-
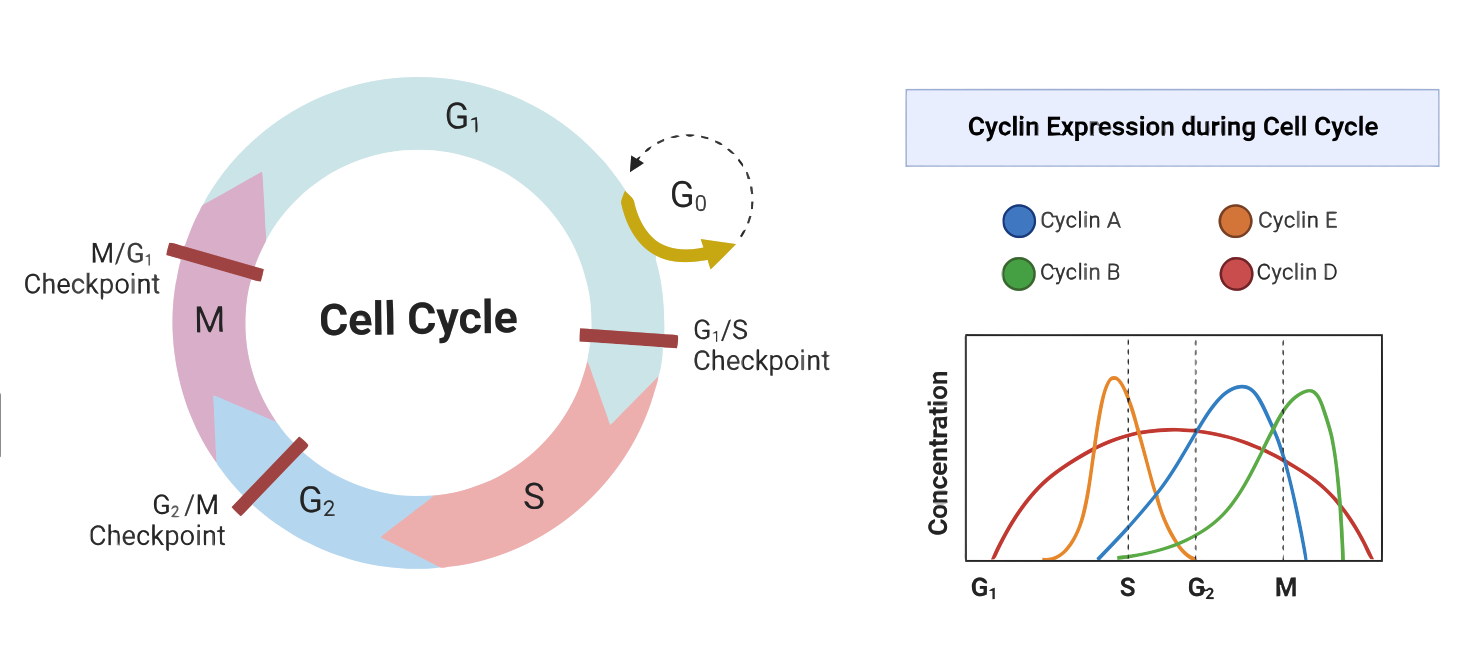
The Cell Cycle and Its Regulation
The cell cycle is a series of events that occur as a cell grows and divides into two daughter cells. It can be divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic phase. Interphase can be further divided into three stages: G1, S, and G2. During interphase, the cell grows and carries out necessary biosynthetic…
-
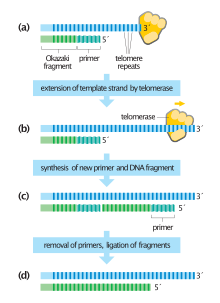
Telomere Replication
Introduction: Functions of Telomeres: Telomere Replication: Extension: Replication: Factors Influencing Telomere Replication: Conclusion:
-
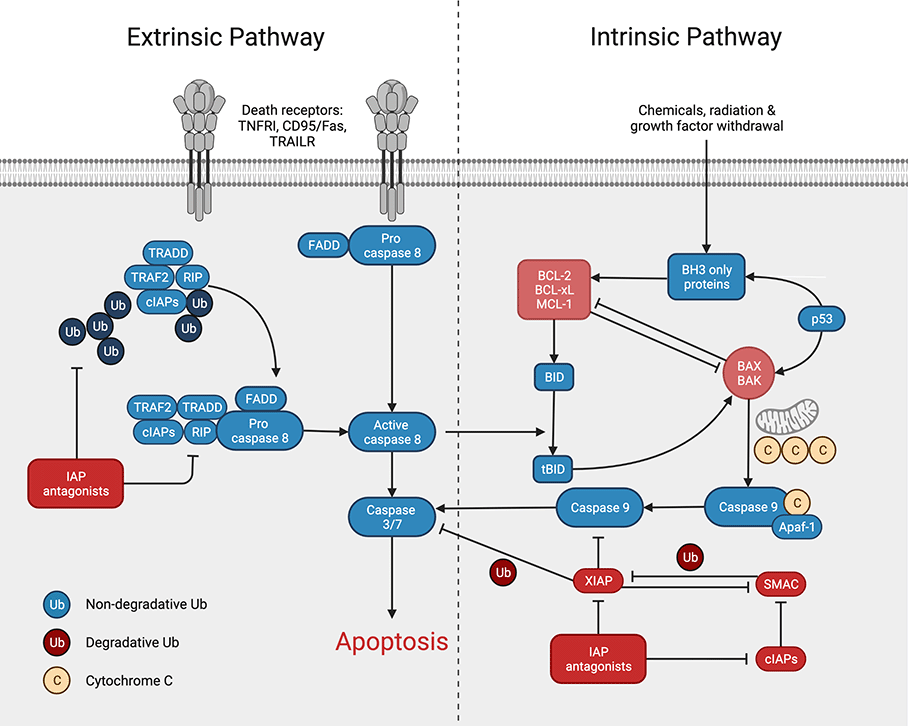
Apoptotic Pathway
