-
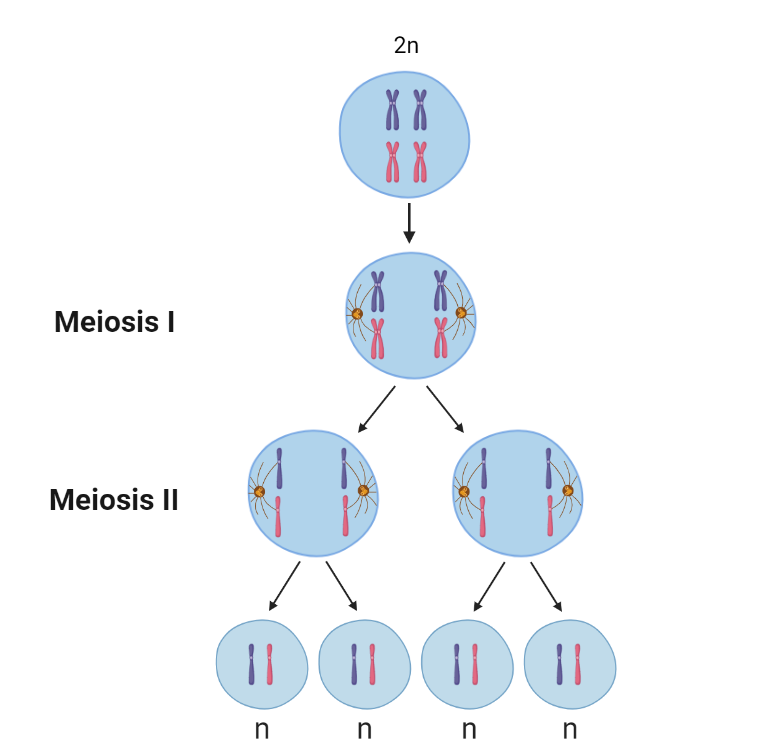
Meiosis: Cell Division
The text explains the process of meiosis, which is a type of cell division that produces reproductive cells or gametes. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half and is divided into two rounds of cell division: meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, the chromosomes pair up with their homologous partner, exchange genetic material…
-

DNA Footprinting
The DNA footprinting technique is used to study the interactions between DNA and proteins. This allows researchers to identify which regions of DNA are bound by specific proteins and how they interact with DNA. DNA footprinting has various methods like chemical, thermal, and electrophoretic mobility shift assays, which are used to map protein-DNA interactions, study…
-
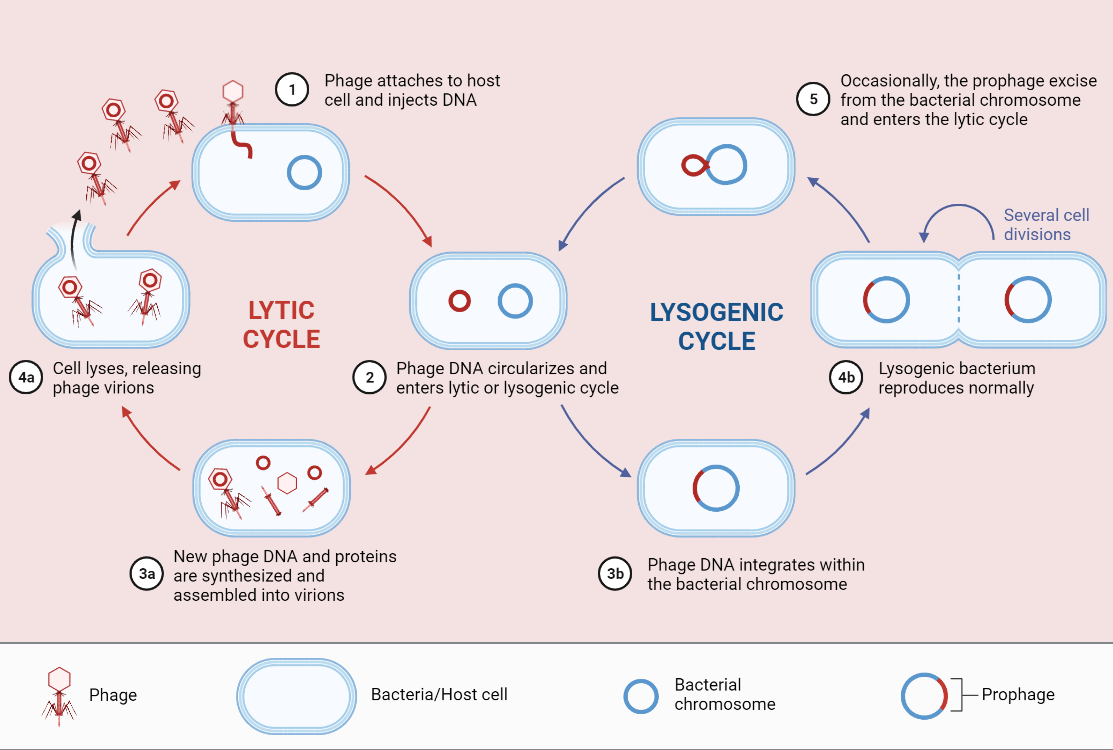
Lysogenic Cycle
