-
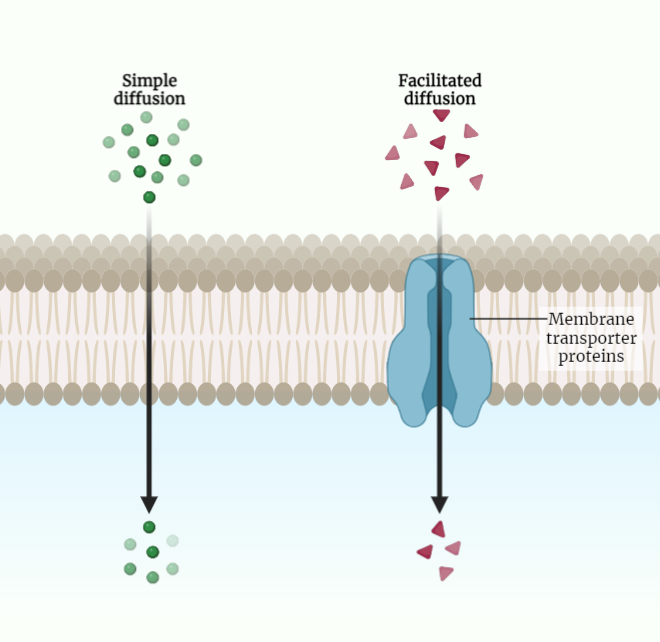
Passive Transport
Passive transport refers to the movement of substances across cell membranes without the use of energy. This study note explores key concepts such as diffusion, osmosis, the role of the cell membrane, concentration gradients, and how passive transport contributes to maintaining cellular homeostasis. Understanding these mechanisms is vital in comprehending the fundamental processes of substance…
-
Mendel’s First Law
The excerpt provides an in-depth study of Mendel’s First Law, also known as the Law of Segregation. It delves into Gregor Mendel’s groundbreaking experiments with pea plants, unraveling the principles of inheritance and genetic traits. Mendel’s work laid the foundation for modern genetics, and his findings continue to influence genetic research across various disciplines. Understanding…
-
Nitrogen Fixation
Discover the fascinating world of nitrogen fixation in life science. This in-depth study explores the process’s vital role in converting atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for living organisms. Learn about symbiotic and free-living examples, the impact on ecosystems and agriculture, and how it sustains life on Earth.
-
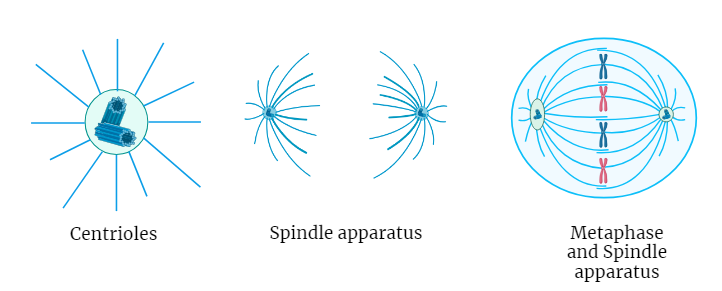
Centrioles : Structure and Function
Centrioles, cylindrical organelles found in the centrosome, play pivotal roles in cell division and cytoskeletal organization. Composed of triplet microtubules, they serve as the primary microtubule organizing center during mitosis, ensuring accurate chromosome segregation. Additionally, centrioles function as basal bodies, enabling the formation of cilia and flagella. Their influence extends to cell shape, intracellular transport,…