Apoptotic pathways, the intricate networks regulating programmed cell death, are vital for various biological processes and disease outcomes. Understanding these pathways, including the intrinsic and extrinsic routes, sheds light on cell death mechanisms and their implications in health and disease. The interplay between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins and the activation of caspases shape the fate…
-
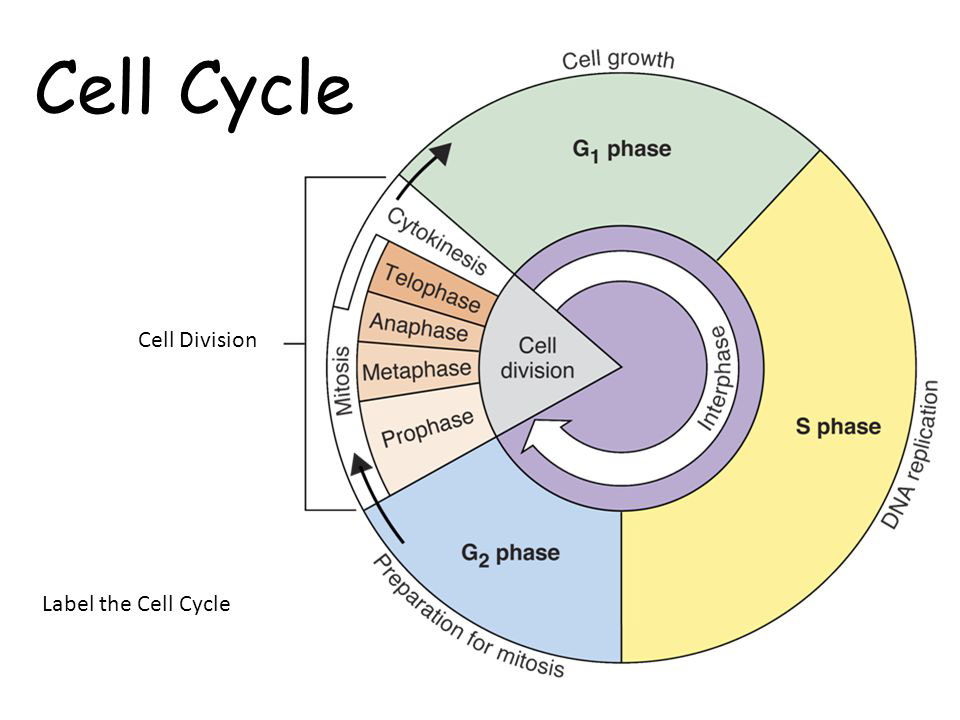
Cell Cycle (Basic)
I. Introduction II. Interphase A. G1 phase B. S phase C. G2 phase III. Mitotic Phase IV. Conclusion
-
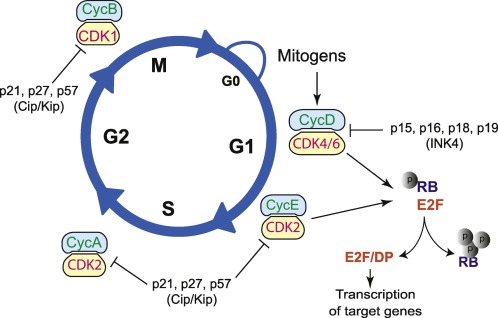
Cell cycle regulatory proteins
I. Introduction II. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) III. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs) IV. Retinoblastoma protein (Rb) V. Tumor protein p53 (p53) VI. Conclusion