The lysogenic cycle is a reproductive cycle used by certain viruses to infect and replicate within a host cell. During this cycle, the virus inserts its genetic material into the host cell’s DNA, becoming a dormant or latent infection. This period of dormancy allows the virus to evade the host immune response and persist within…
-
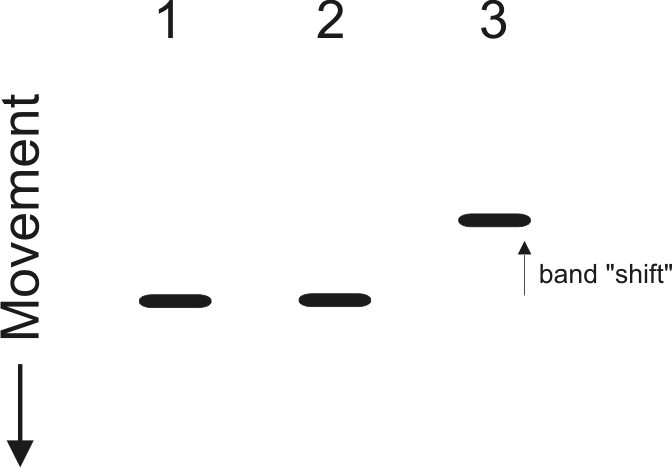
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay: EMSA
The text describes Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA), a molecular biology technique used to study protein-DNA interactions. EMSA is based on the principle that proteins can bind to specific regions of DNA and alter its conformation, affecting the mobility of the DNA in an electric field. This technique is used to study transcription regulation, DNA…
-
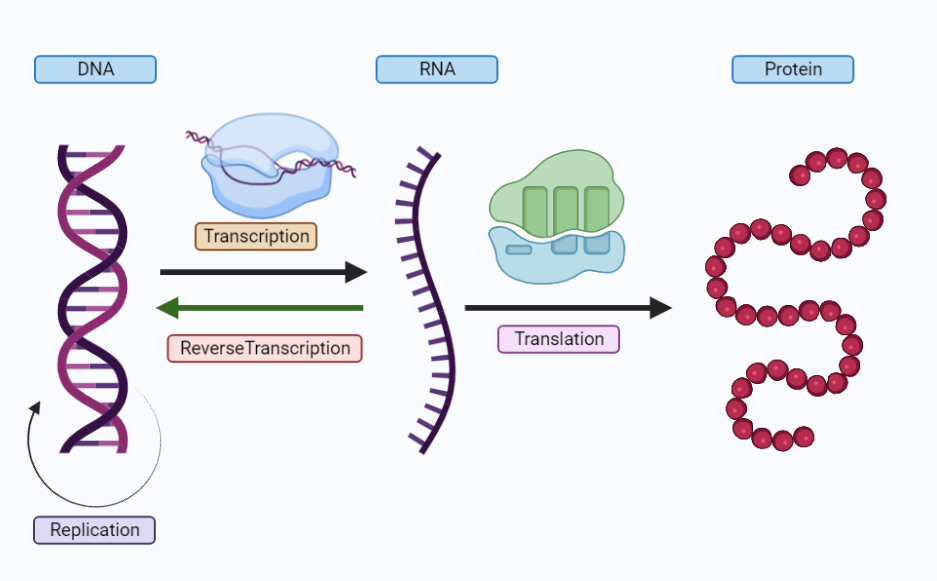
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The central dogma of molecular biology is a fundamental principle that explains the flow of genetic information in living organisms. It states that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins, but not the reverse. This principle has been a fundamental concept in the field of molecular biology and has helped to understand many…