-

The Living World
The excerpt explores the fascinating realm of the living world, encompassing the vast diversity of organisms and their interactions. From the unity in basic life functions to the hierarchical organization of organisms, the study delves into the significance of cells as the fundamental units of life. It touches upon energy flow, homeostasis, and the profound…
-
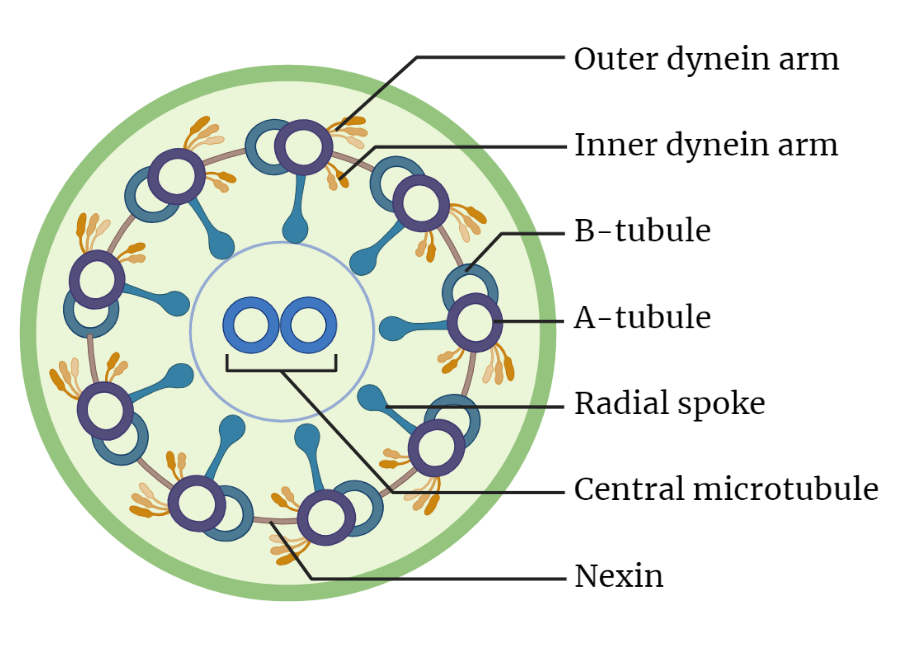
Microtubular arrangement
The 9+2 microtubular arrangement, a fascinating structure found in cilia and flagella, drives the coordinated movement of these hair-like appendages. Comprising 9 doublet microtubules encircling a central pair, this arrangement relies on the motor protein dynein to generate sliding motion, propelling cilia and flagella forward. Essential for cell movement, fluid transport, and sperm motility, understanding…
-

Spectroscopy and Beer-Lambert’s Law
Spectroscopy, a fascinating scientific technique, delves into the captivating interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation. By analyzing how substances interact with light at different wavelengths, spectroscopy provides crucial insights into the composition, structure, and behavior of materials. One of the fundamental principles in spectroscopy is the Beer-Lambert’s Law, a cornerstone in quantitative analysis. This law…
-
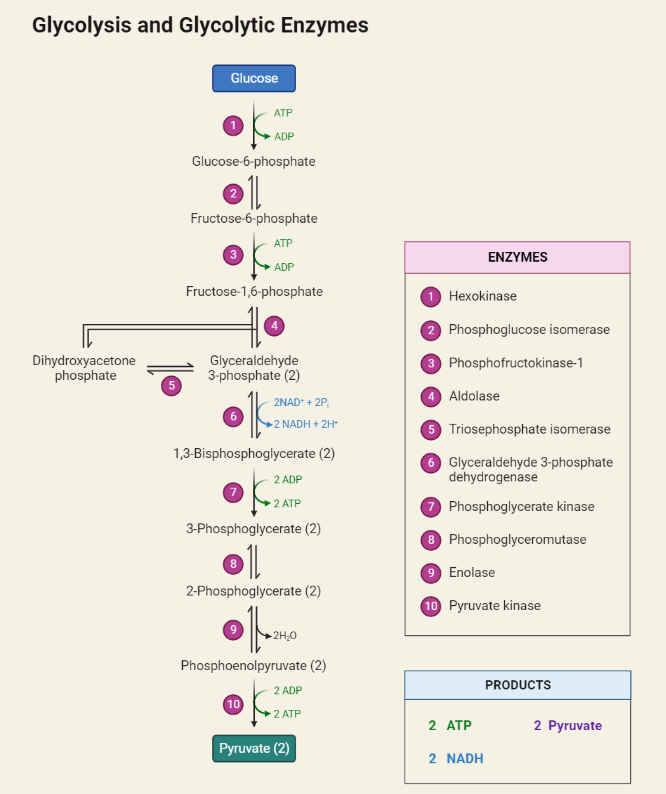
Steps of Glycolysis
