-
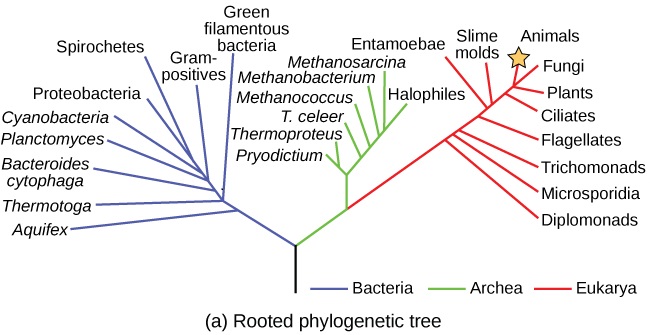
Evolution of viruses
Introduction Origination of Viruses Viral Genomes Recent Discoveries Conclusion
-
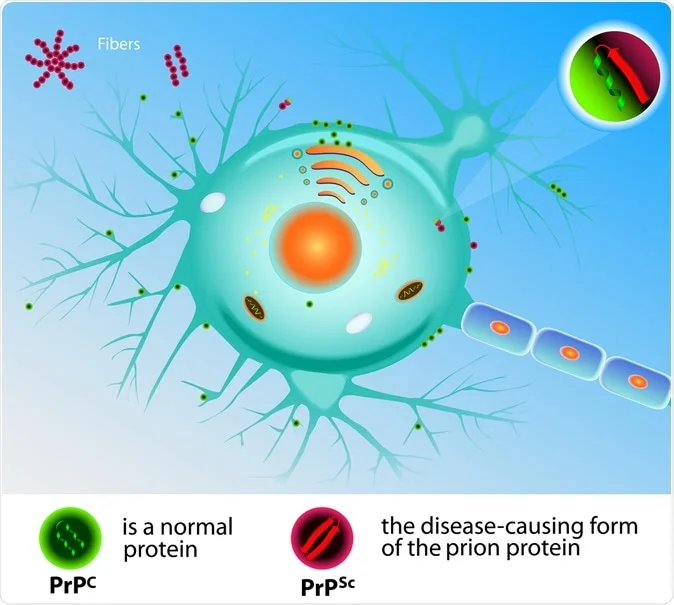
Viroids and Prions
I. Introduction II. Viroids III. Prions IV. Prion Mechanism of Infection V. Conclusion
-
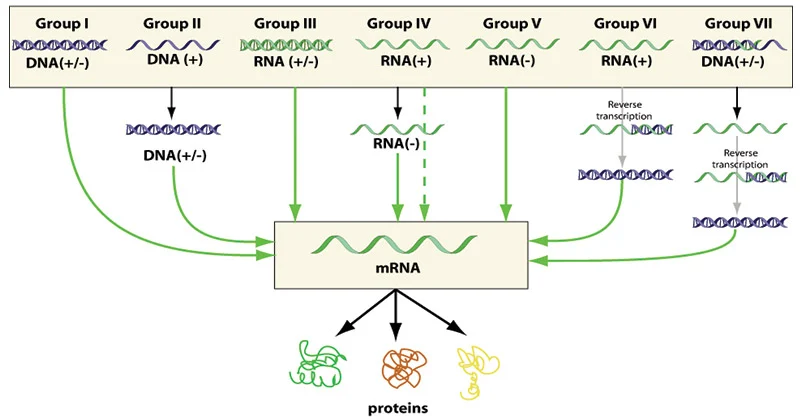
RNA Viruses
Introduction Class IV RNA Viruses Class V RNA Viruses Retroviruses (Class VI) The Replicative Cycle of HIV Conclusion In conclusion, RNA viruses that infect animals have a variety of RNA genomes, each with its own unique replicative cycle. From simple replicative cycles in class IV viruses to the complex replicative cycle of retroviruses, RNA viruses…
-
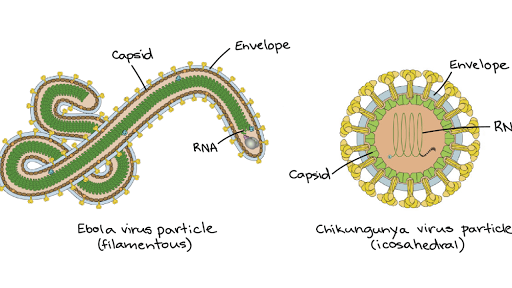
Replicative Cycles of Animal Viruses
Introduction Viral Envelopes RNA as Genetic Material
-
