-
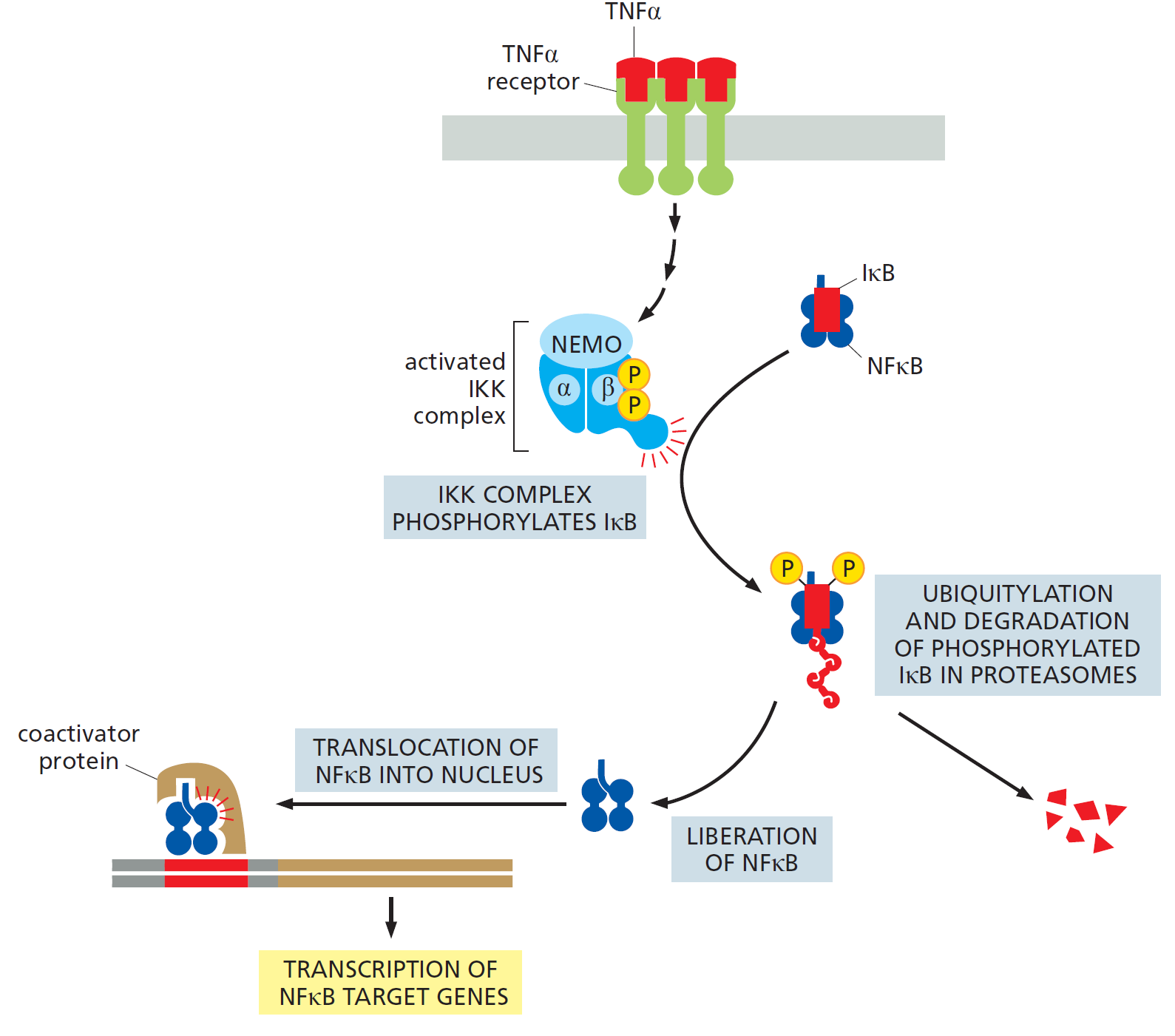
NFκB Signaling Pathway
NFκB Signaling Pathway Excerpt: The NFκB signaling pathway is a critical regulator of gene expression in response to stimuli like inflammation and infection. NFκB proteins, normally inactive due to IκB proteins, become activated upon signals such as TNFα. This leads to the degradation of IκB and the release of NFκB, which enters the nucleus to…
-
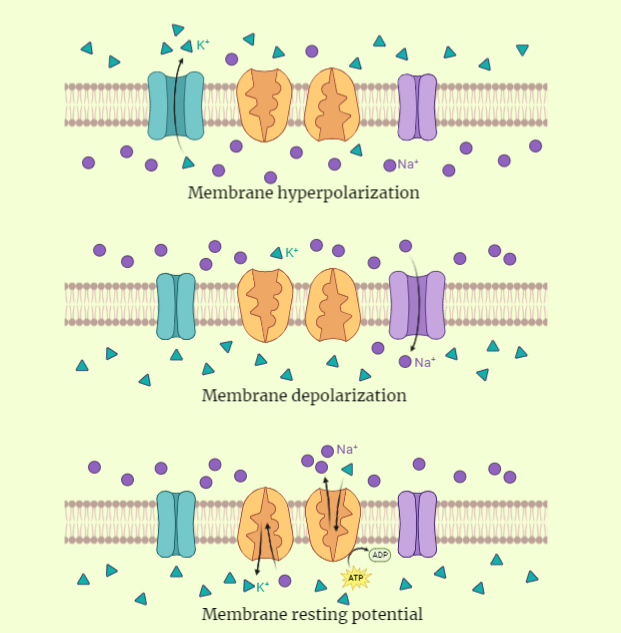
Membrane Potential
The membrane potential is a fundamental concept in cellular physiology, playing a crucial role in the proper functioning of cells. It refers to the electrical potential difference across a biological cell membrane, which is maintained by ion gradients. These gradients are created by the selective permeability of the membrane to ions such as sodium, potassium,…
-
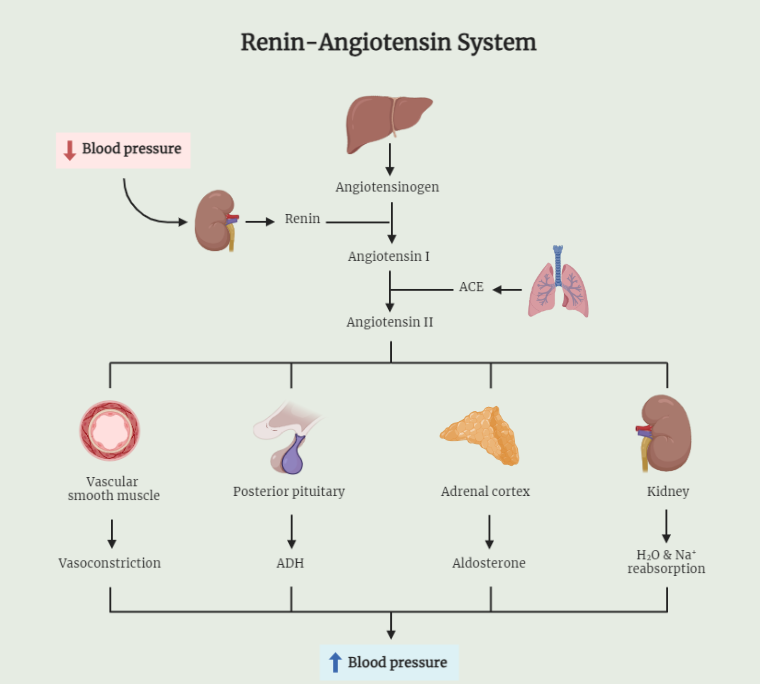
Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS)
Explore the intricate workings of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS), a crucial endocrine system responsible for blood pressure regulation and fluid balance. Dive into the functions of renin, angiotensin I and II, and their role in vasoconstriction and aldosterone release. Discover the clinical significance of RAS dysregulation and the use of RAS inhibitors in managing hypertension…