The text provides a comprehensive overview of glycolysis, a crucial metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, ATP, and NADH. It explores the process, enzymes involved, and its significance in cellular energy production. Glycolysis’s versatility, occurring in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, makes it fundamental for cell survival and energy generation in various organisms, from…
-
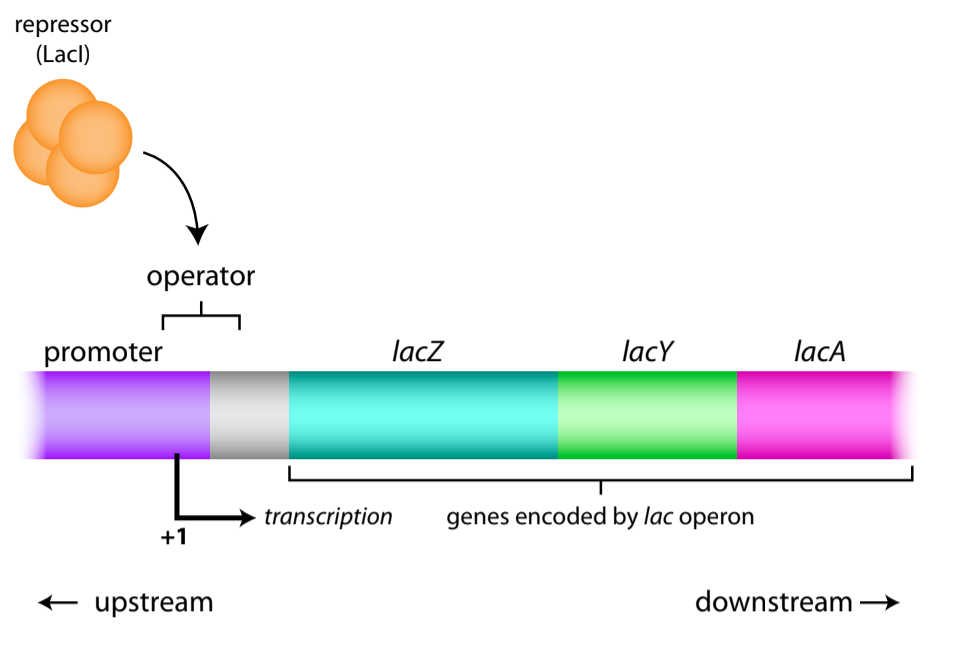
Lac Operon- Gene Regulation in Bacteria
The lac operon, found in E. coli bacteria, is a remarkable genetic system that controls the metabolism of lactose, a sugar commonly present in milk. This operon comprises three crucial structural genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA, responsible for encoding the essential enzymes needed to break down lactose into glucose and galactose. Its significance in the…
-
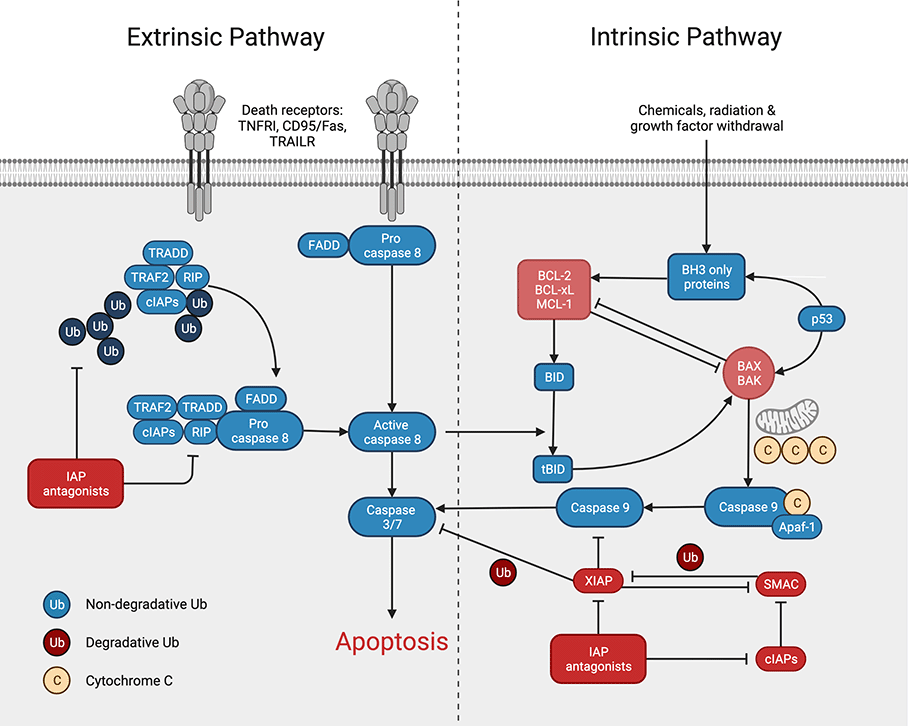
Apoptotic Pathway
Apoptotic pathways, the intricate networks regulating programmed cell death, are vital for various biological processes and disease outcomes. Understanding these pathways, including the intrinsic and extrinsic routes, sheds light on cell death mechanisms and their implications in health and disease. The interplay between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins and the activation of caspases shape the fate…
-

Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife conservation is a crucial endeavor aimed at managing and safeguarding wild animals and their habitats. Preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem services are key reasons behind its significance, along with supporting human well-being. However, various threats, such as habitat destruction, climate change, overexploitation, invasive species, and pollution, pose challenges to wildlife. To combat these issues,…