-
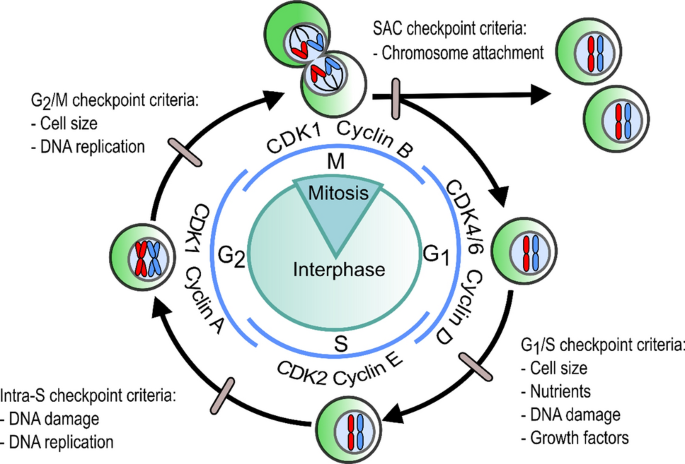
Eukaryotic cell cycle regulation
The cell cycle is a precisely regulated process essential for cell growth and division. It consists of four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and mitosis. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate cell division and maintaining genomic integrity. The cell cycle is governed by various checkpoints that assess DNA integrity, availability of growth…
-
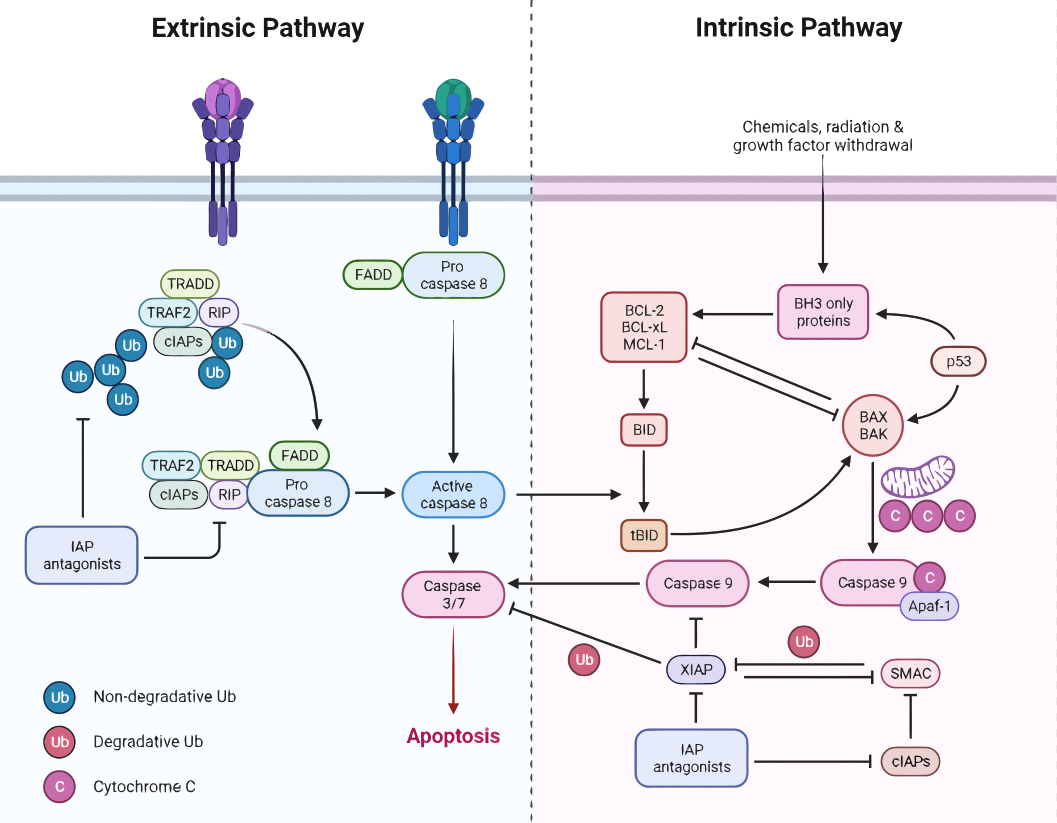
Apoptosis – Molecular Basis
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a crucial process in multicellular organisms that plays a key role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and responding to cellular stress and damage. Dysregulation