-
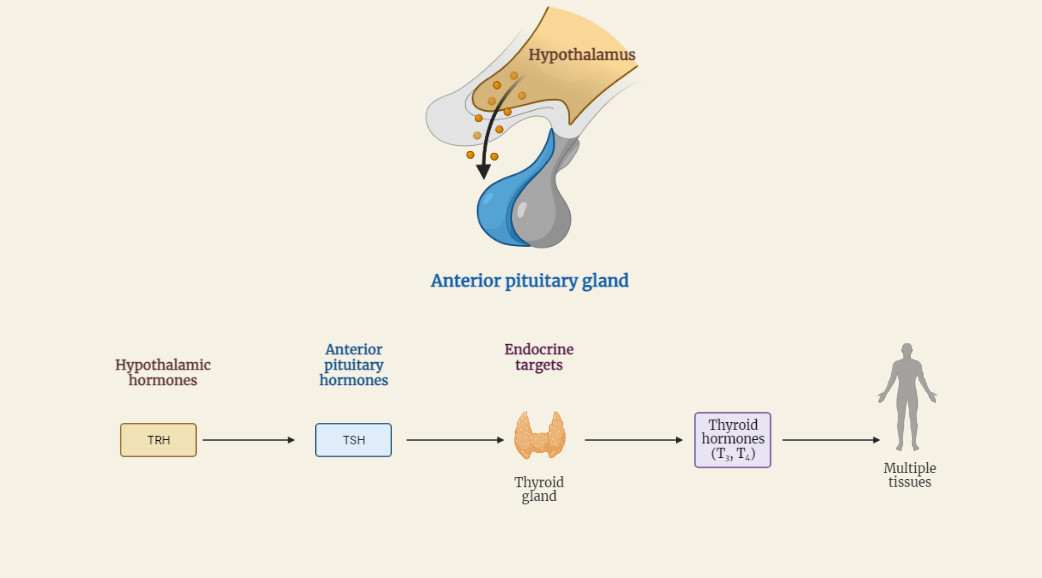
Thyroid Hormone Biosynthesis
Thyroid hormone biosynthesis is a complex process that takes place in the thyroid gland. This in-depth study explores the steps involved, including iodide uptake, oxidation, organification, coupling reactions, and hormone release. The regulation of this pathway through feedback mechanisms is also discussed. Understanding thyroid hormone biosynthesis is crucial for comprehending thyroid disorders and developing effective…
-
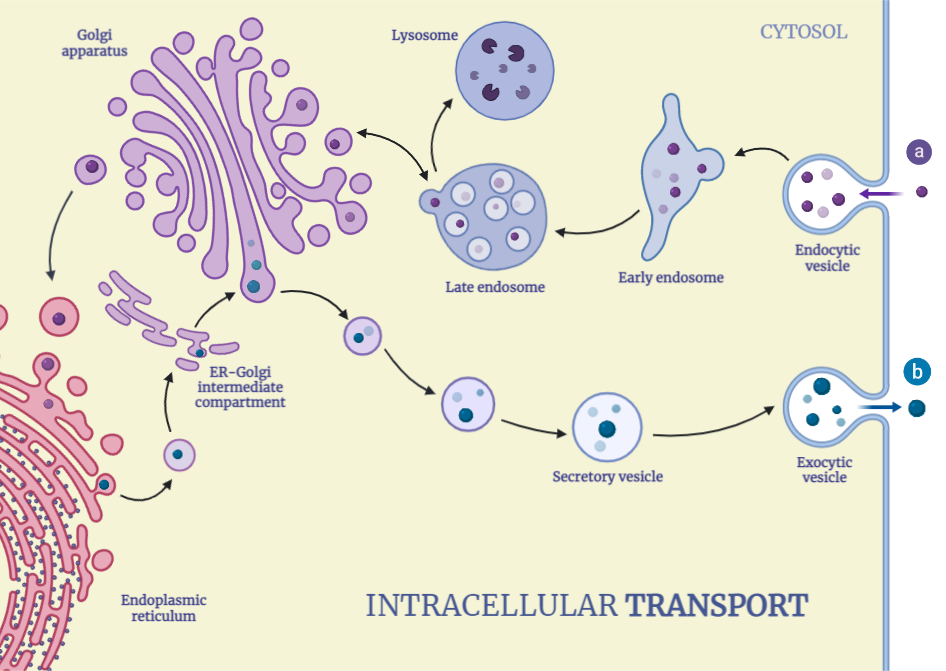
Intracellular Transport
Intracellular transport is a vital process that ensures the proper functioning of cells by facilitating the movement of molecules, organelles, and structures within them. Two main categories of intracellular transport are vesicular transport and cytoskeletal transport. Vesicular transport relies on the use of membrane-bound vesicles to transport materials within the cell through processes like endocytosis…
-
