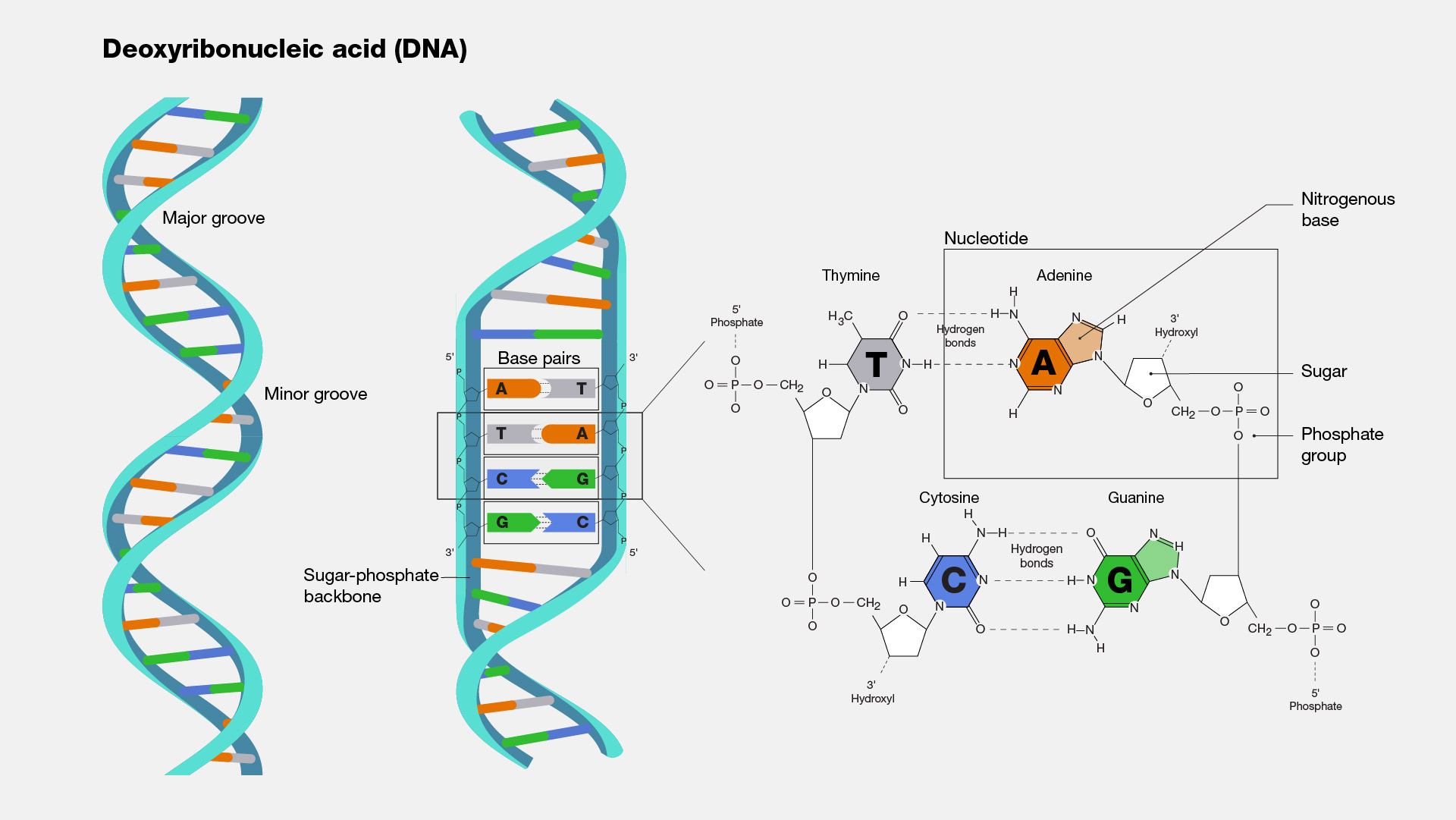
Structure of DNA
I. Introduction II. Chemical Composition III. Double Helix Structure IV. Chromosomes V. Replication VI. Conclusion
-
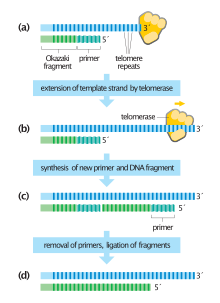
Telomere Replication
Introduction: Functions of Telomeres: Telomere Replication: Extension: Replication: Factors Influencing Telomere Replication: Conclusion:
-
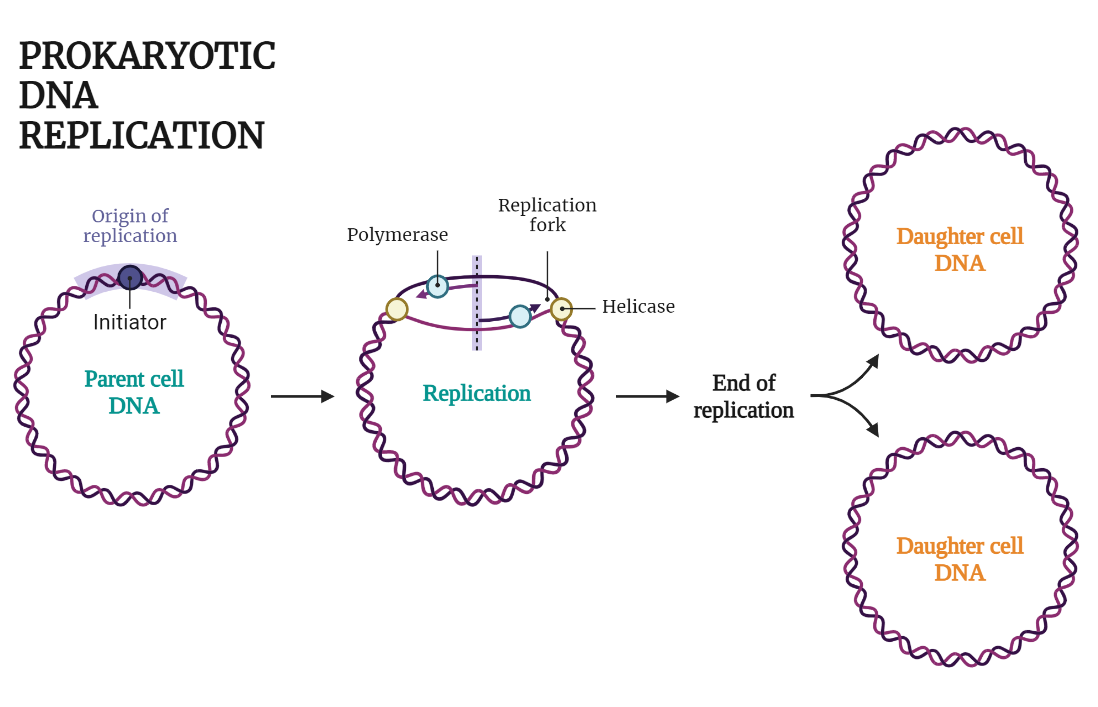
Prokaryotic DNA Replication
Prokaryotic DNA replication is a tightly regulated and coordinated process in which bacterial cells duplicate their genetic material before cell division. The process is semi-conservative and includes the initiation, elongation, and termination of replication, involving enzymes such as DNA polymerase, primase, and helicase. The replication is initiated by the binding of the replication initiator protein…
-
Cellular dynamics
Delve into the intricate world of cellular dynamics during embryonic development. Discover how cells orchestrate the formation of complex organisms through processes like division, shape-shifting, migration, growth, and even programmed death. Unveil the role of cellular behavior in sculpting life’s earliest stages.