-
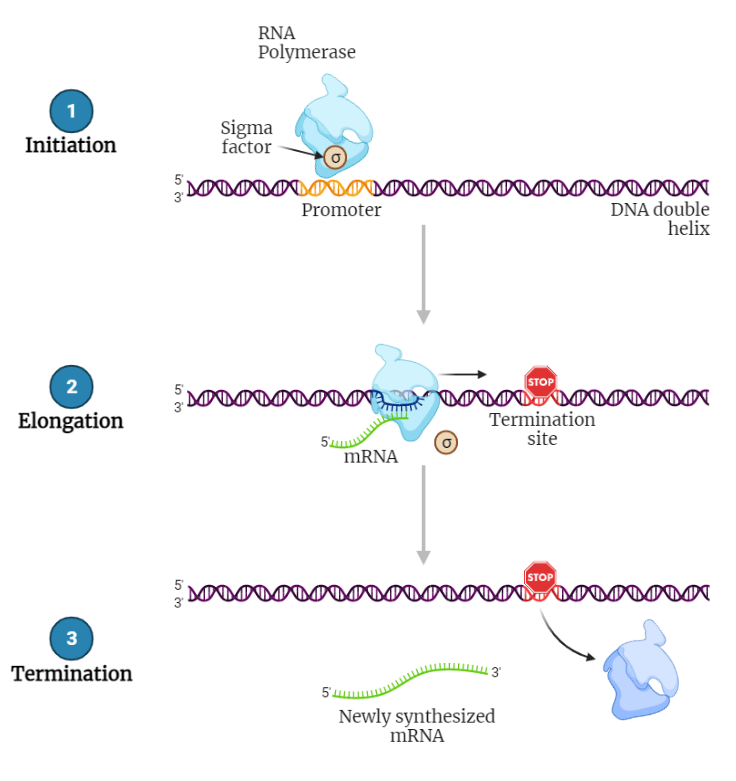
Prokaryotic Transcription
Introduction: Promoter recognition and binding: Initiation: Elongation: Termination: In summary, Prokaryotic transcription is the process of converting genetic information from DNA to RNA. This process is mediated by the enzyme RNA polymerase. The process includes promoter recognition and binding, initiation, elongation, and termination. The RNA polymerase recognizes the promoter by the help of sigma factor…
-
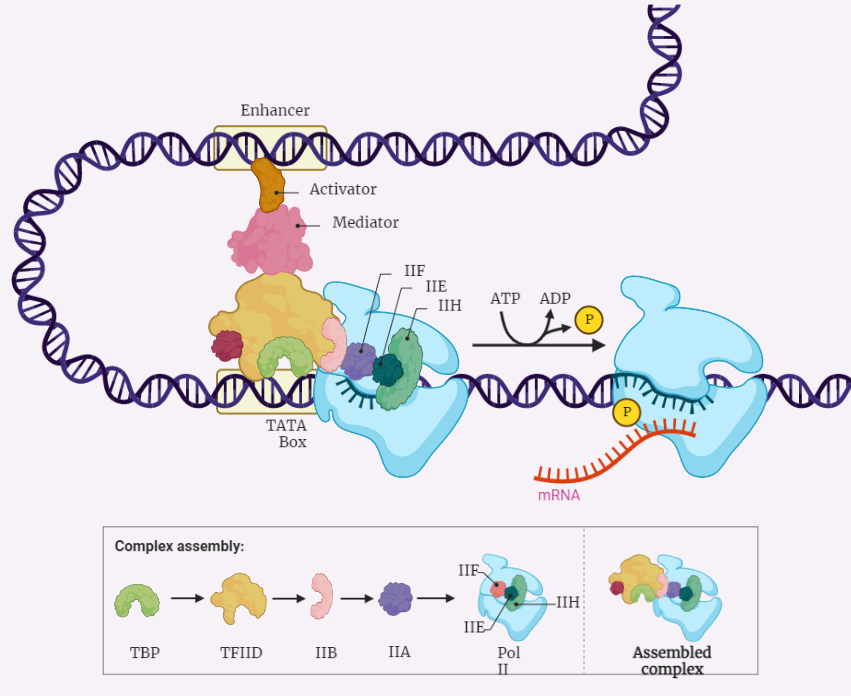
Eukaryotic transcription
The eukaryotic transcription process is a fundamental process for gene expression in eukaryotic cells. This process involves several steps that are tightly regulated and require the coordinated action of multiple proteins and regulatory factors. The initiation step is the first and most critical step in the transcription process. It involves the recruitment of RNA polymerase…