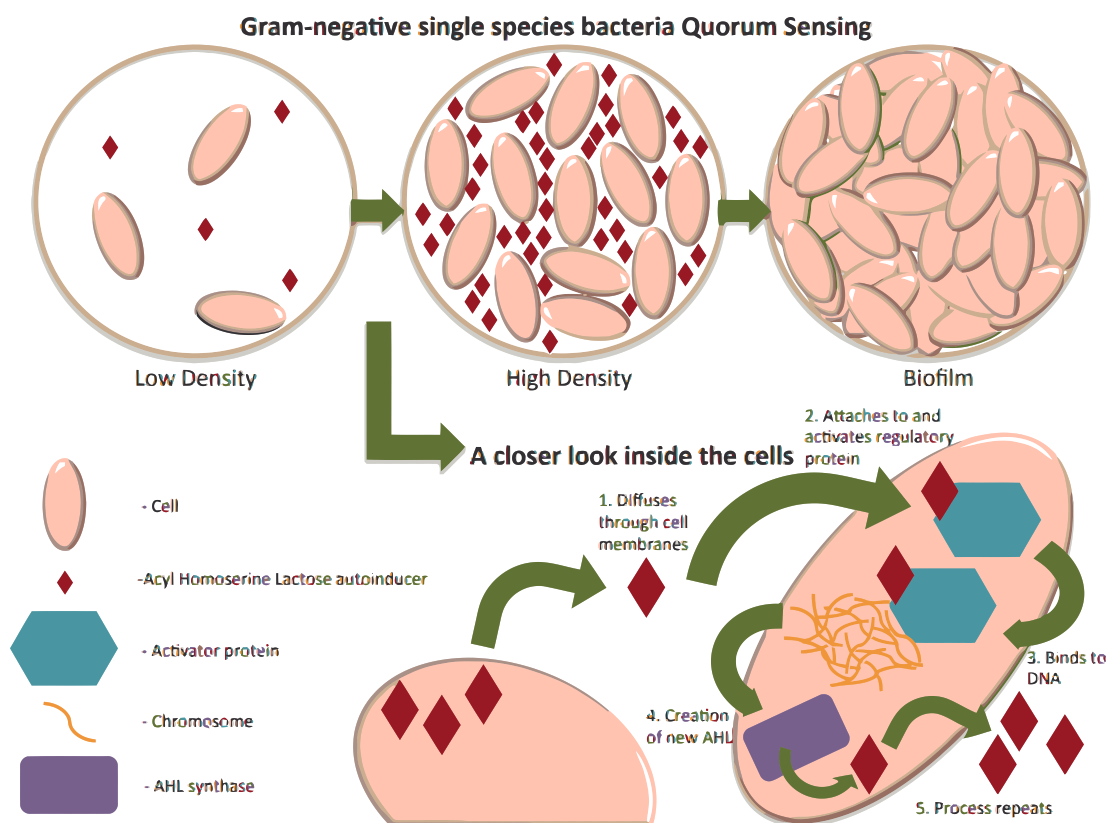
Quorum Sensing
Quorum sensing is a fascinating process that allows bacteria to communicate with each other, coordinate their behavior, and respond to changes in population density. This communication is mediated by small signaling molecules known as autoinducers, which are produced, detected, and responded to by bacterial cells. Quorum sensing plays a critical role in regulating a wide…
-
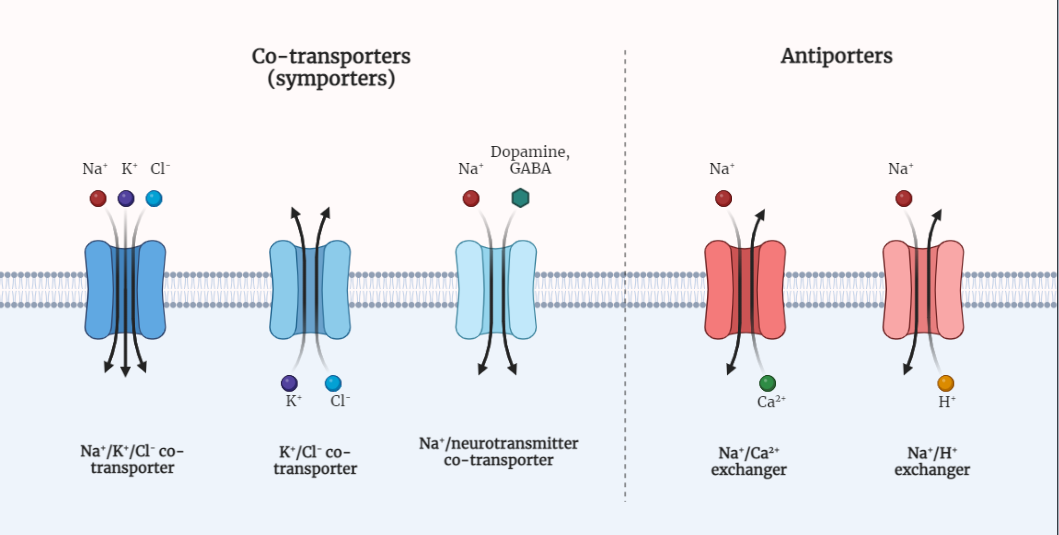
Active Transport
Active transport is a fundamental process in cellular biology that enables the movement of molecules across cell membranes against their concentration gradient. It requires the expenditure of energy, typically derived from ATP. This article explores the different types of active transport, including primary and secondary active transport, as well as cotransport. It highlights the significance…
-
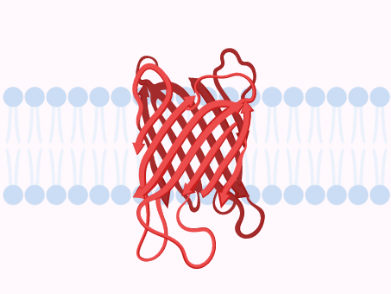
Aquaporins
Aquaporins, integral membrane proteins, play a critical role in water transport, maintaining cell hydration, osmoregulation, and facilitating water movement in the lens and epidermis. Discover their significance in various physiological processes.