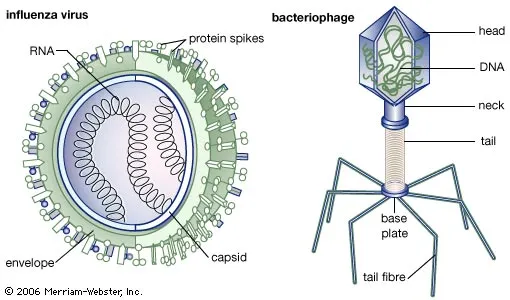
Discovery of Viruses
Introduction: Early Observations: Discovery of Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV): Discovery of Other Plant Viruses: Discovery of Animal Viruses: Discovery of Human Viruses: Conclusion:
-
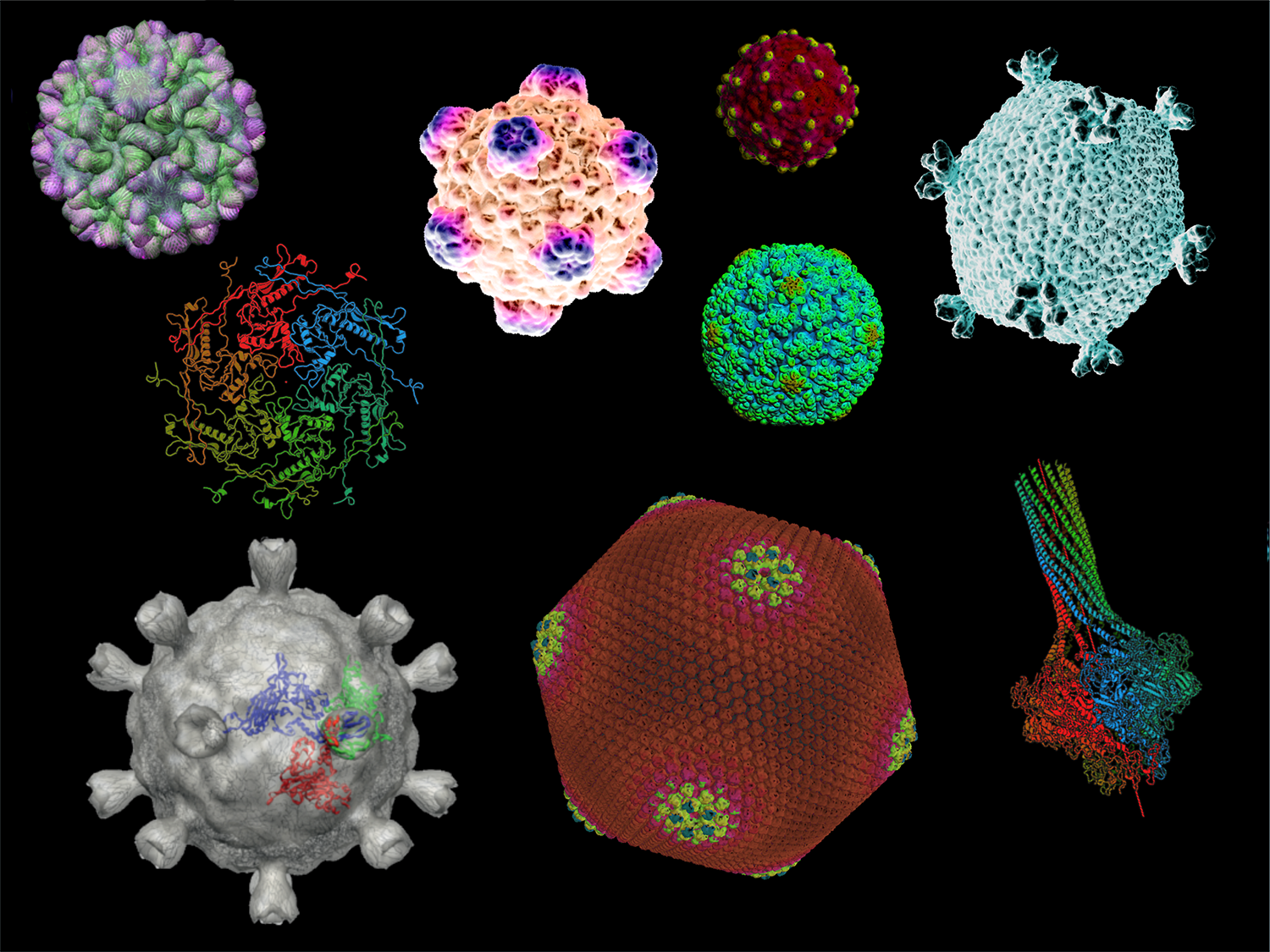
Structure of Viruses
Introduction Viral Genomes Capsids and Envelopes Conclusion
-
Ciliary Locomotion in Paramoecium
Embark on a journey into the intricate world of ciliary locomotion in Paramoecium, where tiny hair-like cilia orchestrate remarkable movements. Explore the molecular choreography driven by dynein motor proteins, propelling this single-celled wonder through water. Delve into the “9+2” microtubule arrangement, unveiling the metachronal wave phenomenon. Witness cilia’s multifaceted role – from aquatic navigation to…
-
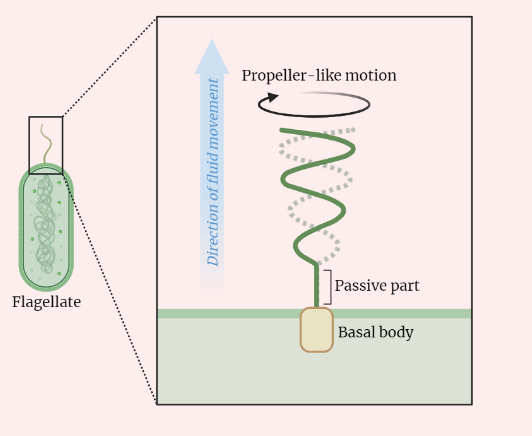