-
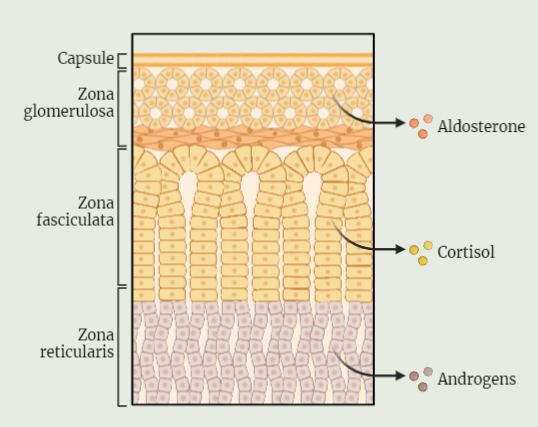
Histology of Adrenal Gland
The adrenal glands, also known as the suprarenal glands, are a vital part of our endocrine system. Positioned on top of each kidney, these small triangular-shaped glands produce and release a variety of hormones that play crucial roles in our body’s functioning. The outer region, called the adrenal cortex, consists of three layers that produce…
-
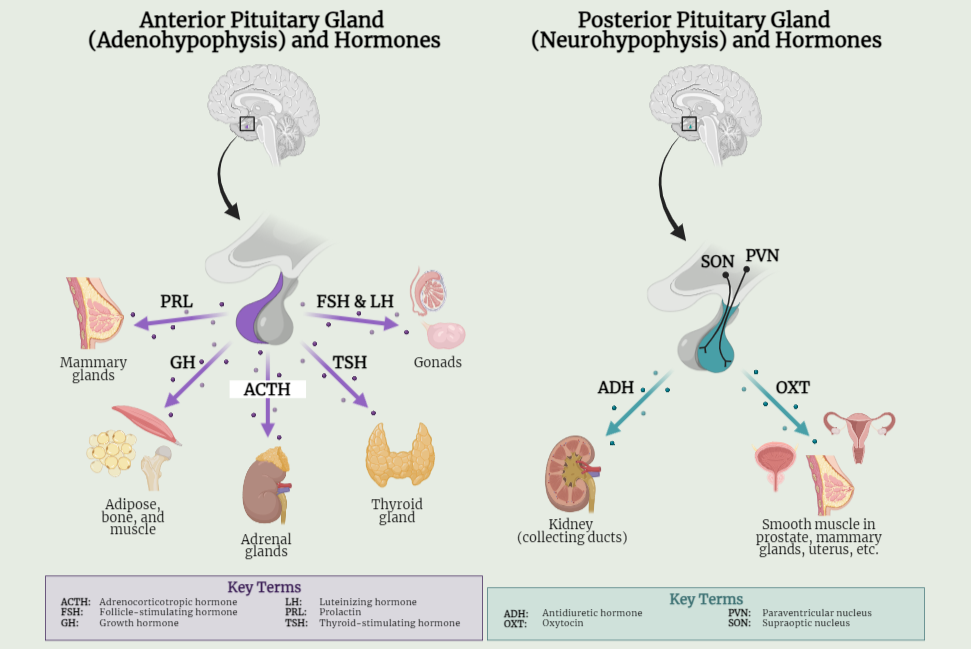
The Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland, often called the “master gland,” plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. Located at the base of the brain, it produces hormones that control other endocrine glands and impact processes like growth, metabolism, fertility, and thyroid function. The gland consists of two parts: the anterior pituitary, responsible for hormones like…
-
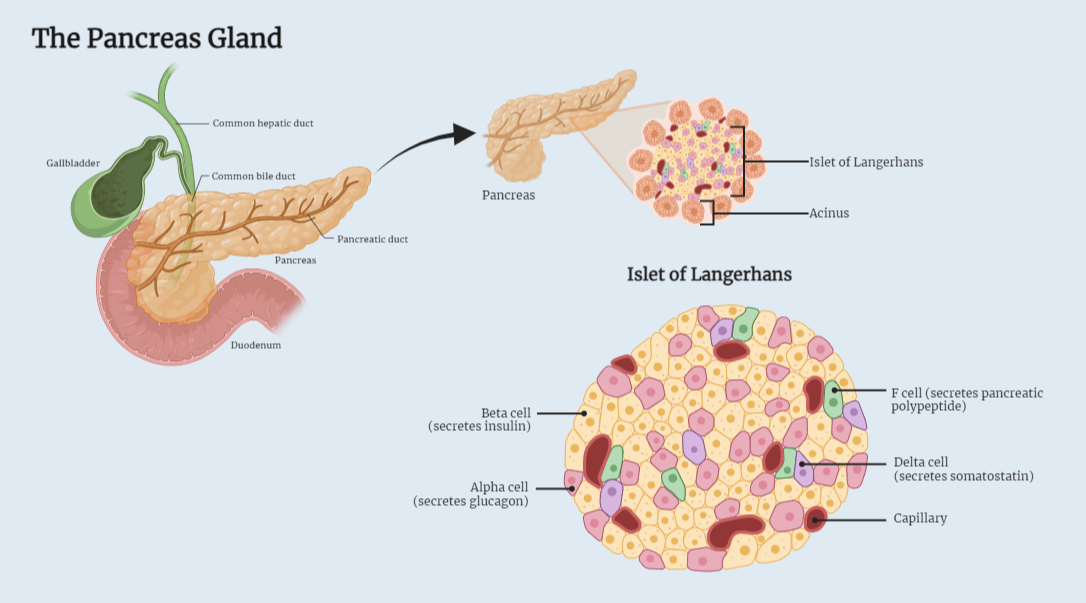
The pancreas gland
The pancreas, situated behind the stomach in the upper abdomen, plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism regulation. It produces insulin and glucagon, which control blood sugar levels. Dysfunction of the pancreas can lead to conditions like diabetes mellitus and pancreatitis, necessitating accurate diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the pancreas’ significance helps comprehend its impact on…
-

Molecular Events of Amphibian Fertilization