-
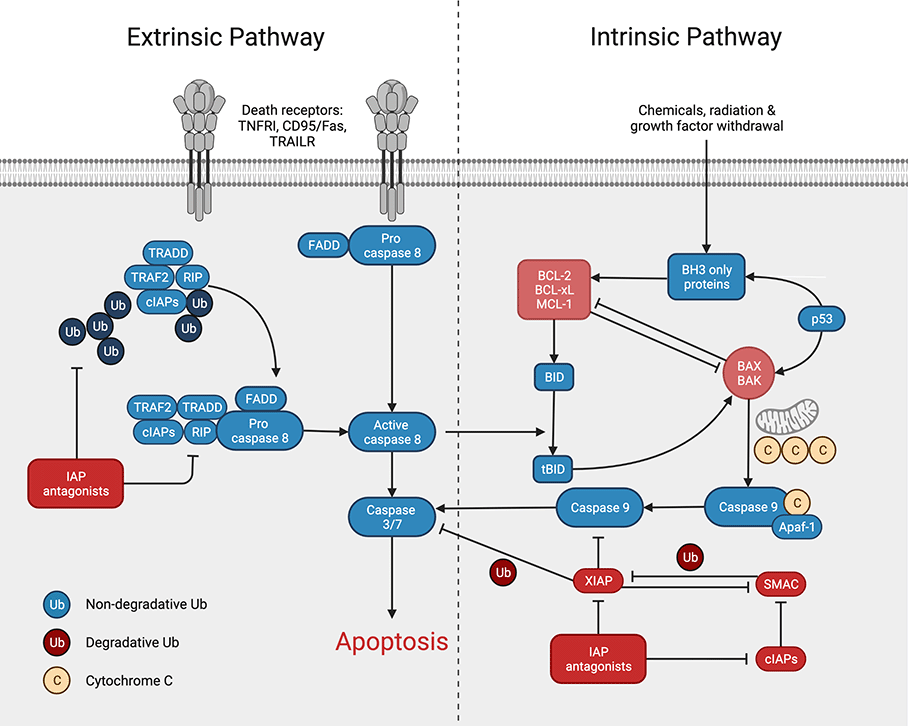
Apoptotic Pathway
Apoptotic pathways, the intricate networks regulating programmed cell death, are vital for various biological processes and disease outcomes. Understanding these pathways, including the intrinsic and extrinsic routes, sheds light on cell death mechanisms and their implications in health and disease. The interplay between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins and the activation of caspases shape the fate…
-
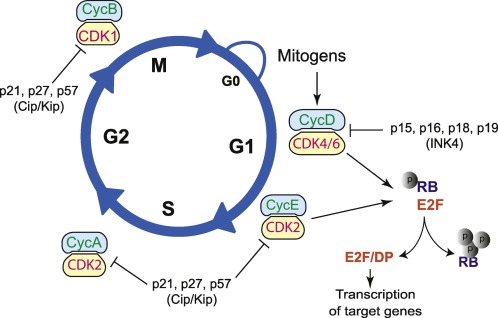
Eukaryotic cell cycle regulation
The cell cycle is a precisely regulated process essential for cell growth and division. It consists of four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and mitosis. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate cell division and maintaining genomic integrity. The cell cycle is governed by various checkpoints that assess DNA integrity, availability of growth…
-
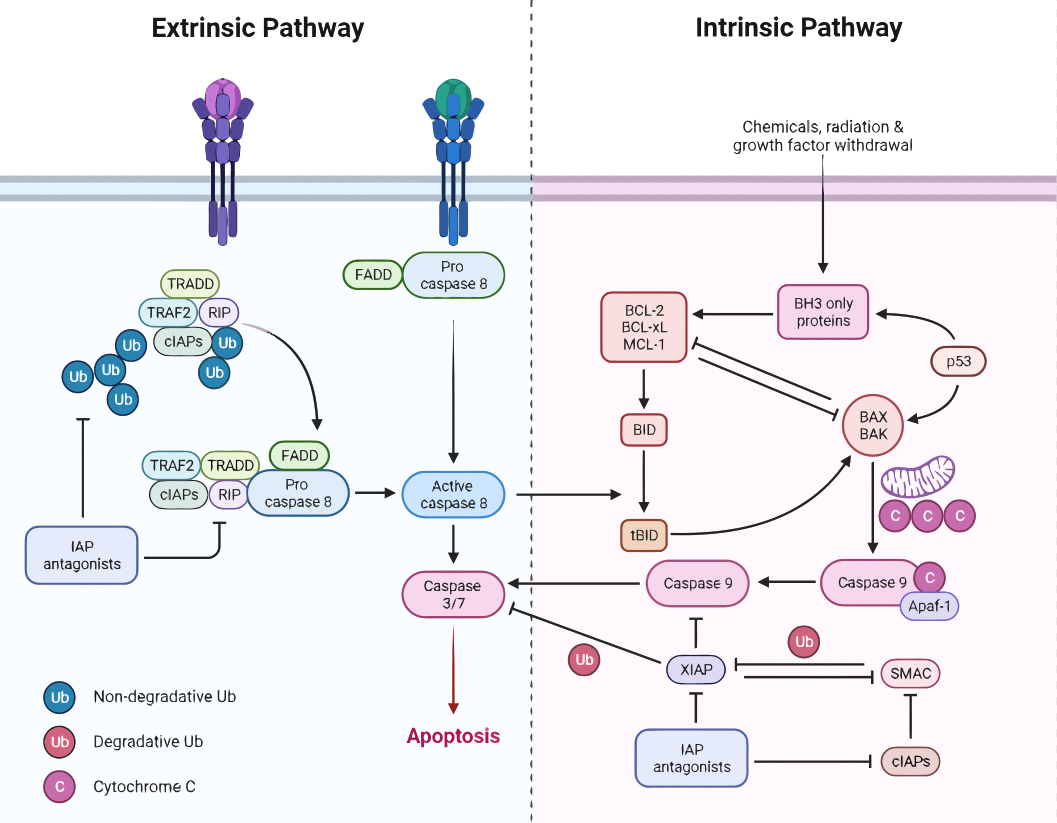
Apoptosis – Molecular Basis
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a crucial process in multicellular organisms that plays a key role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and responding