of apoptosis can lead to various diseases, including cancer and autoimmunity. The molecular basis of apoptosis involves two main pathways: the extrinsic pathway, which…
-
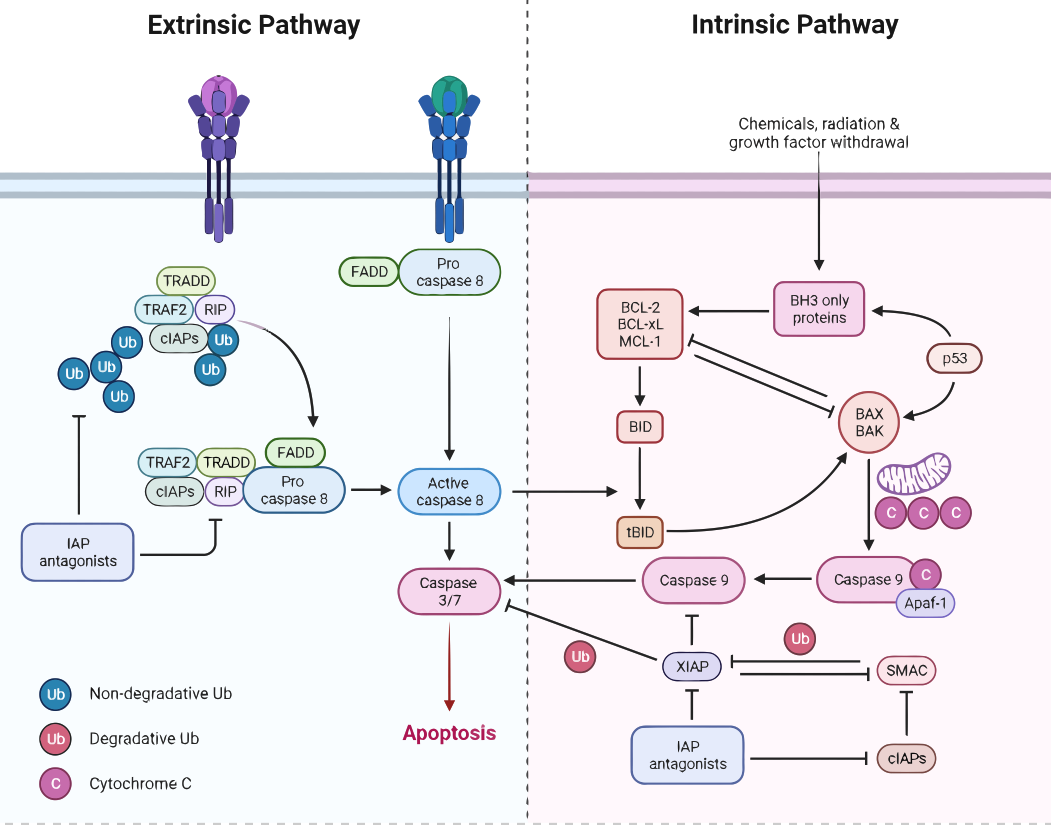
Apoptotic pathways
Apoptosis is a crucial physiological process that plays a key role in the development and maintenance of tissue homeostasis, as well as in the response to cellular stress and damage. The process of apoptosis is regulated by a complex network of molecular pathways, including the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. In the extrinsic pathway, signals from…
-

Regulation of the Cell Cycle
he cell cycle is a crucial process in the growth and development of multicellular organisms, and its regulation is essential