Flagellar movement
Embark on a journey into the world of flagellar movement, where whip-like flagella orchestrate cellular dynamics. Traverse the intricate structure of microtubules, unravel the motor proteins propelling these movements, and decode the biochemical signals triggering their activation. From sperm’s voyage through the female reproductive tract to bacteria’s quest for sustenance, discover how flagella’s synchronized beats…
-
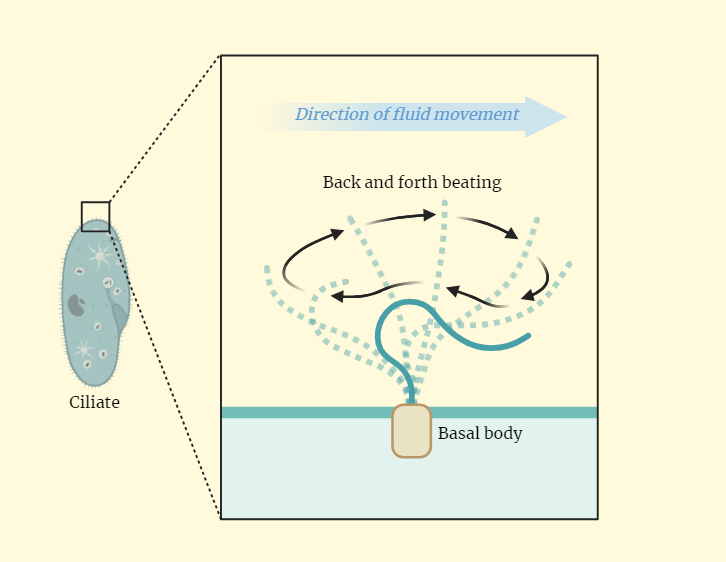
Ciliary movement
Discover the intricate world of ciliary movement—a remarkable process driven by tiny hair-like structures called cilia. From their structural composition to their role in propelling cells, fluids, and particles, delve into the mechanisms underpinning this fascinating phenomenon. Explore how cilia’s coordinated motion aids in functions like mucociliary clearance in the respiratory tract, fluid transport in…