to cellular stress and damage. Dysregulation of apoptosis can lead to various diseases, including cancer and autoimmunity. The molecular basis of apoptosis involves two main pathways: the extrinsic pathway, which…
-
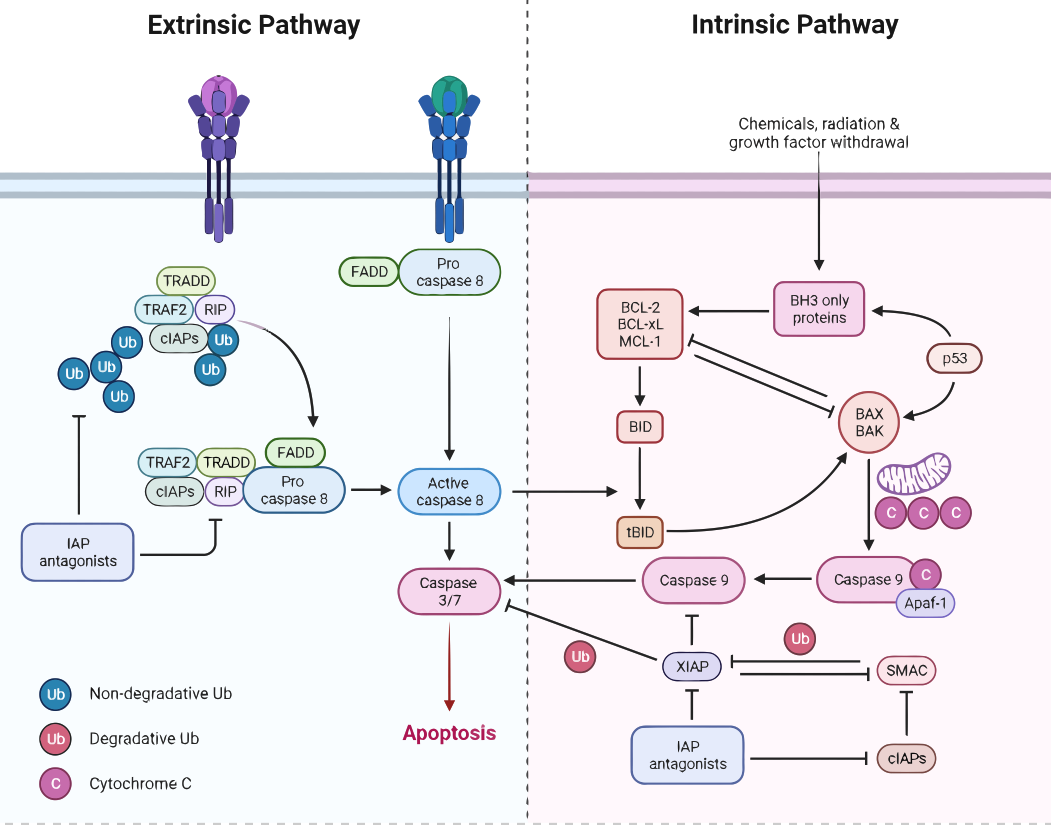
Apoptotic pathways
Apoptosis is a crucial physiological process that plays a key role in the development and maintenance of tissue homeostasis, as well as in the response to cellular stress and damage. The process of apoptosis is regulated by a complex network of molecular pathways, including the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. In the extrinsic pathway, signals from…
-
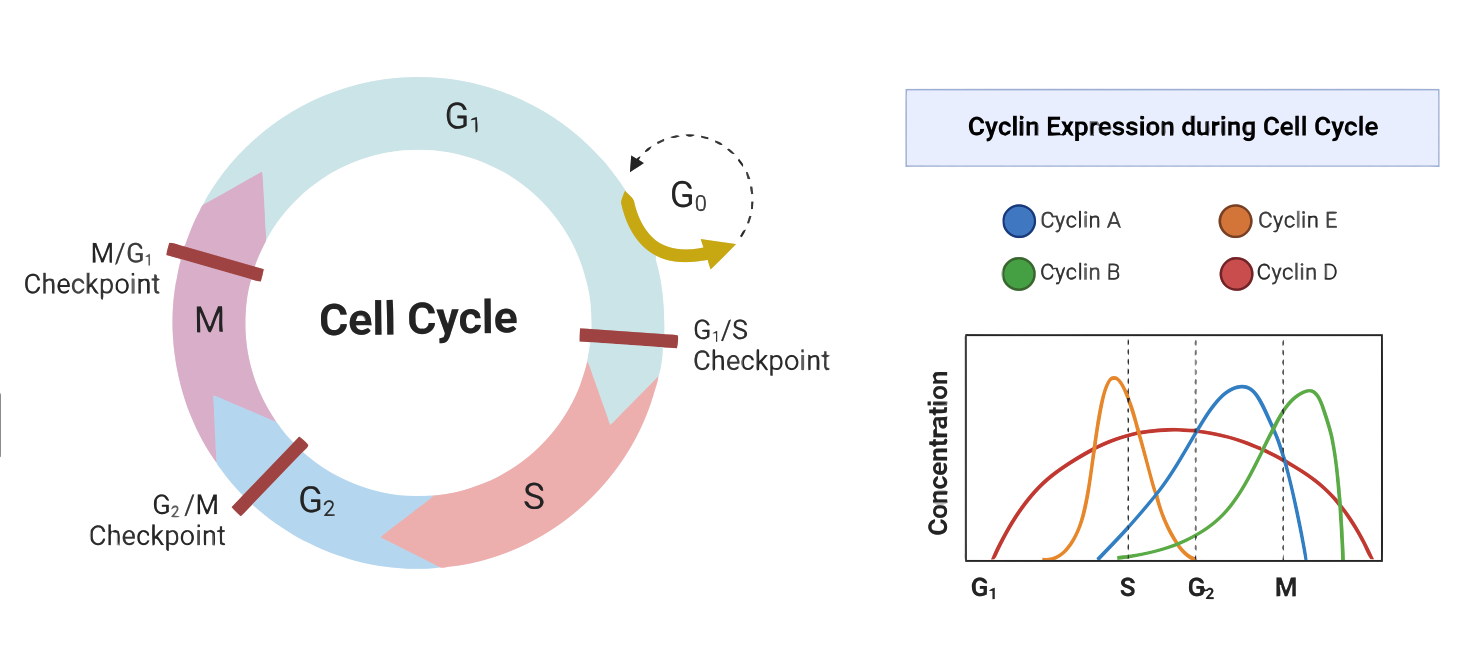
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
he cell cycle is a crucial process in the growth and development of multicellular organisms, and its regulation is essential for maintaining proper cell function. Dysregulation of the cell cycle can lead to various diseases, including cancer, where cells divide uncontrollably. The regulation of the cell cycle is a complex process that involves a delicate…
-

Lipids