Fertilization in amphibians is a fascinating process that involves a unique set of molecular events governing the successful fusion of male and female gametes. Unlike mammals, amphibians employ external fertilization, where the male releases sperm into the surrounding water, and the female lays her eggs. This process requires intricate cellular interactions, starting with chemotaxis and…
-
The Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Function
The Golgi apparatus, a crucial organelle in eukaryotic cells, plays a vital role in processing, sorting, and transporting proteins and lipids. Comprising stacked cisternae with distinct regions, it employs a myriad of enzymes for modifications. This dynamic structure ensures proper cellular function by facilitating the formation of lysosomes, secretory vesicles, and the extracellular matrix. Understanding…
-
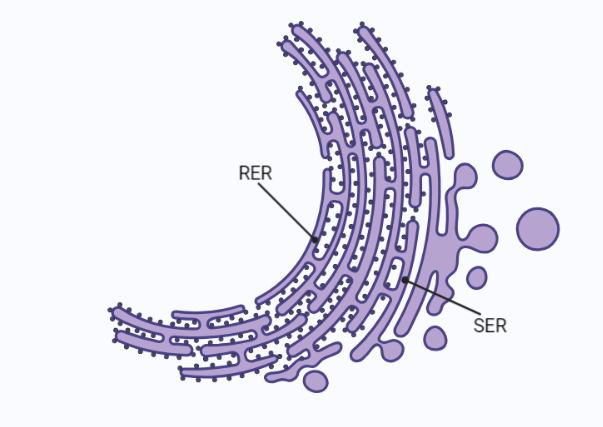
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a vital organelle in eukaryotic cells, playing multiple crucial roles. From protein synthesis, folding, and modification to lipid metabolism and calcium storage, the ER ensures the cell’s proper functioning. The Rough ER, adorned with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins, while the Smooth ER is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification. Additionally, the…
-
Lysozomes
Lysozomes, the essential organelles in eukaryotic cells, play a pivotal role in cellular material degradation. Enclosed within a lipid bilayer, these spherical structures house hydrolytic enzymes responsible for breaking down bacteria, old organelles, and other cellular components. Additionally, lysozomes contribute to autophagy, cellular protection against harmful agents, and lipid metabolism. Formation from the Golgi apparatus…