for maintaining proper cell function. Dysregulation of the cell cycle can lead to various diseases, including cancer, where cells divide uncontrollably. The regulation of the cell cycle is a complex process that involves a delicate…
-

Cell Cycle and Its Regulation
The cell cycle is a fundamental process that is essential for the growth, development, and maintenance of all living organisms. It is a series of events that a cell undergoes to replicate and divide into two daughter cells. The cell cycle can be divided into two main stages: interphase and mitosis. Interphase is the period…
-
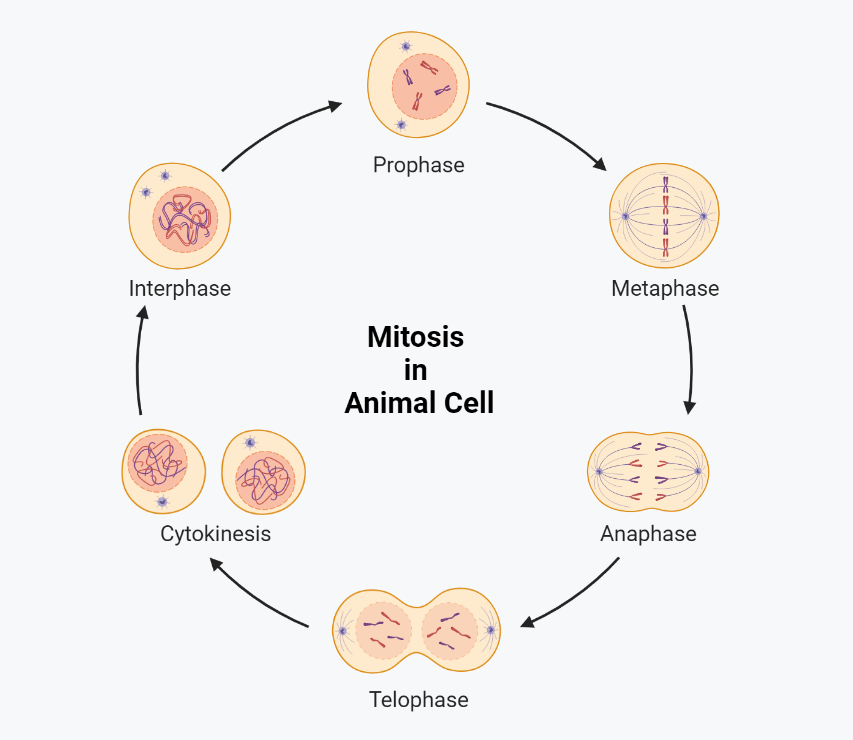
Mitosis: Cell Division