Lipids are essential macromolecules that play a vital role in various biological processes. This guide explores the structure and function of lipids, their types, and their importance in energy storage, signaling, and cell membrane formation. We discuss the building blocks of lipids, including fatty acids and glycerol, and the types of lipids, including triglycerides, phospholipids,…
-
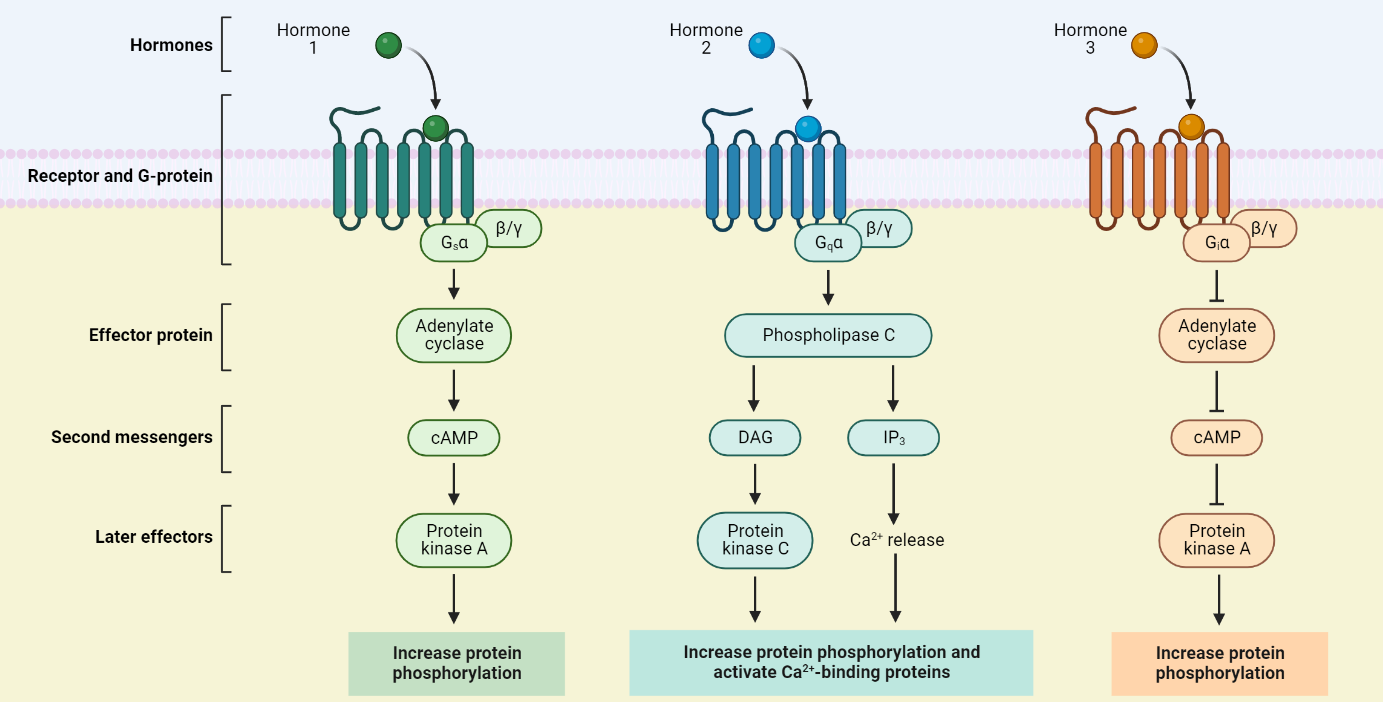
GPCR Signalling Pathway
The G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signalling pathway plays a vital role in transmitting signals from extracellular molecules, such as hormones, to intracellular effectors. This pathway involves a series of steps, including hormone binding to the GPCR, activation of the G protein, signal transduction, termination of the signal, and ultimately leading to a cellular response. The…
-
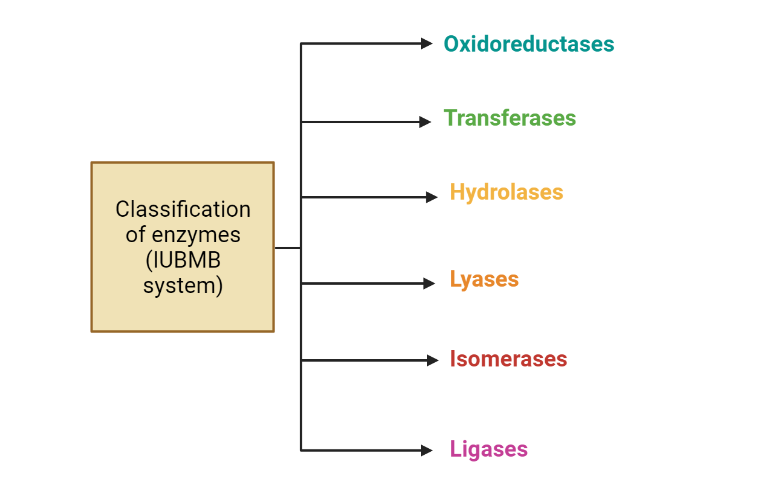
Enzymes : classification
Enzymes are incredibly important biomolecules that play a crucial role in the proper functioning of living organisms. They catalyze specific chemical reactions, making it possible for various biological processes such as metabolism, DNA replication, and cell signaling to occur efficiently. The structure of enzymes is complex, with different levels of organization, including the primary, secondary,…