-
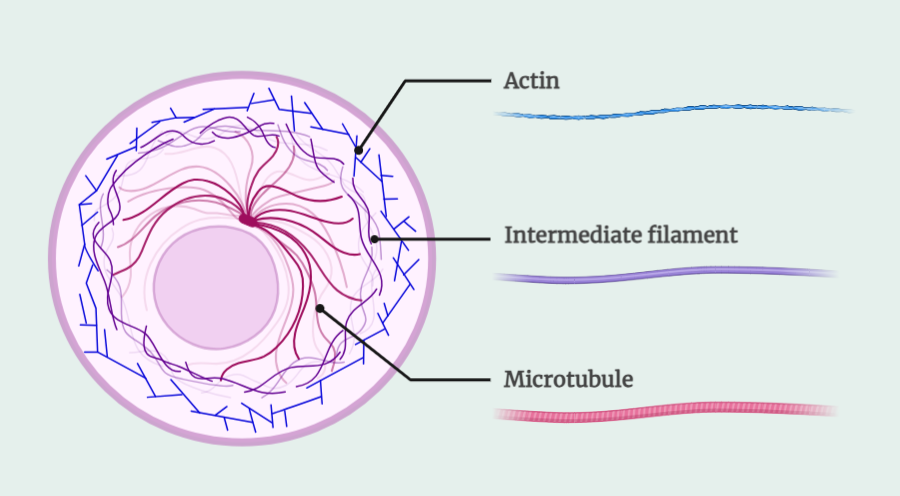
The cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton, a complex network of protein filaments, serves as the architectural backbone of eukaryotic cells. Comprised of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, it provides structural support, cell shape, and motility. Functionally versatile, the cytoskeleton plays crucial roles in cell division, endocytosis, and exocytosis. Regulated by specific proteins, its dynamic nature underlies various cellular processes.…
-
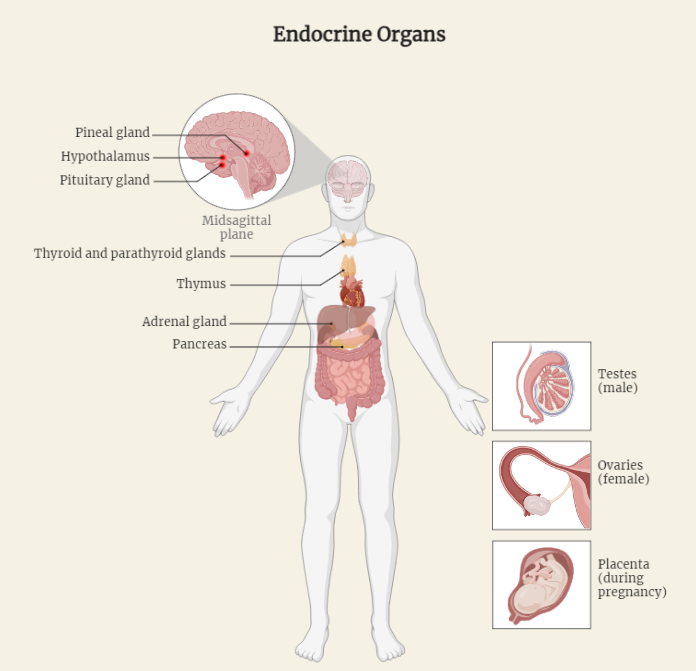
Endocrine Organs of the Human Body
The endocrine system is a complex network of organs in the human body that produces and regulates hormones. These endocrine organs, including the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and others, play crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis, metabolism, reproduction, and overall health. Understanding the functions and interactions of these organs is essential for comprehending the…
-

Beer-Lambert Law and Spectrophotometry
Discover the principles of the Beer-Lambert Law and its application in spectrophotometry. Explore how this law relates the concentration of a solute to absorbance, and its significance in quantitative analysis, chemical kinetics, environmental monitoring, pharmaceutical analysis, and biochemical assays. Unlock the power of spectrophotometry in understanding chemical substances and their characteristics.