-
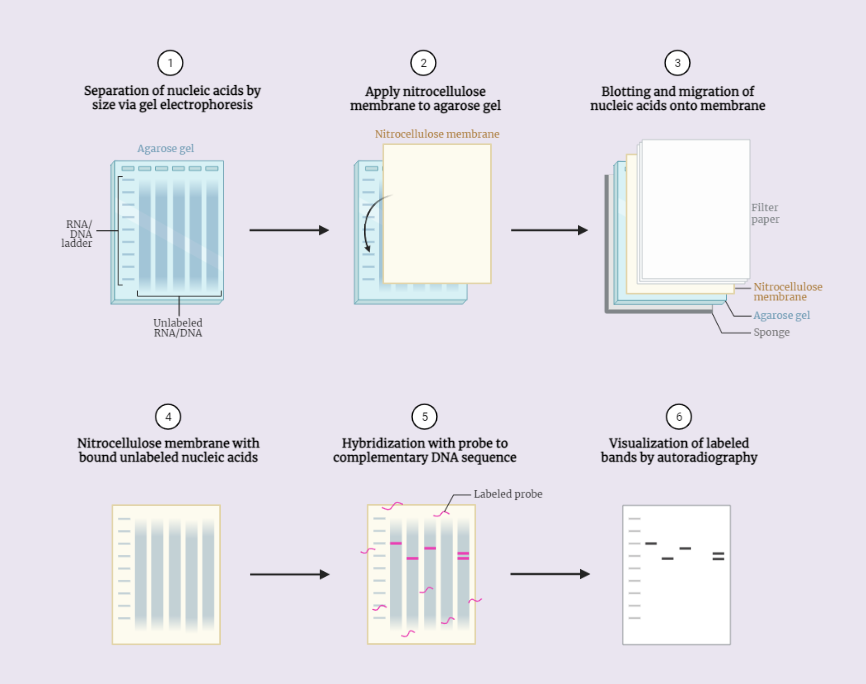
Northern blotting
Northern blotting is a technique used in molecular biology and medical research to analyze and detect specific RNA sequences. It involves the separation of RNA by electrophoresis and detection through hybridization. This powerful method has applications in genetics, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, providing valuable insights into diseases and genetic disorders. Discover more about the principles,…
-

Southern blotting
Southern blotting is a powerful technique used in molecular biology and genetics to analyze and identify specific DNA sequences. It involves the separation of DNA by electrophoresis and detection by hybridization. With applications in medical research, genetic engineering, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, Southern blotting plays a crucial role in understanding DNA-related phenomena. Discover the principles,…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