-
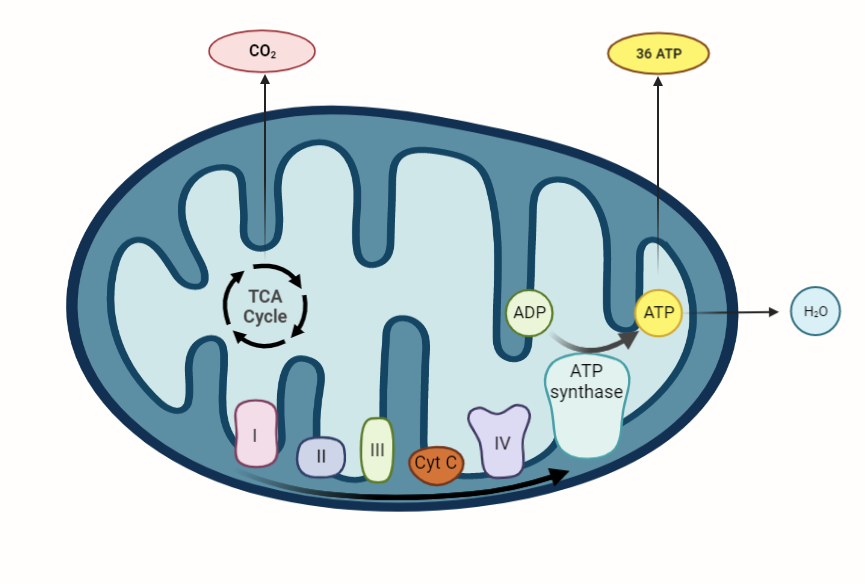
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
The chemiosmotic hypothesis proposed by Peter Mitchell in 1961 is a widely accepted model that explains how living organisms convert energy from electron transfer reactions into ATP synthesis. This hypothesis revolutionized our understanding of how cells generate ATP, the universal energy currency of living systems, and it is a fundamental principle of bioenergetics. The chemiosmotic…
-
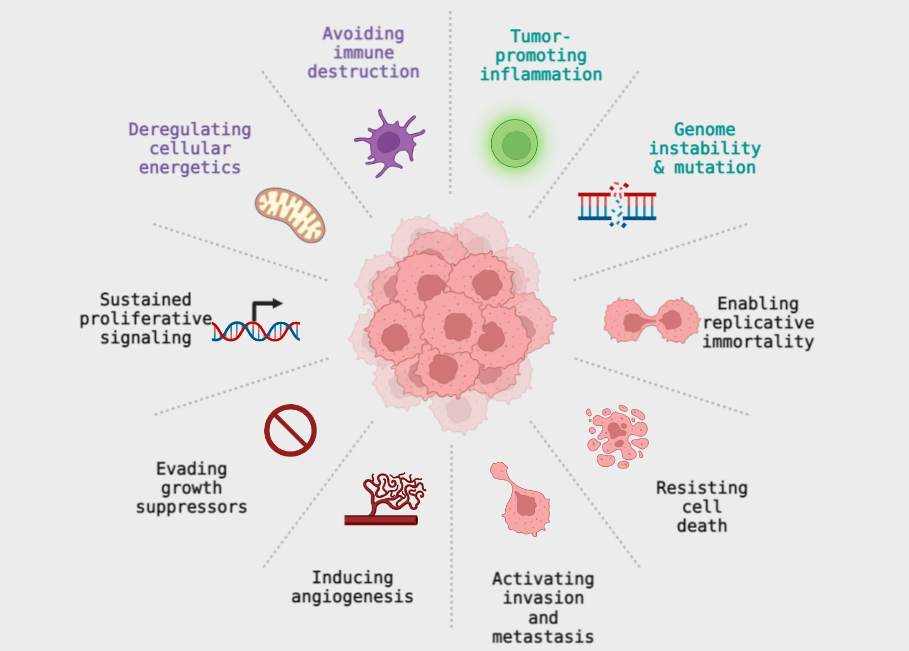
Molecular genetics of cancer
This topic discusses the molecular genetics of cancer, which involves the study of genetic and molecular changes that occur in cells as they become cancerous. It explains the role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in the development of cancer and how mutations in these genes can disrupt the balance between cell growth and proliferation.…
-
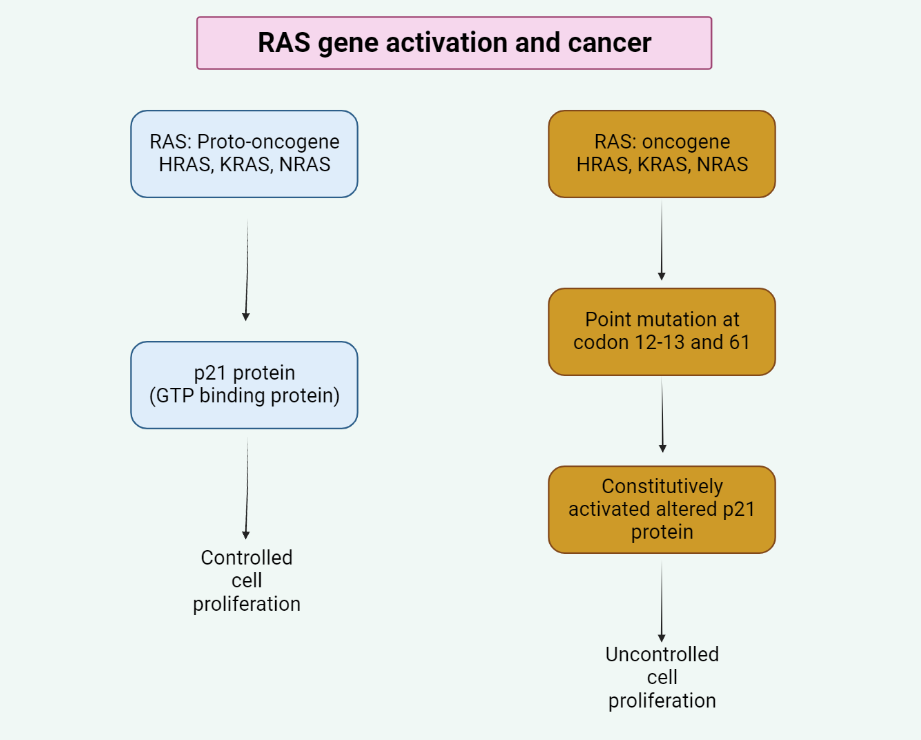
The RAS gene
This text describes the significance of RAS gene mutations in the development and treatment of cancer. RAS genes play a vital role in regulating cell growth, and mutations in these genes can lead to the development of various cancers, including colorectal, lung, and pancreatic cancer. The three main isoforms of the RAS gene – KRAS,…