-
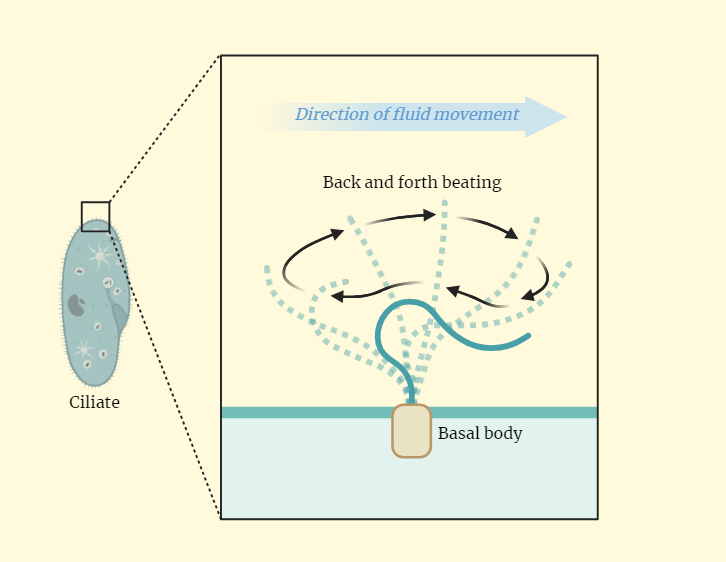
Ciliary movement
Discover the intricate world of ciliary movement—a remarkable process driven by tiny hair-like structures called cilia. From their structural composition to their role in propelling cells, fluids, and particles, delve into the mechanisms underpinning this fascinating phenomenon. Explore how cilia’s coordinated motion aids in functions like mucociliary clearance in the respiratory tract, fluid transport in…
-
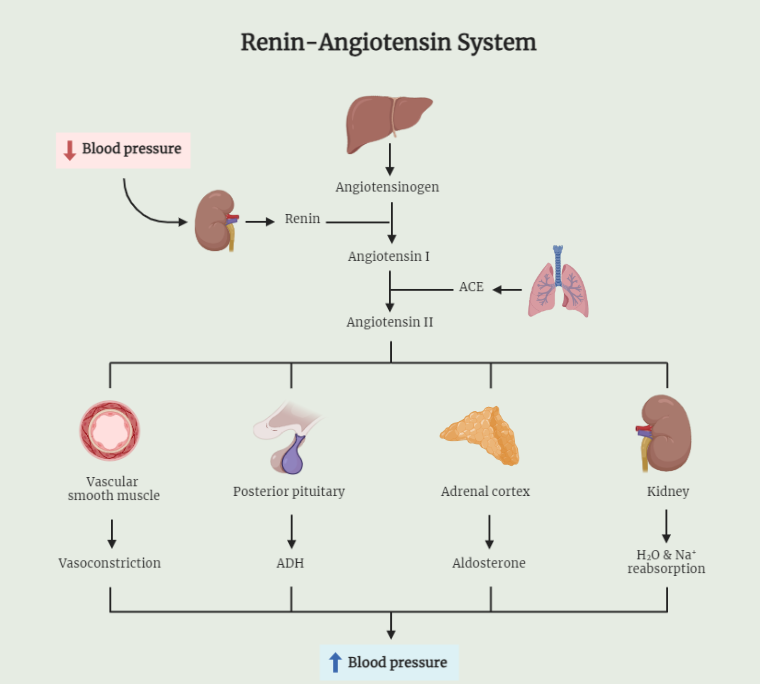
Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS)
Explore the intricate workings of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS), a crucial endocrine system responsible for blood pressure regulation and fluid balance. Dive into the functions of renin, angiotensin I and II, and their role in vasoconstriction and aldosterone release. Discover the clinical significance of RAS dysregulation and the use of RAS inhibitors in managing hypertension…
-
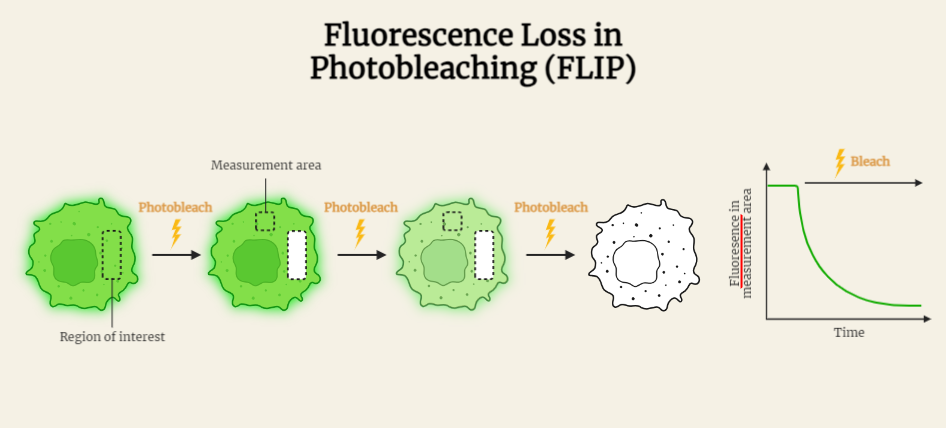
FLIP (Fluorescence Loss in Photobleaching)
Discover the power of Fluorescence Loss in Photobleaching (FLIP), a technique used to investigate molecular dynamics within cells. Explore its applications in protein and membrane dynamics, protein-protein interactions, intracellular transport, and subcellular compartmentalization. FLIP provides valuable spatial and temporal information, allowing researchers to study biological processes in their natural state. Embrace the versatility of FLIP…
-
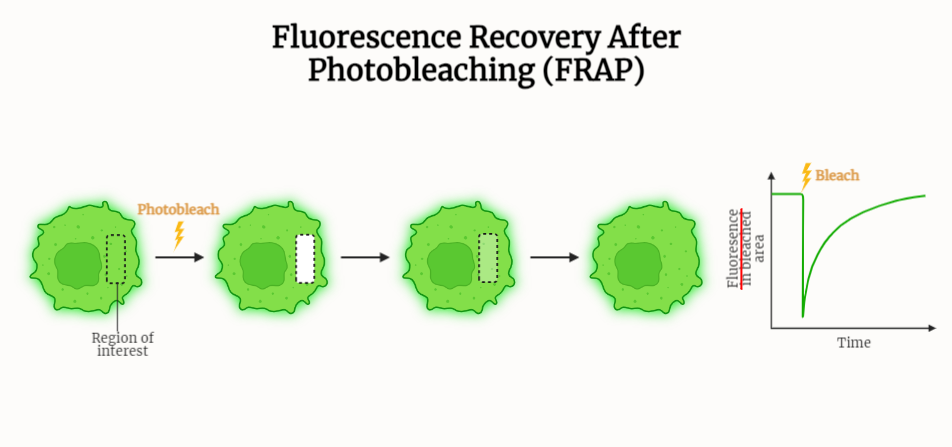
FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching)
Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) is a powerful technique widely employed in the study of biomolecules within biological systems. By selectively bleaching a small region of a sample and monitoring the subsequent fluorescence recovery, FRAP enables the investigation of molecular mobility. Its applications encompass protein dynamics, intracellular organelle movements, cytoskeleton organization, membrane dynamics, intracellular transport,…
-

Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) is a powerful imaging technique used to visualize and manipulate materials at the nanoscale. By scanning a sharp probe over a sample surface, AFM measures the interaction forces between the probe and the sample, providing high-resolution images and information about surface properties. This study note delves into the principles, instrumentation, operational…
-
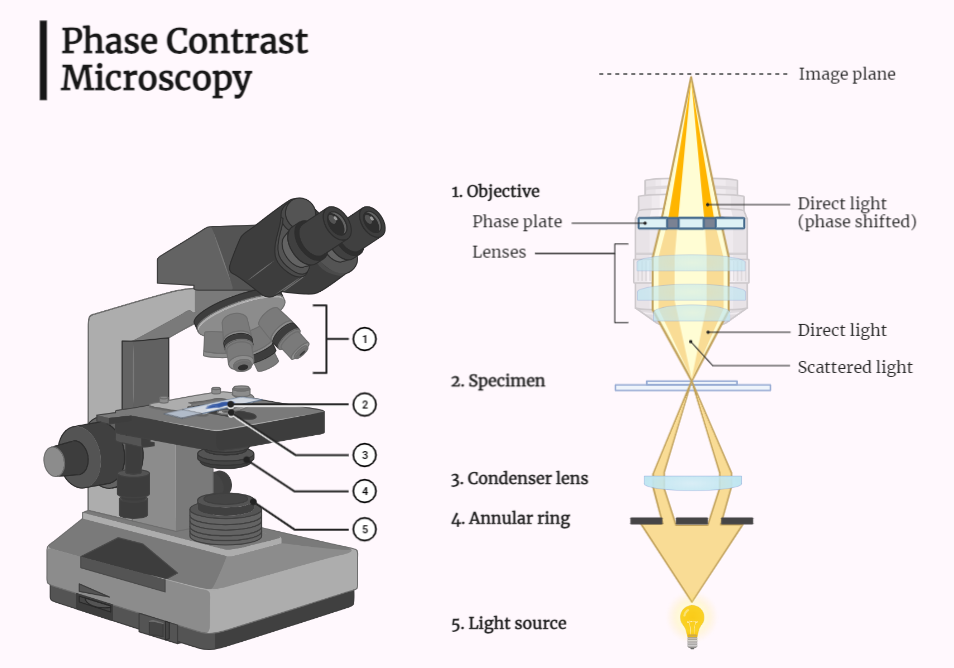
Phase Contrast Microscopy
Discover the power of a phase contrast microscope, an essential tool for enhancing sample contrast in fields like biology and materials science. Learn about its components, working principle, and applications in studying cell structures and analyzing materials. Explore the advancements in microscopy techniques and scientific instruments for improved research and imaging capabilities.