Mitosis cell division is essential for the growth and repair of an organism. Mitosis involves four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, followed by cytokinesis, the final stage where the cell physically divides into two identical daughter cells. The proper execution of mitosis is critical for the accurate replication and segregation of DNA and…
-
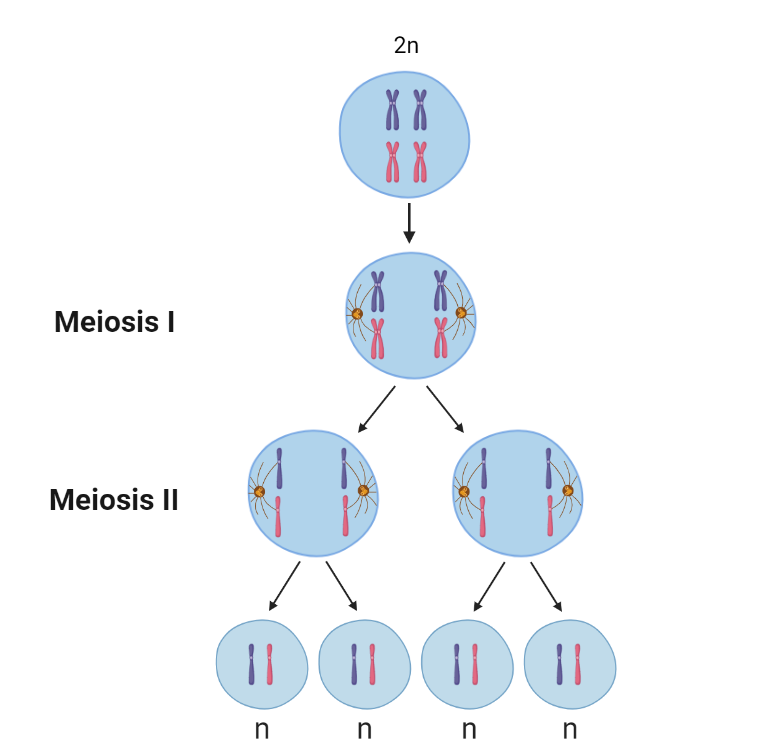
Meiosis: Cell Division
The text explains the process of meiosis, which is a type of cell division that produces reproductive cells or gametes. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half and is divided into two rounds of cell division: meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, the chromosomes pair up with their homologous partner, exchange genetic material…
-
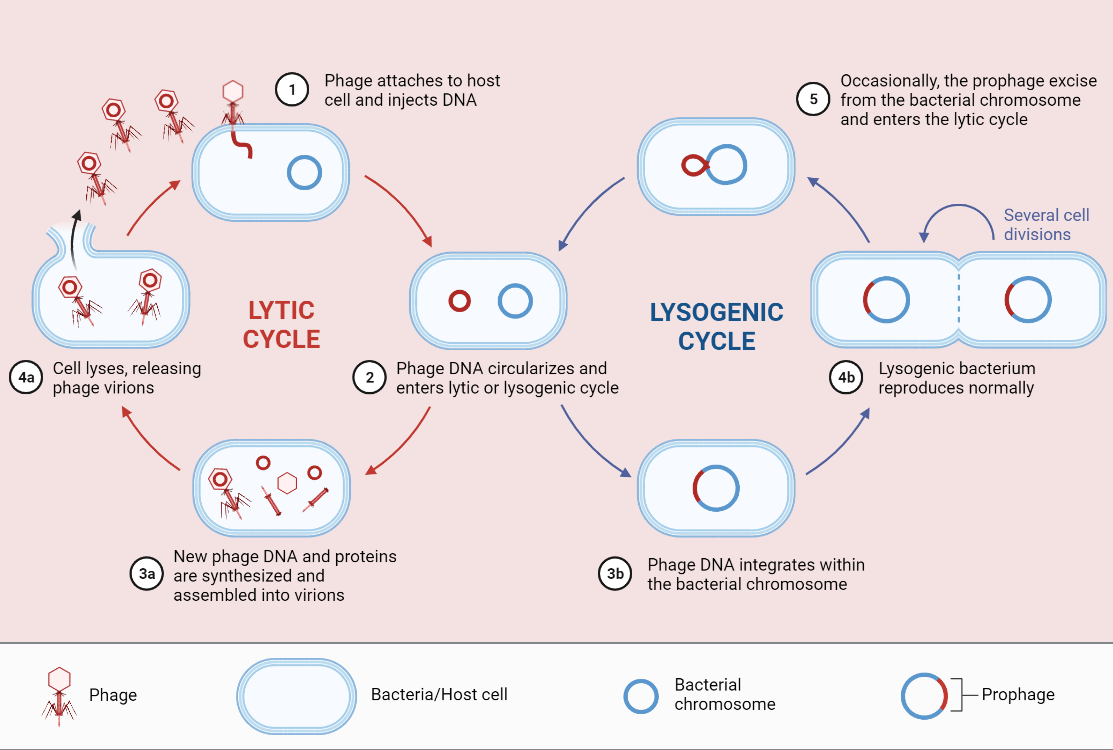
Lysogenic Cycle