-
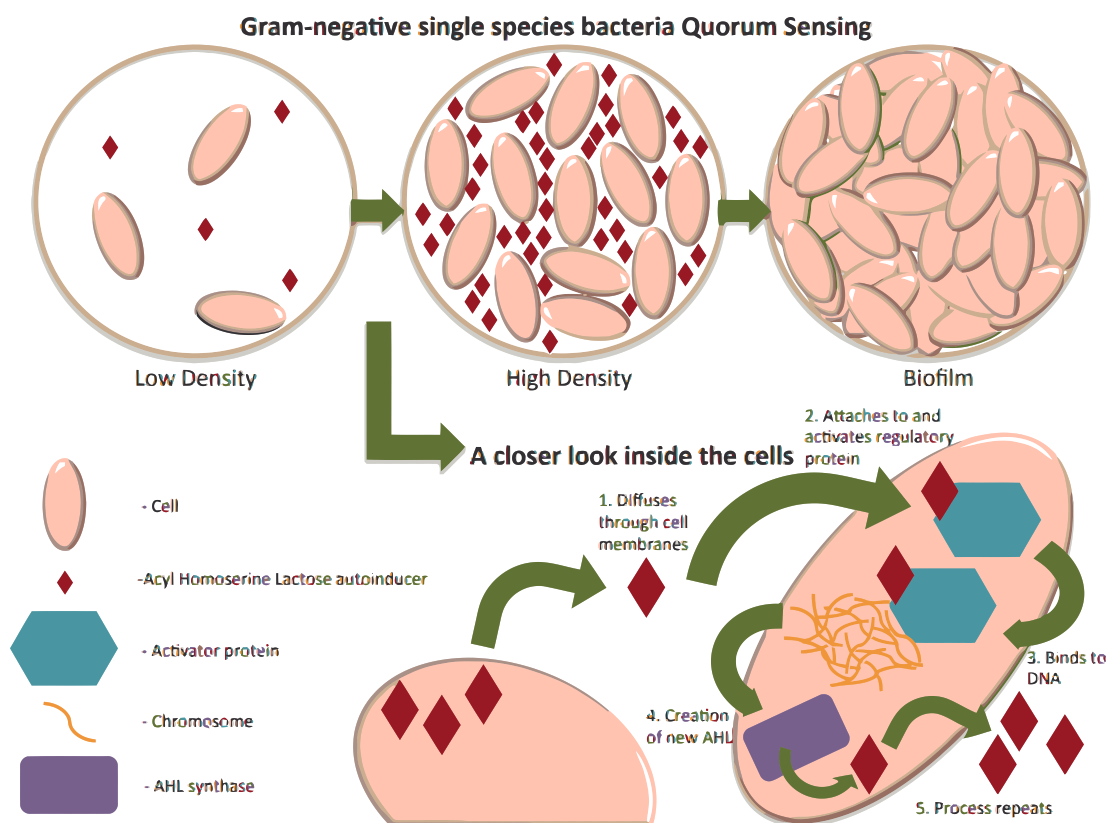
Quorum Sensing
Quorum sensing is a fascinating process that allows bacteria to communicate with each other, coordinate their behavior, and respond to changes in population density. This communication is mediated by small signaling molecules known as autoinducers, which are produced, detected, and responded to by bacterial cells. Quorum sensing plays a critical role in regulating a wide…
-
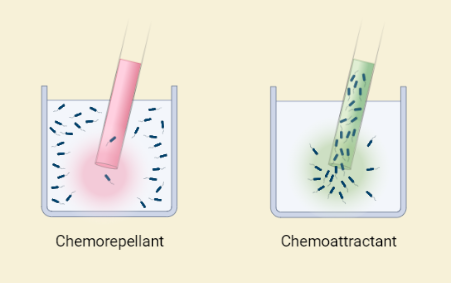
Bacterial Chemotaxis
This article provides an in-depth study of bacterial chemotaxis, which is the ability of bacteria to sense and respond to chemical gradients in their environment. The article discusses the chemotaxis mechanisms, including receptors, signal transduction, the flagellar motor, and adaptation mechanisms, along with their significance for bacterial survival and adaptation to different environments. The article…