-

Light Microscopy
Light microscopy is a versatile technique used in various scientific disciplines such as biology, chemistry, and materials science. By illuminating a sample with light and capturing the transmitted image, this essential tool enables the study of cell structure, materials analysis, and scientific research. With its simplicity and ability to produce high-resolution images, light microscopy plays…
-
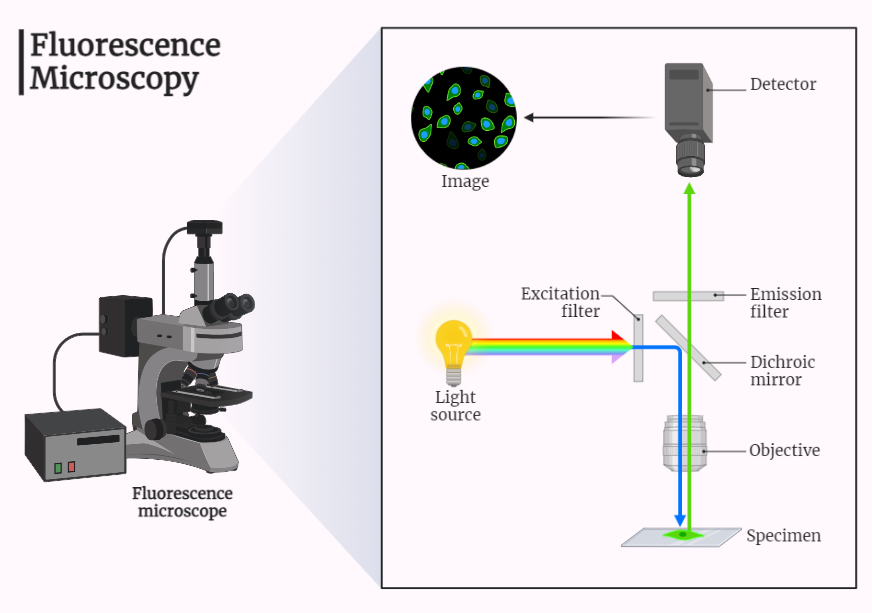
Fluorescence Microscope
A fluorescence microscope is an essential tool in science and technology, enabling high-resolution imaging of samples using fluorescence techniques. It is widely used in biology, chemistry, and materials science for analyzing cell structures, molecular imaging, and sample analysis. By exciting specific molecules and selectively detecting fluorescence, it provides valuable insights into biological samples and their…
-
Confocal Microscope
Embark on a fascinating journey into the world of confocal microscopy. Discover its role in high-resolution imaging, sample preparation, and applications in biology, chemistry, and materials science. Uncover the groundbreaking advancements made possible by selectively detecting fluorescence, enabling detailed study of biological samples and components. Witness the transformative power of confocal microscopy in unlocking the…
-
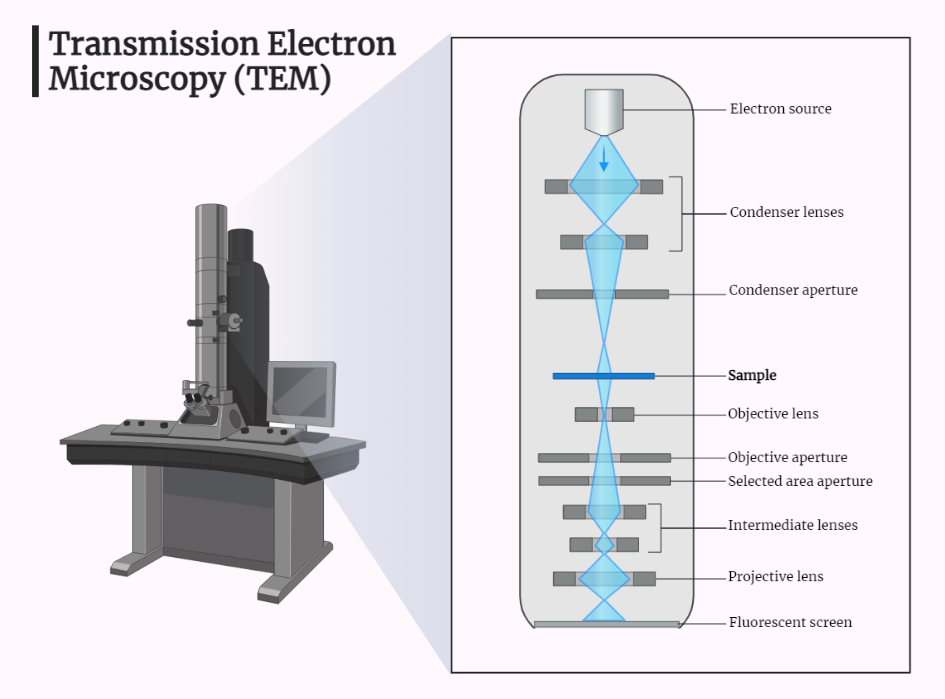
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Embark on a journey through the world of transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Explore its significance in materials science, biology, and chemistry. Discover the remarkable high-resolution imaging capabilities, sample preparation, and applications across various fields. Uncover the instrumental role of TEM in advancing scientific knowledge and understanding through its ability to reveal the internal structure of…
-
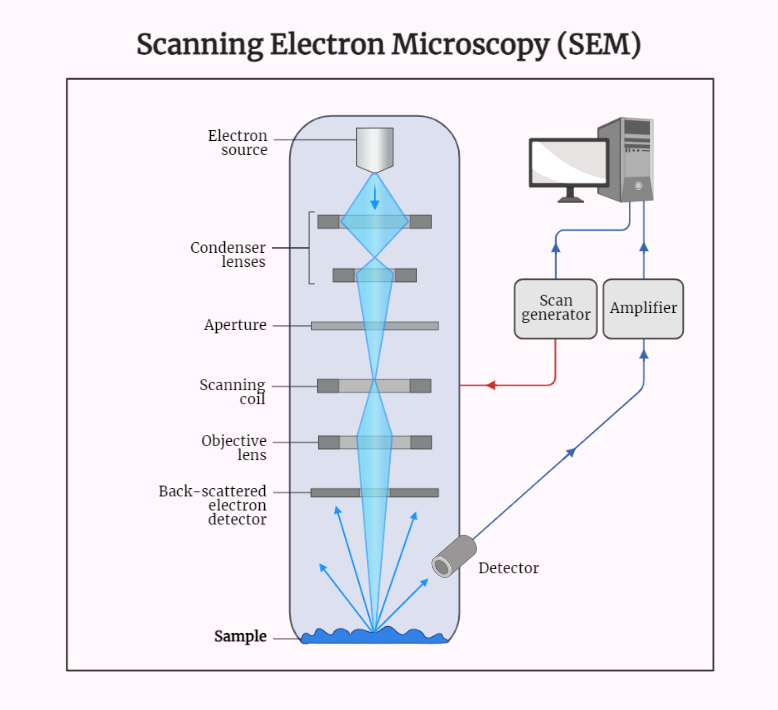
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Discover the powerful world of scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Explore its working principle, from the electron gun to image analysis. Uncover its applications in materials science, biology, geology, and semiconductor manufacturing. Gain insights into the remarkable high-resolution imaging capabilities of SEM and its significant impact on scientific discoveries and advancements.
-
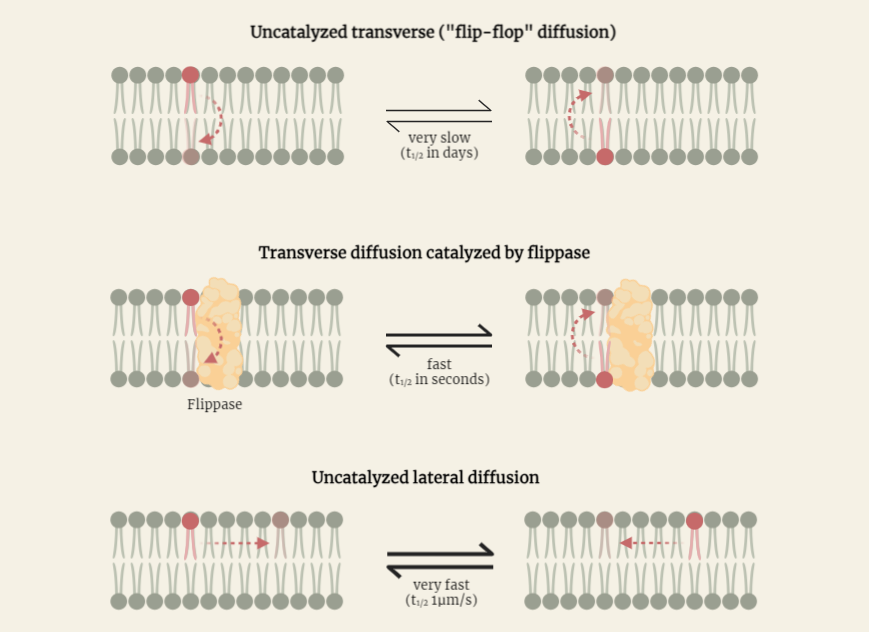
Phospholipid Movement
Phospholipids, essential components of cell membranes, play a pivotal role in maintaining membrane integrity. Explore the dynamic movements of phospholipids through lateral and transverse diffusion, as well as the crucial processes of fusion and fission. Gain insights into the intricate dynamics of cell membranes and their significance in cellular function.