-
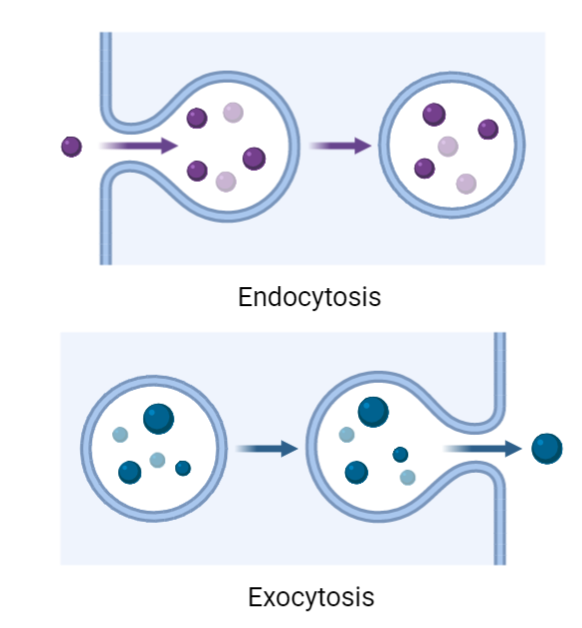
Vesicular Transport
Vesicular transport is a fundamental process that enables the movement of molecules, organelles, and macromolecules within cells. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, facilitating intercellular communication, and carrying out essential physiological functions. This comprehensive study note provides an in-depth exploration of vesicular transport, including its mechanisms, types, regulation, and significance in cellular…
-
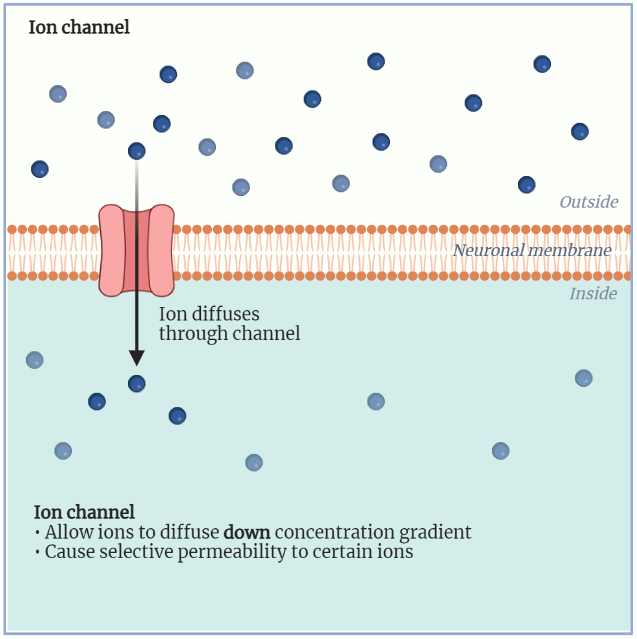
Ion Channels
Ion channels are vital membrane proteins that regulate the passage of ions, influencing cell physiology and essential processes like nerve impulses and muscle contraction. They can be categorized based on ion selectivity, gating mechanisms, and regulatory processes. Examples include voltage-gated channels that respond to membrane potential changes and ligand-gated channels activated by specific molecules. Cyclic…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