-
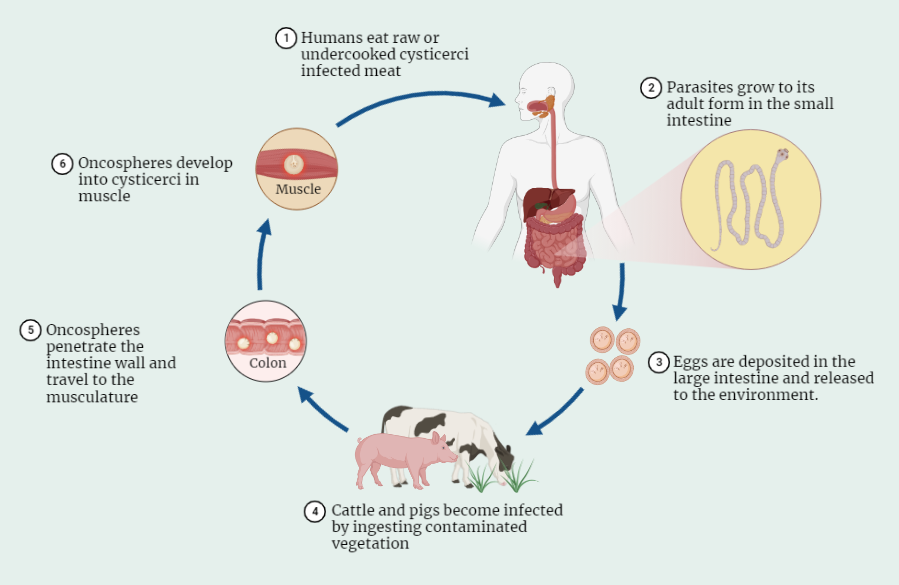
Taenia solium
Embark on a detailed study of Taenia solium, the pork tapeworm, and its impact on human health. Explore its morphology, complex life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations. Gain insights into effective treatments and preventive measures against this parasitic infection.
-
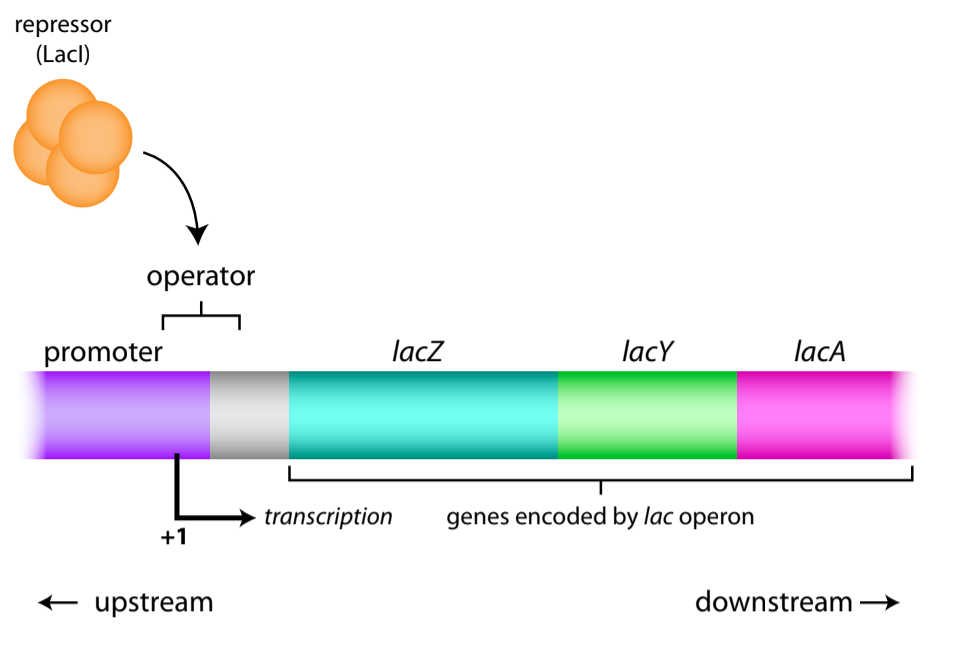
Lac Operon- Gene Regulation in Bacteria
The lac operon, found in E. coli bacteria, is a remarkable genetic system that controls the metabolism of lactose, a sugar commonly present in milk. This operon comprises three crucial structural genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA, responsible for encoding the essential enzymes needed to break down lactose into glucose and galactose. Its significance in the…