-
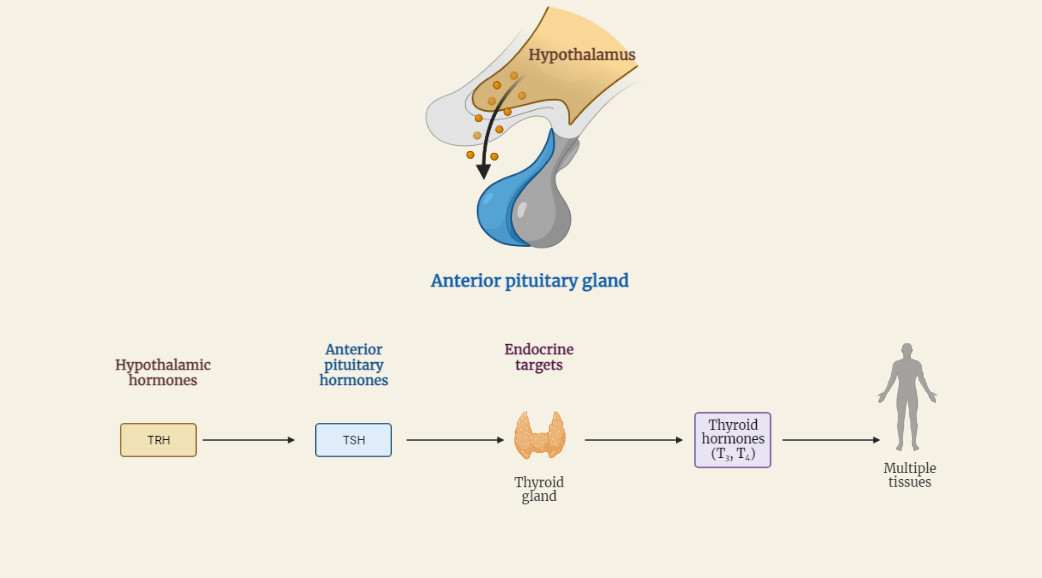
Thyroid Hormone Biosynthesis
Thyroid hormone biosynthesis is a complex process that takes place in the thyroid gland. This in-depth study explores the steps involved, including iodide uptake, oxidation, organification, coupling reactions, and hormone release. The regulation of this pathway through feedback mechanisms is also discussed. Understanding thyroid hormone biosynthesis is crucial for comprehending thyroid disorders and developing effective…
-
Attenuation in TRP Operon
Attenuation is a sophisticated gene regulation mechanism found in the TRP operon, responsible for tryptophan synthesis in bacteria. By utilizing the leader peptide and tryptophan as key players, attenuation allows precise control of gene expression based on tryptophan levels. The leader peptide acts as a sensor, adjusting the secondary structure to either block or allow…
-
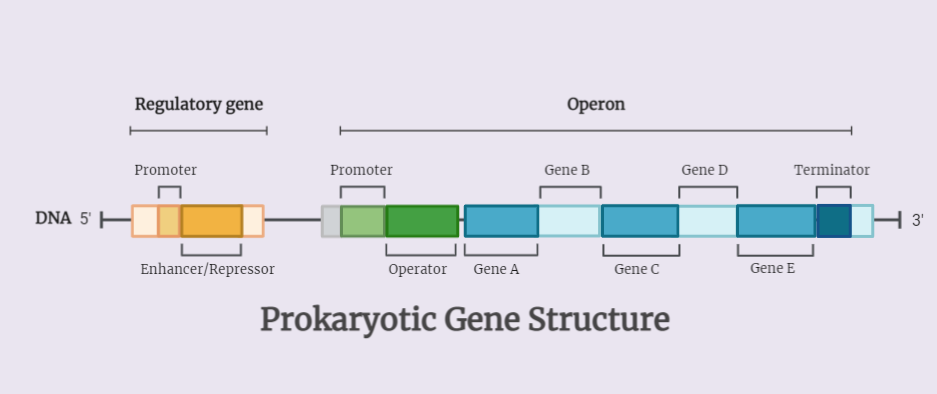
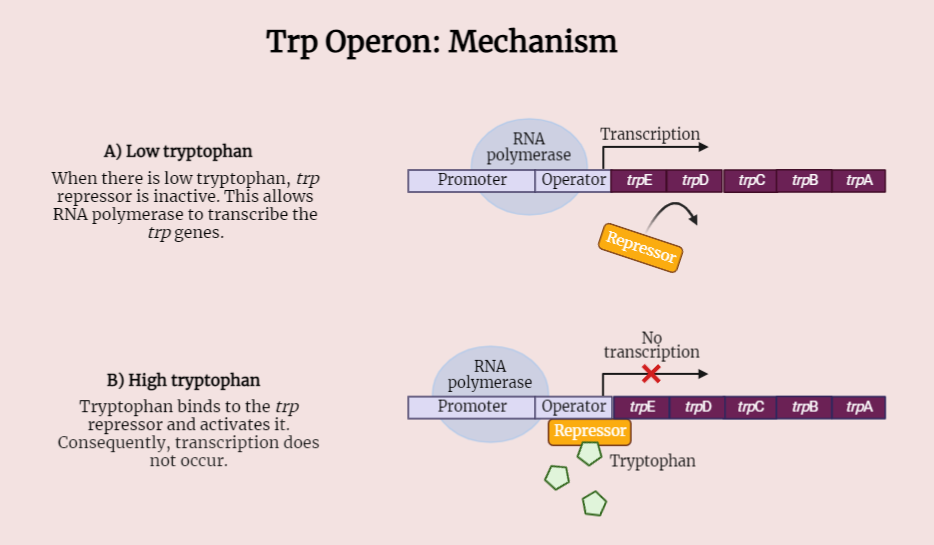
Trp Operon
The Trp operon is a genetic regulatory system in bacteria that controls the production of enzymes for tryptophan synthesis. It consists of a promoter, operator, and structural gene region. Induction and repression mechanisms regulate transcription based on tryptophan levels. Feedback inhibition further modulates the operon. Understanding the Trp operon sheds light on genetic regulation, cell…
-
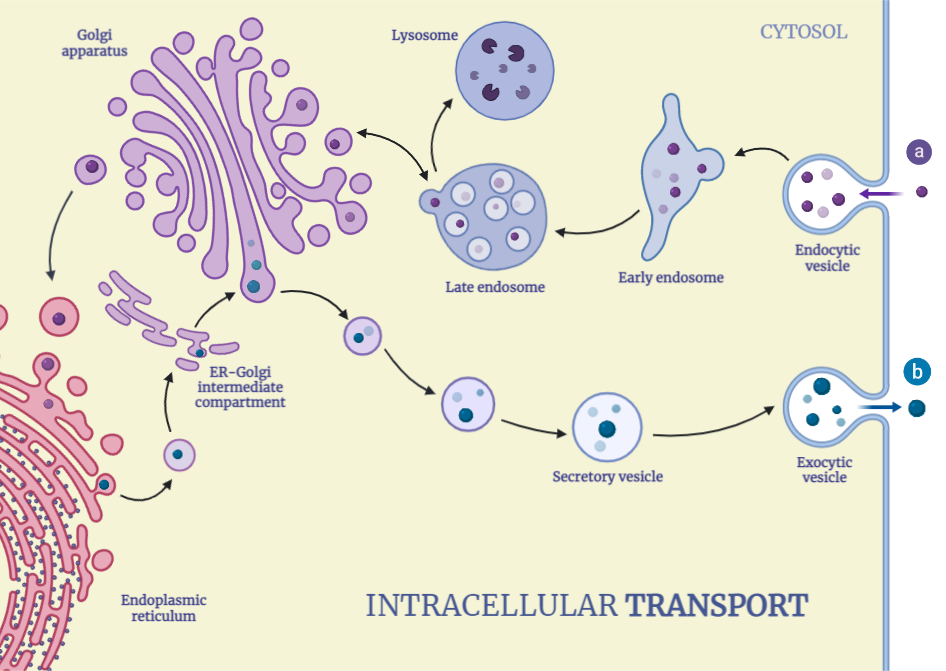
Intracellular Transport
Intracellular transport is a vital process that ensures the proper functioning of cells by facilitating the movement of molecules, organelles, and structures within them. Two main categories of intracellular transport are vesicular transport and cytoskeletal transport. Vesicular transport relies on the use of membrane-bound vesicles to transport materials within the cell through processes like endocytosis…
-
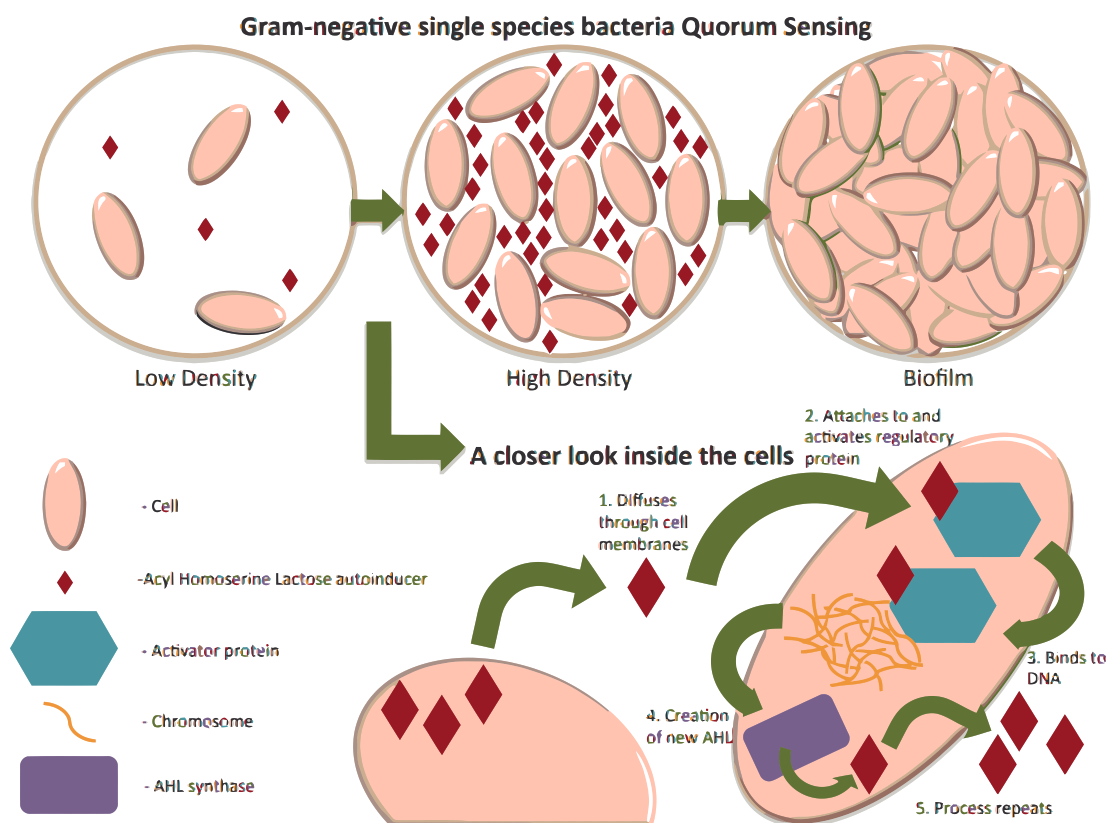
Quorum Sensing