-
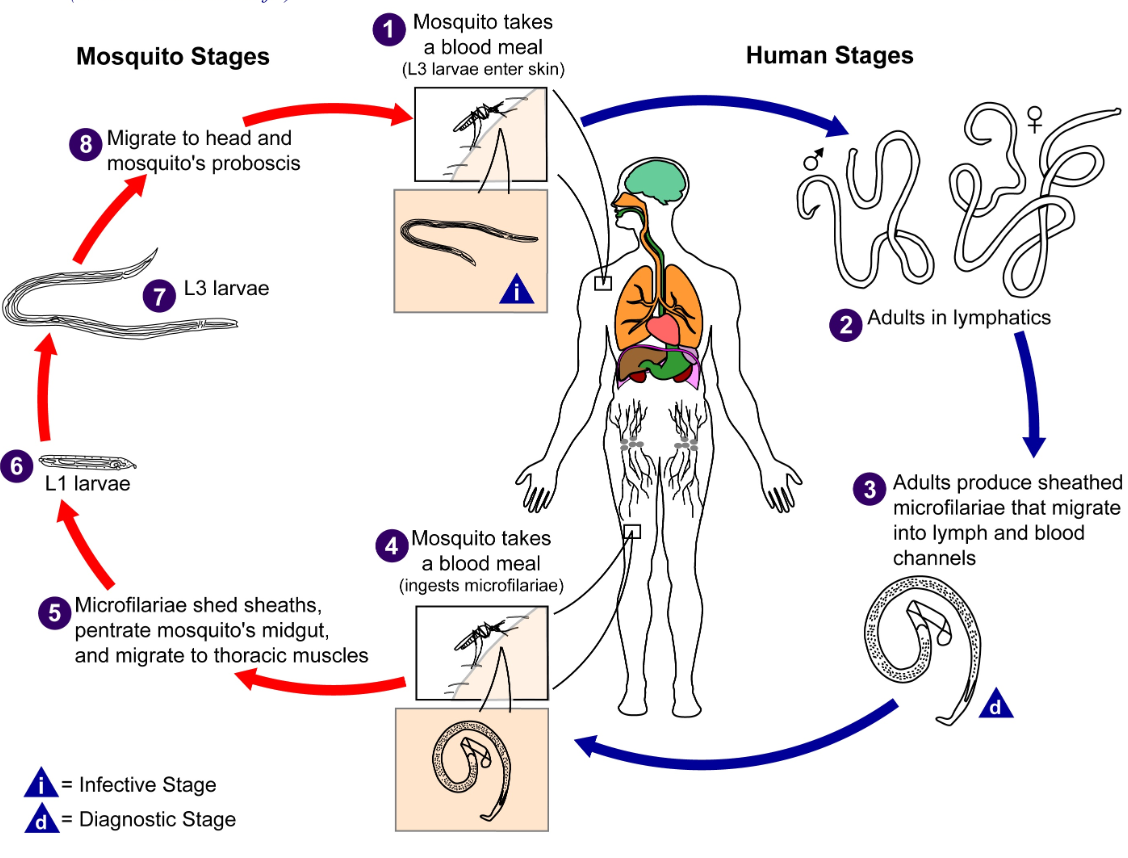
Wuchereria bancrofti
Delve into a detailed study on Wuchereria bancrofti, a parasitic nematode causing lymphatic filariasis. Explore its morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations such as elephantiasis. Gain insights into this debilitating disease to enhance treatment and prevention strategies.