The lysogenic cycle is a reproductive cycle used by certain viruses to infect and replicate within a host cell. During this cycle, the virus inserts its genetic material into the host cell’s DNA, becoming a dormant or latent infection. This period of dormancy allows the virus to evade the host immune response and persist within…
-
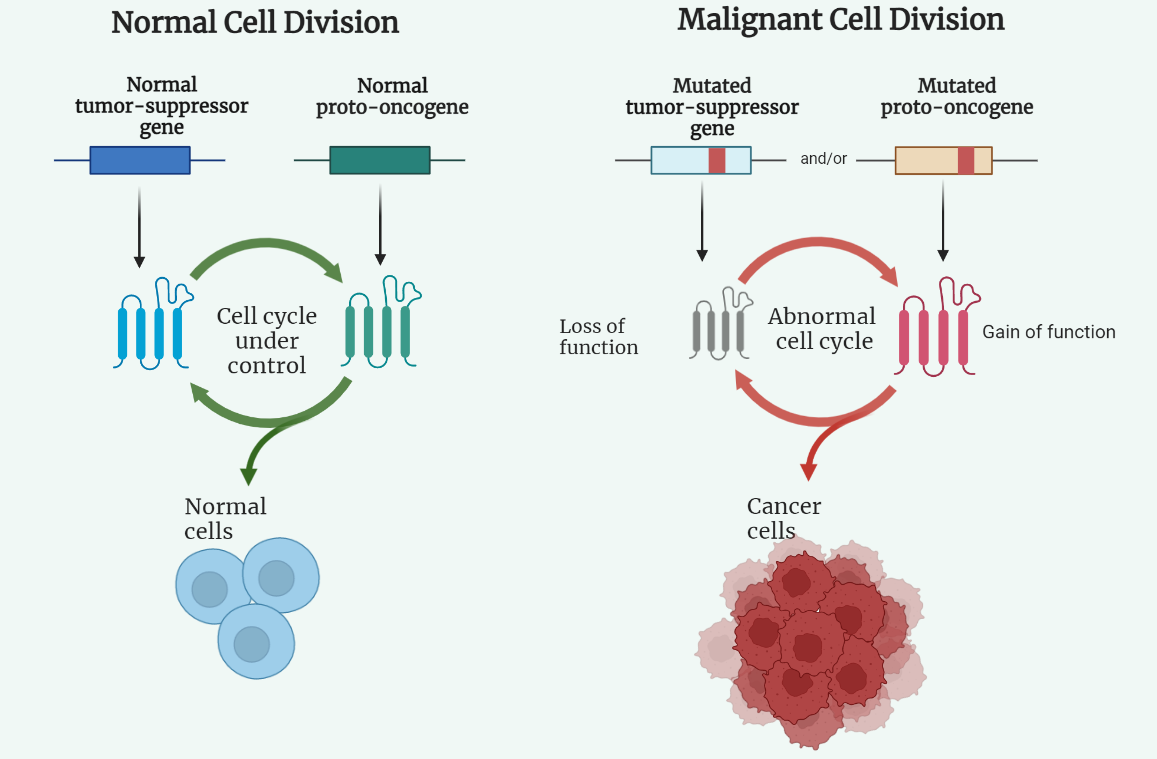
Cancer and cell cycle
The article explains the role of the cell cycle in the development of cancer. The cell cycle is a series of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides into two daughter cells. Disruption in the regulation of the cell cycle can lead to uncontrolled growth and proliferation of cells, causing cancer.…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