Quorum sensing is a fascinating process that allows bacteria to communicate with each other, coordinate their behavior, and respond to changes in population density. This communication is mediated by small signaling molecules known as autoinducers, which are produced, detected, and responded to by bacterial cells. Quorum sensing plays a critical role in regulating a wide…
-
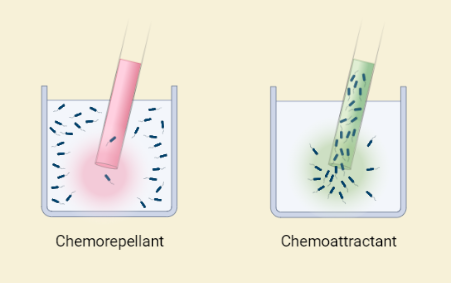
Bacterial Chemotaxis
This article provides an in-depth study of bacterial chemotaxis, which is the ability of bacteria to sense and respond to chemical gradients in their environment. The article discusses the chemotaxis mechanisms, including receptors, signal transduction, the flagellar motor, and adaptation mechanisms, along with their significance for bacterial survival and adaptation to different environments. The article…
-
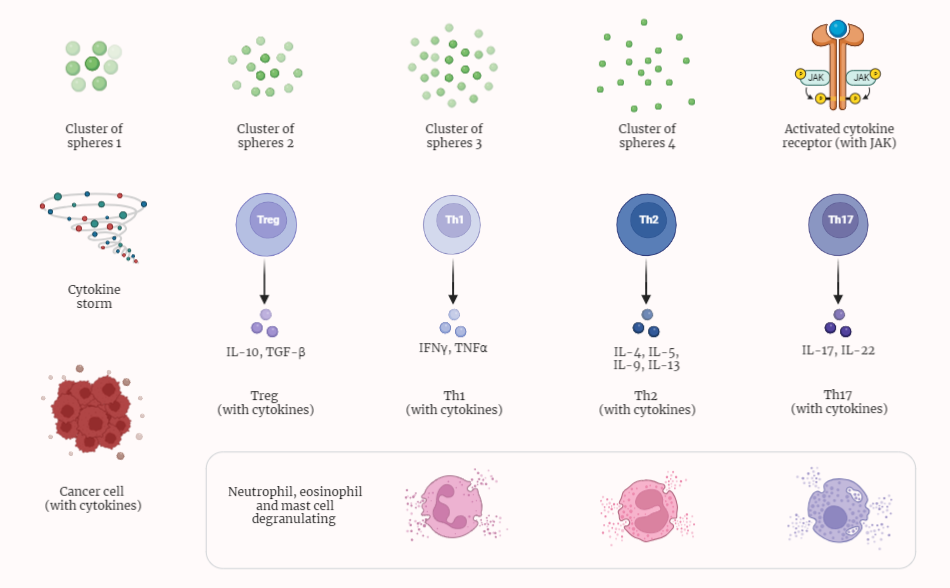
Cytokines
Cytokines are vital signaling molecules that play a crucial role in the immune response. This detailed study explores the functions, types, and significance of cytokines in various physiological processes, including inflammation and cell growth. It delves into the two main categories of cytokines: pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, shedding light on their roles in initiating and…
-
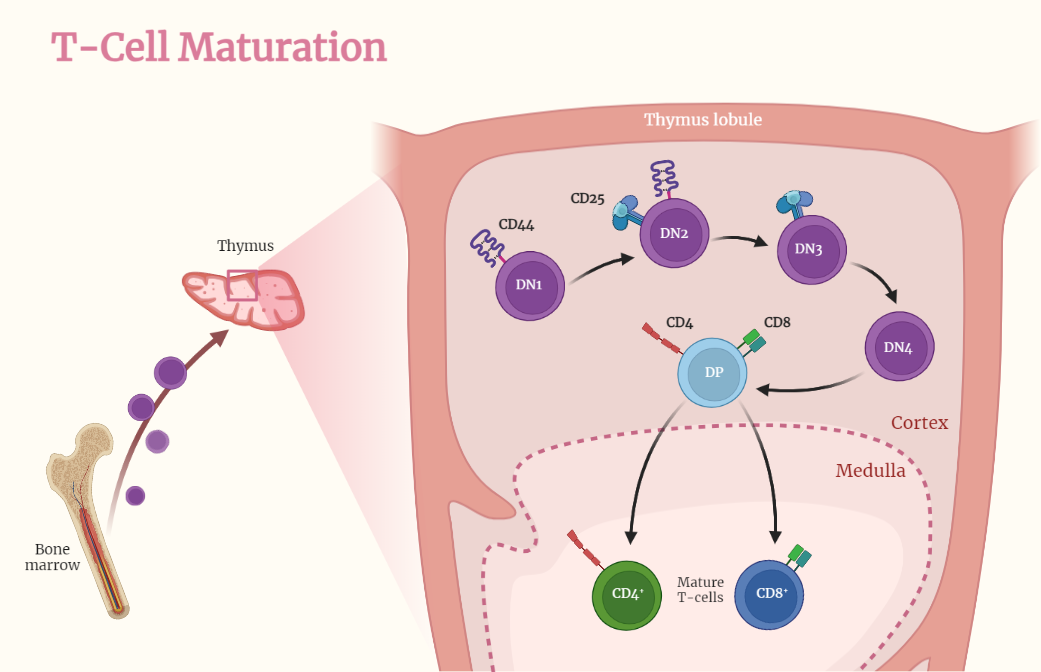
T Cell Maturation
T cell maturation is a critical process in the development of functional T cells, which are key players in the adaptive immune response. Starting in the bone marrow and progressing through the thymus, immature thymocytes undergo positive and negative selection, ensuring the survival of T cells that can recognize foreign antigens while preventing autoimmunity. Upon…
-
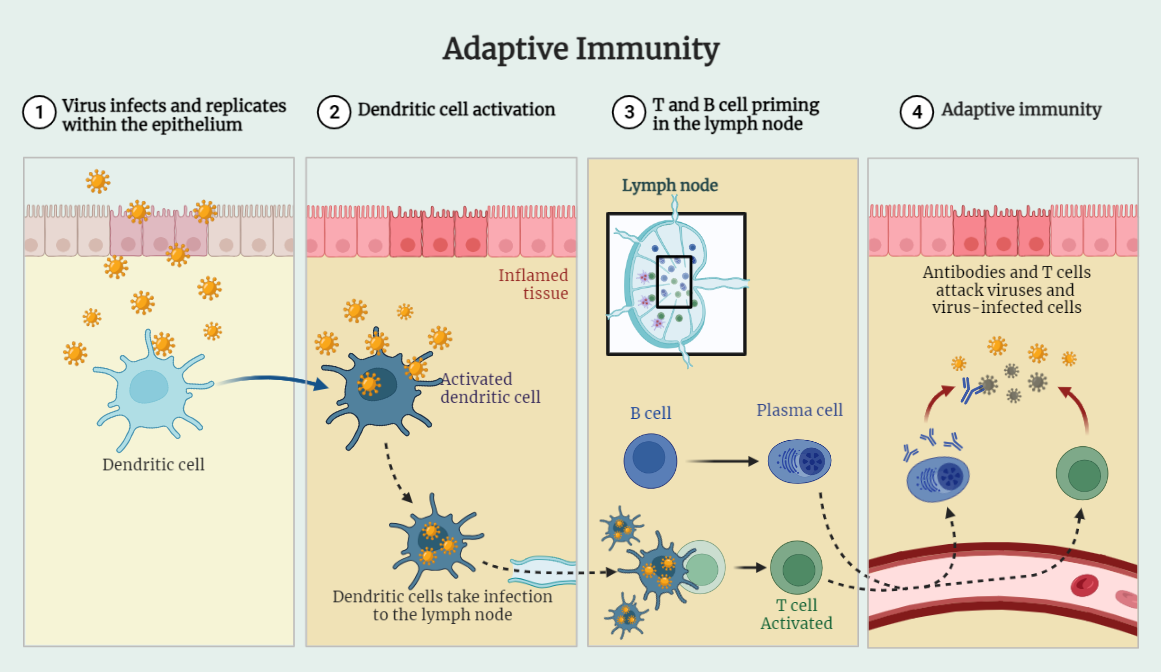
Adaptive Immune Response
The adaptive immune response is a powerful defense mechanism that comes into play when the innate immune response falls short in eliminating pathogens. This intricate system involves specific antibodies produced by B cells, which bind to antigens, such as viruses and bacteria, marking them for destruction. Antibodies can neutralize pathogens, impeding their ability to infect…
-

Gene Therapy: A study note