-
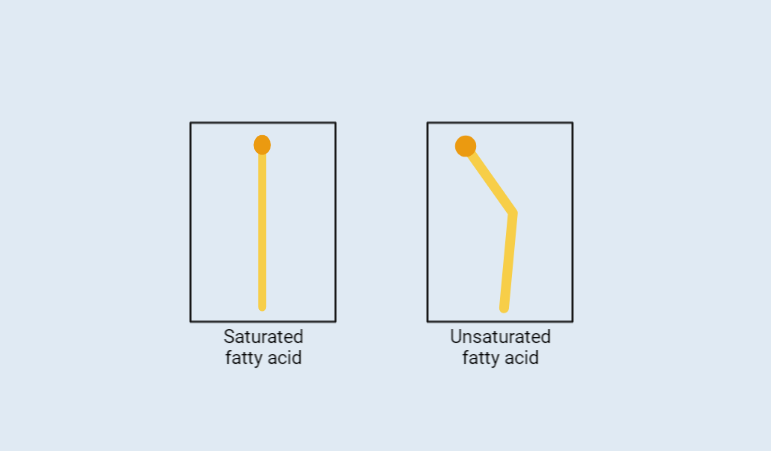

Saturated vs Unsaturated Fatty Acids
This excerpt compares saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, highlighting their differences in physical state, melting point, double bonds, stability, and their effects on cholesterol, heart diseases, diabetes, obesity, cancer, and other health risks. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed dietary choices and maintaining overall well-being.
-
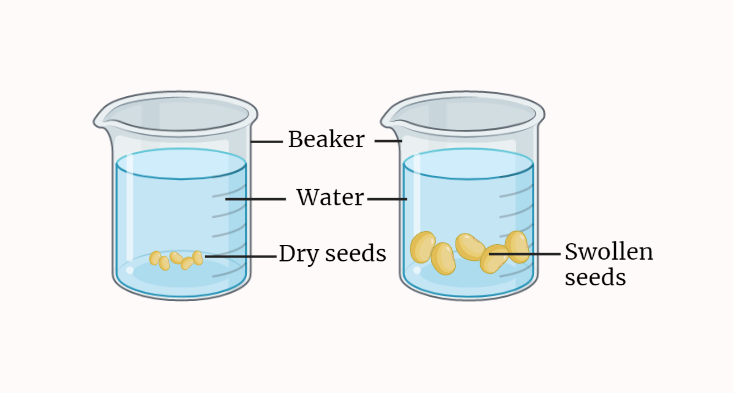
Imbibition
Imbibition is a fascinating process observed in both plants and materials science. It involves the absorption of liquid by solids, resulting in interesting phenomena such as seed germination, polymer swelling, and capillary action. Understanding imbibition provides insights into various natural and synthetic systems, contributing to advancements in agriculture, materials engineering, and more.
-
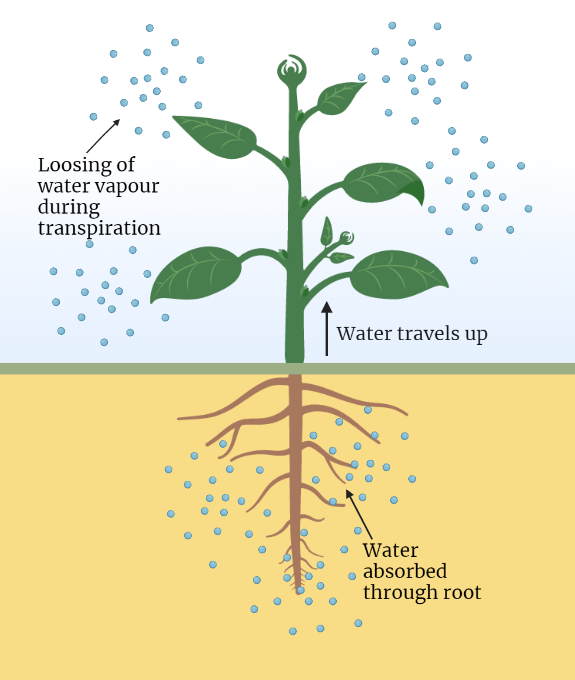
Transpiration
In this chapter, we delve into the fascinating world of transpiration in plants. We explore the intricate mechanism behind this process, including the role of stomata and the water cycle. Discover how plants adapt to various environmental factors and examine the contrasting strategies of xerophytes and hydrophytes. Gain insight into the ecological impact of transpiration…
-

Facilitated Diffusion
Discover the intricacies of facilitated diffusion, a vital mechanism that allows specific molecules to cross cell membranes with the help of specialized proteins. Explore the principles, proteins involved, and examples of this selective transport process. Gain insights into how facilitated diffusion contributes to cellular homeostasis and essential molecule transport.
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