Gene therapy is a groundbreaking medical approach that holds tremendous potential for revolutionizing disease treatment. By altering the genetic material within cells, gene therapy aims to correct abnormal genes or introduce therapeutic genes to combat a wide range of conditions. This study note provides a comprehensive overview of gene therapy, exploring its principles, techniques, applications,…
-
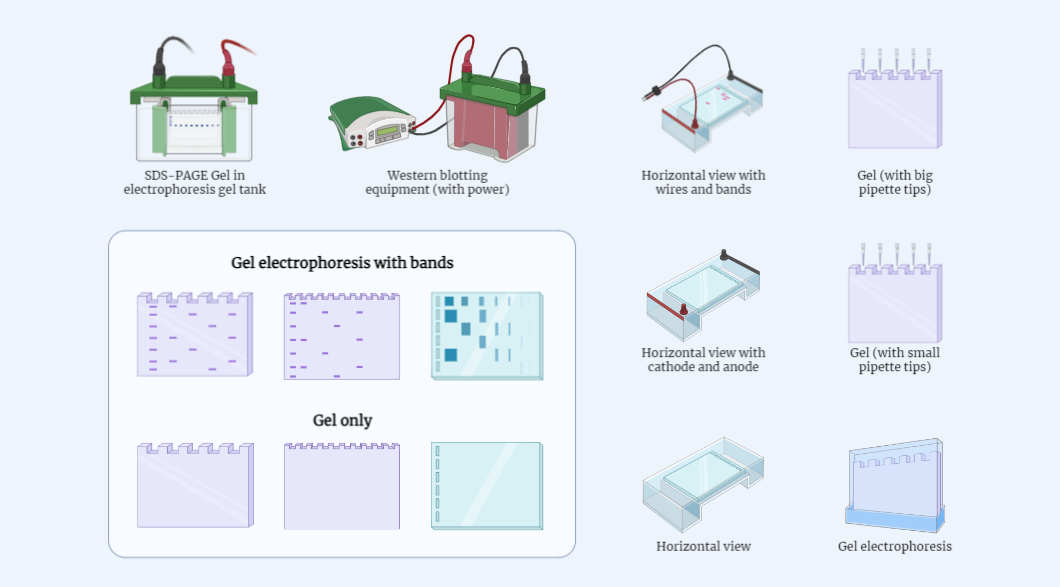
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique in molecular biology for separating and analyzing DNA, RNA, and proteins. It plays a crucial role in various applications such as DNA analysis, protein characterization, and clinical diagnostics. This study note provides an in-depth understanding of the principles, procedure, and applications of gel electrophoresis, making it a valuable…
-
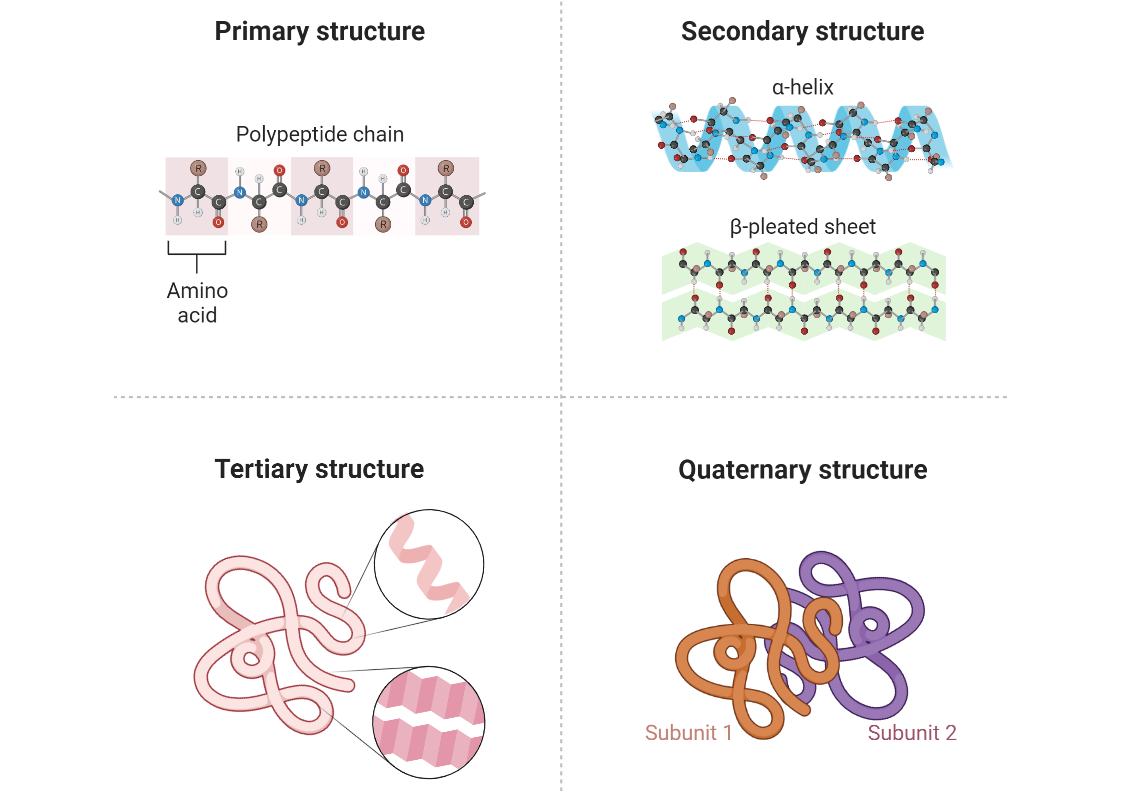
Protein Folding
Dive into the fascinating world of protein folding, where linear sequences of amino acids transform into intricate three-dimensional structures. Discover the driving forces behind protein folding, such as the hydrophobic effect and hydrogen bonding. Explore the stages of protein folding, from primary to tertiary structure, and unravel its applications in understanding protein function, designing drugs,…
-
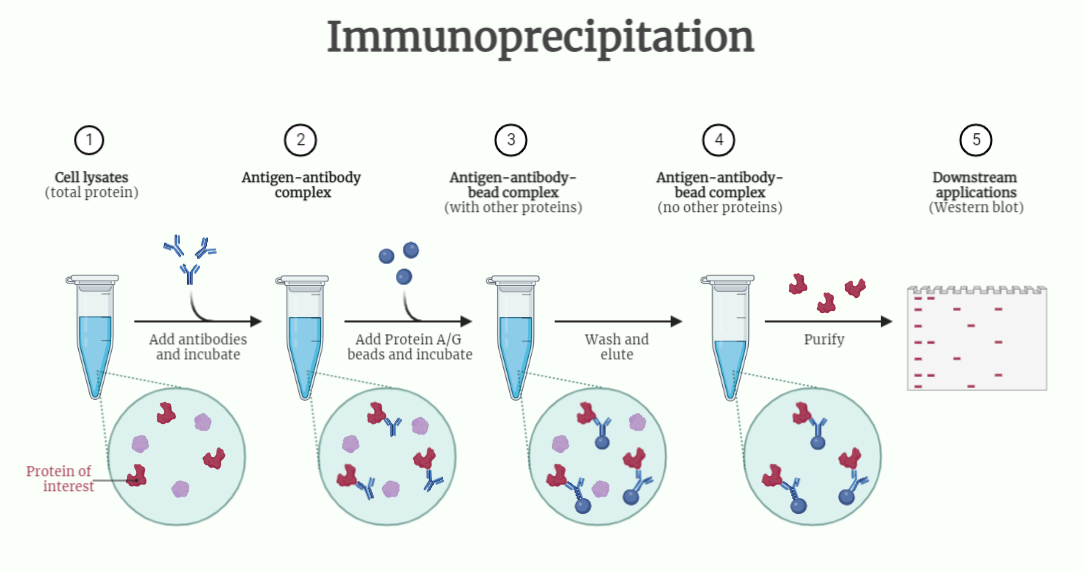
Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation (IP) is a powerful technique used to isolate and purify specific proteins or protein complexes from complex mixtures. Learn about the types, procedure, advantages, and applications of this technique in protein research and analysis. Discover how IP can help in studying protein-protein interactions, signaling pathways, post-translational modifications, and disease-related proteins.
-
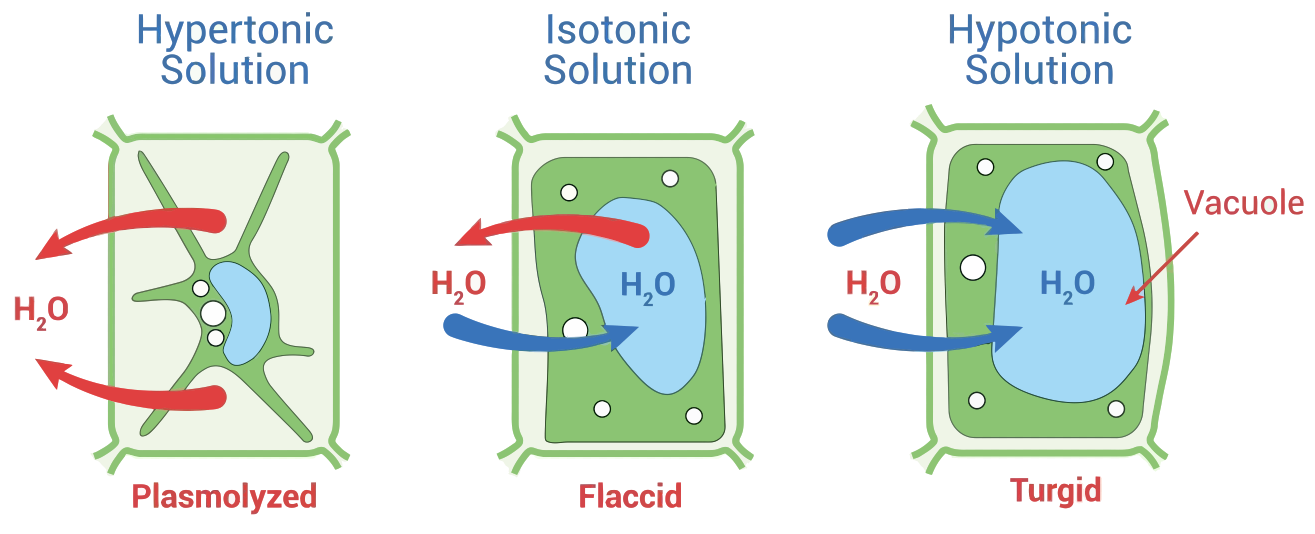
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process by which a plant cell shrinks away from its cell wall when placed in a hypertonic solution. This study note explains the process, types, examples, and the significance of plasmolysis in plant biology and agriculture. Explore the effects of water and solute stress on plants.
-
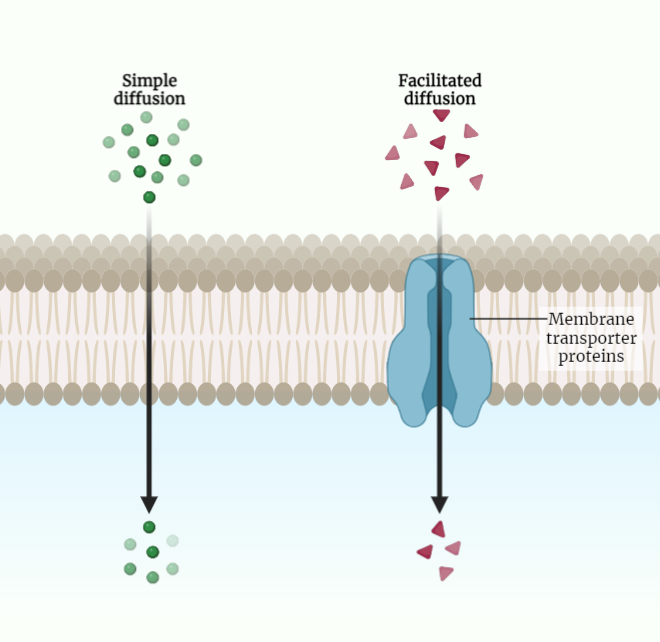
Passive Transport
Passive transport refers to the movement of substances across cell membranes without the use of energy. This study note explores key concepts such as diffusion, osmosis, the role of the cell membrane, concentration gradients, and how passive transport contributes to maintaining cellular homeostasis. Understanding these mechanisms is vital in comprehending the fundamental processes of substance…
-
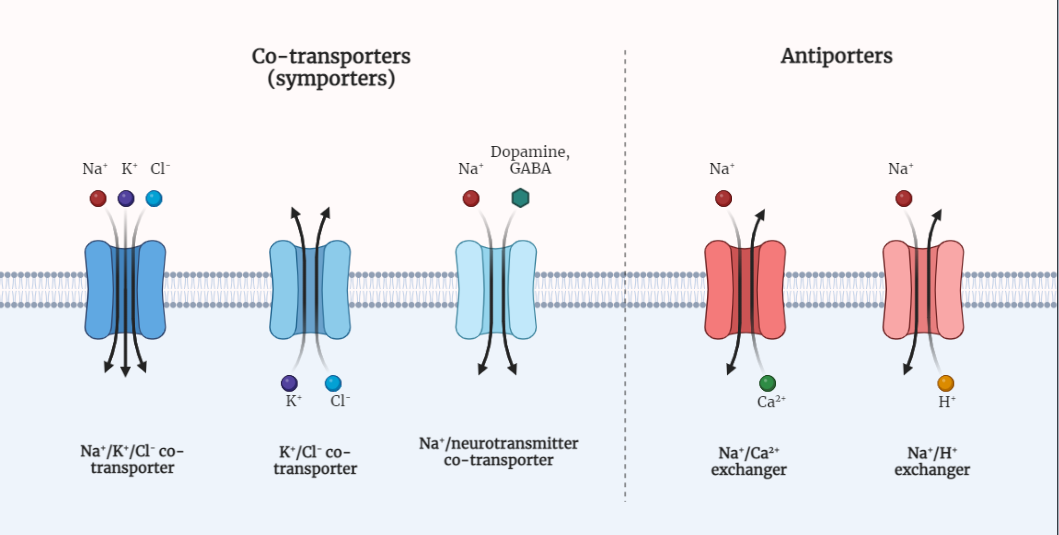
Active Transport
Active transport is a fundamental process in cellular biology that enables the movement of molecules across cell membranes against their concentration gradient. It requires the expenditure of energy, typically derived from ATP. This article explores the different types of active transport, including primary and secondary active transport, as well as cotransport. It highlights the significance…
-
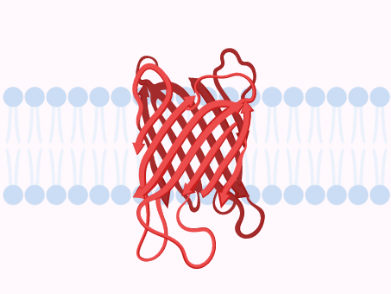
Aquaporins
Aquaporins, integral membrane proteins, play a critical role in water transport, maintaining cell hydration, osmoregulation, and facilitating water movement in the lens and epidermis. Discover their significance in various physiological processes.
-
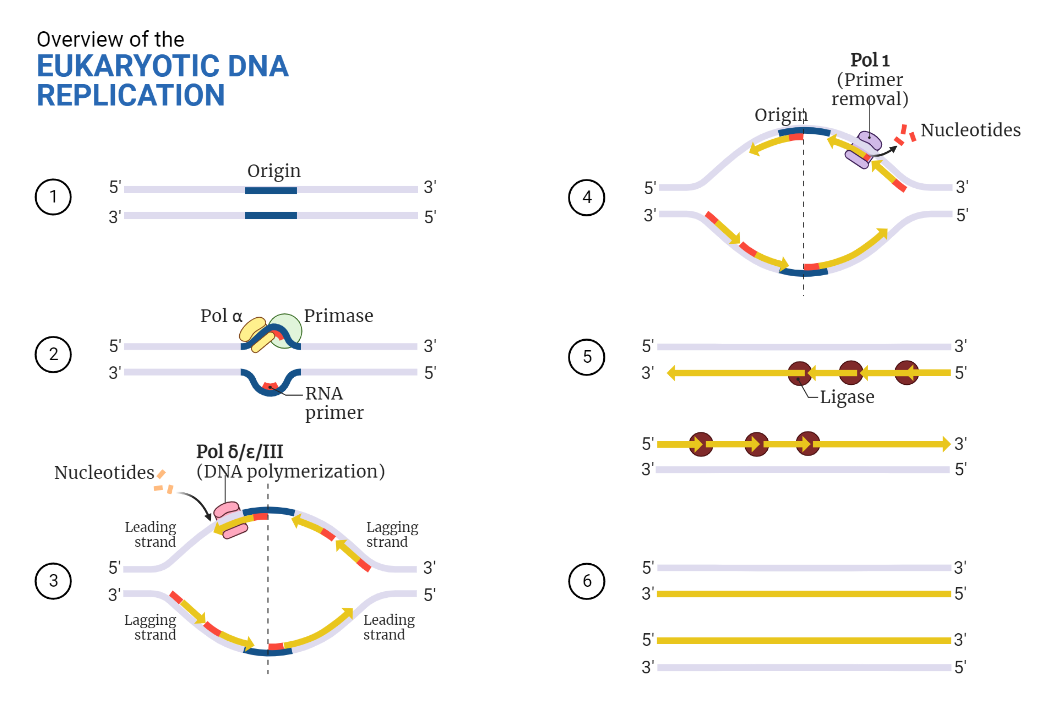
Eukaryotic DNA Replication
This text explains the process of Eukaryotic DNA replication. The article highlights the pre-replication complex formation, initiation, elongation, and termination of the replication process. The author also explains the role of various proteins involved in the process, such as ORC, Cdc6, Cdt1, Mcm2-7, DNA polymerase, and Primase. Overall, the article provides a detailed overview of…
-
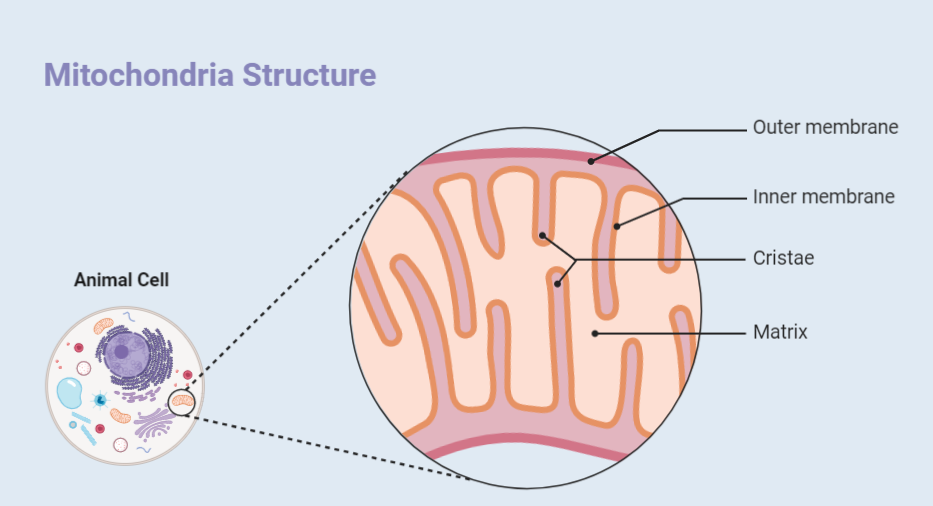
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Due to their essential role in cellular respiration, they are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. Mitochondria have a unique structure consisting of an outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix. They…
-
Mendel’s First Law
The excerpt provides an in-depth study of Mendel’s First Law, also known as the Law of Segregation. It delves into Gregor Mendel’s groundbreaking experiments with pea plants, unraveling the principles of inheritance and genetic traits. Mendel’s work laid the foundation for modern genetics, and his findings continue to influence genetic research across various disciplines. Understanding…
-
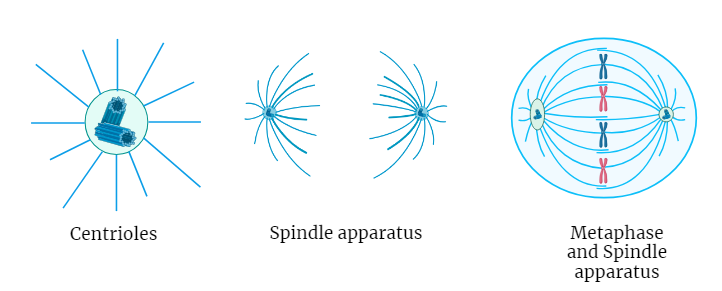
Centrioles : Structure and Function
Centrioles, cylindrical organelles found in the centrosome, play pivotal roles in cell division and cytoskeletal organization. Composed of triplet microtubules, they serve as the primary microtubule organizing center during mitosis, ensuring accurate chromosome segregation. Additionally, centrioles function as basal bodies, enabling the formation of cilia and flagella. Their influence extends to cell shape, intracellular transport,…
-
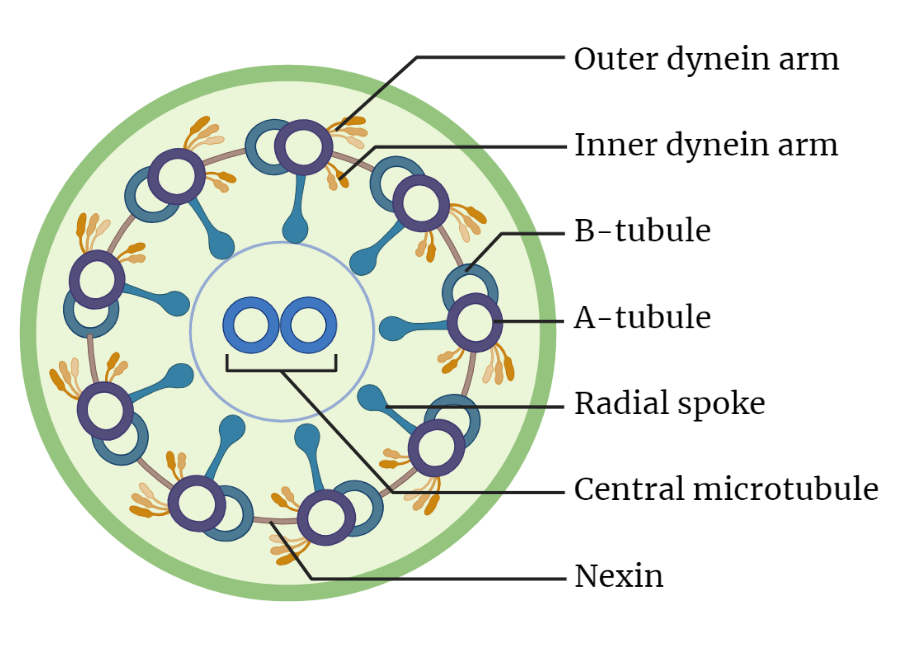
Microtubular arrangement
The 9+2 microtubular arrangement, a fascinating structure found in cilia and flagella, drives the coordinated movement of these hair-like appendages. Comprising 9 doublet microtubules encircling a central pair, this arrangement relies on the motor protein dynein to generate sliding motion, propelling cilia and flagella forward. Essential for cell movement, fluid transport, and sperm motility, understanding…
-
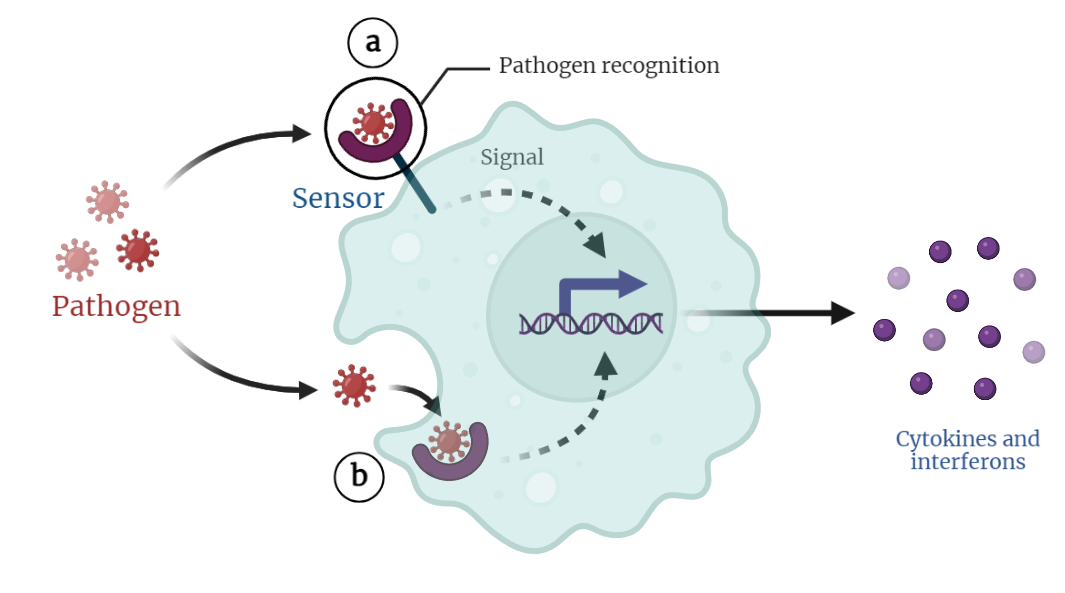
Pathogen Recognition and Innate Immunity
The excerpt delves into the crucial topics of pathogen recognition and innate immunity. It highlights the significance of the innate immune system as the first line of defense against invading pathogens, explaining the role of pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs) in detecting unique pathogen structures known as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). The innate immune response’s rapid…
-
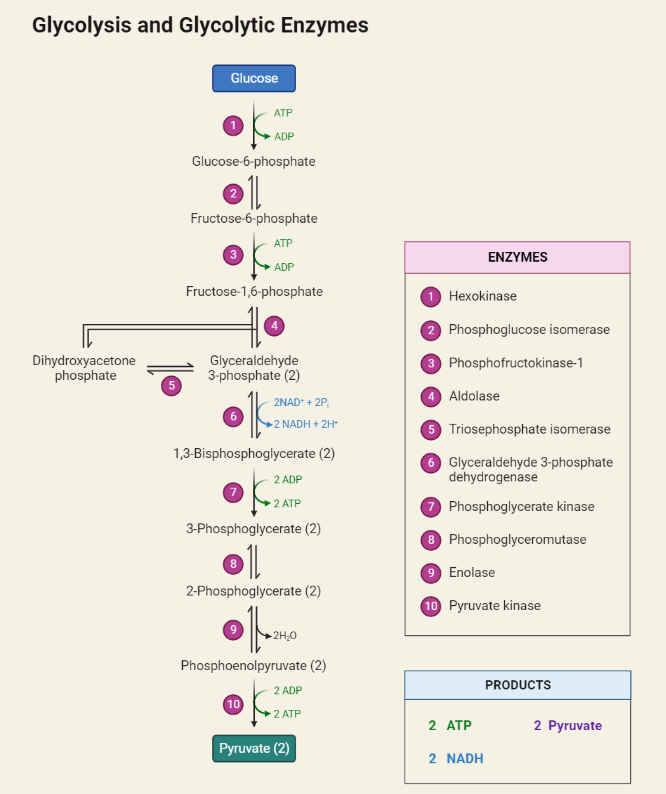
Steps of Glycolysis
The text provides a comprehensive overview of glycolysis, a crucial metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, ATP, and NADH. It explores the process, enzymes involved, and its significance in cellular energy production. Glycolysis’s versatility, occurring in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, makes it fundamental for cell survival and energy generation in various organisms, from…
-

Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic process that occurs in almost all living organisms. It is a critical pathway that provides energy for cells by breaking down glucose to produce ATP. This article will discuss the definition, equation, enzymes, and steps involved in glycolysis. What is Glycolysis? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate,…
-

Cell Cycle and Its Regulation
The cell cycle is a fundamental process that is essential for the growth, development, and maintenance of all living organisms. It is a series of events that a cell undergoes to replicate and divide into two daughter cells. The cell cycle can be divided into two main stages: interphase and mitosis. Interphase is the period…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