-
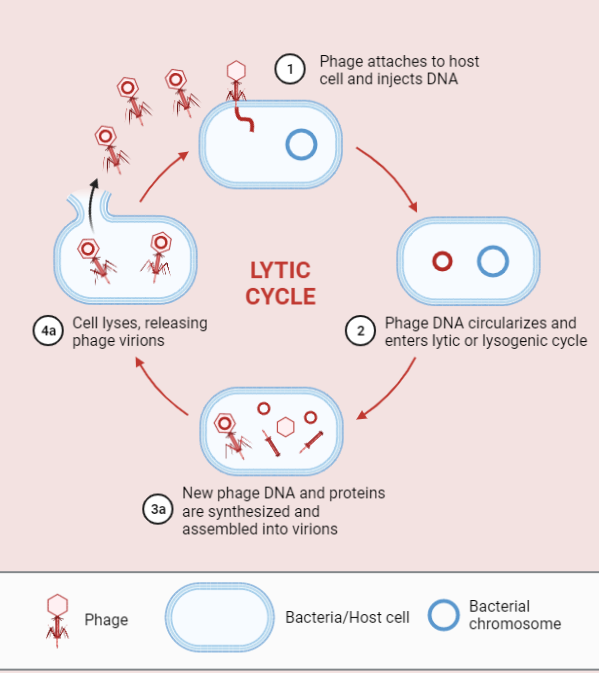
Lytic Cycle
The lytic cycle is a process used by certain viruses to reproduce and spread. It involves the virus infecting a host cell, using the host’s cellular machinery to replicate itself, and causing the host cell to lyse or burst, releasing new viral particles. This cycle can cause significant damage to the host cells and tissues,…
-
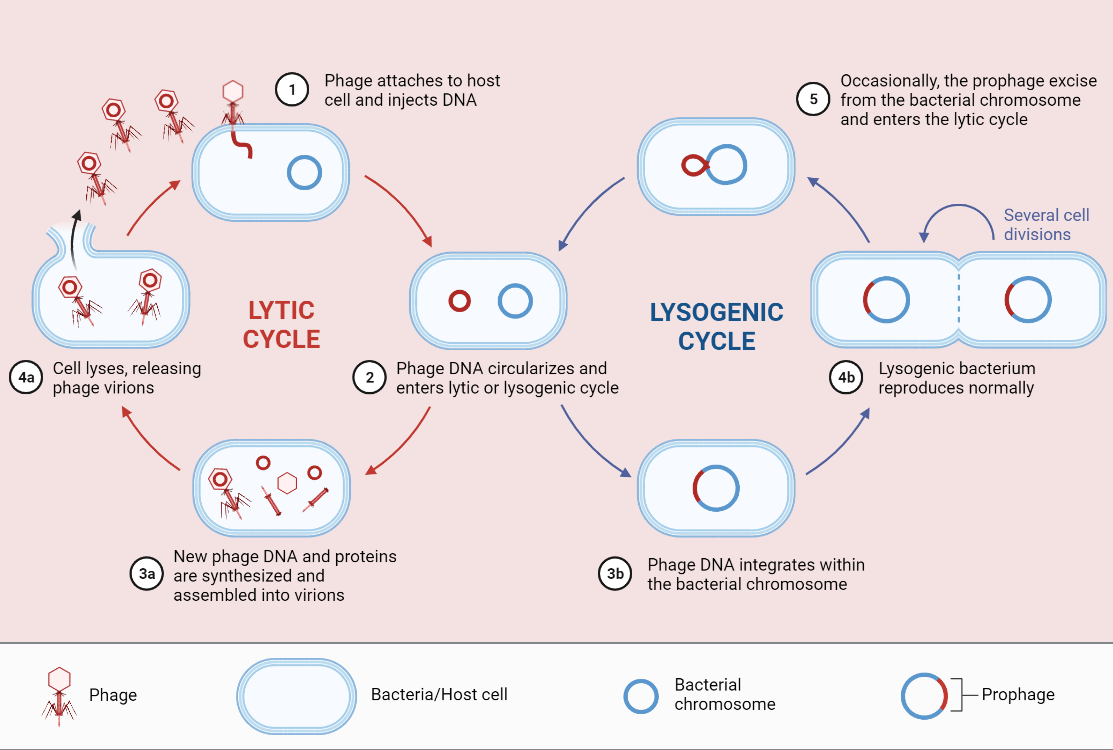
Lysogenic Cycle
The lysogenic cycle is a reproductive cycle used by certain viruses to infect and replicate within a host cell. During this cycle, the virus inserts its genetic material into the host cell’s DNA, becoming a dormant or latent infection. This period of dormancy allows the virus to evade the host immune response and persist within…
-
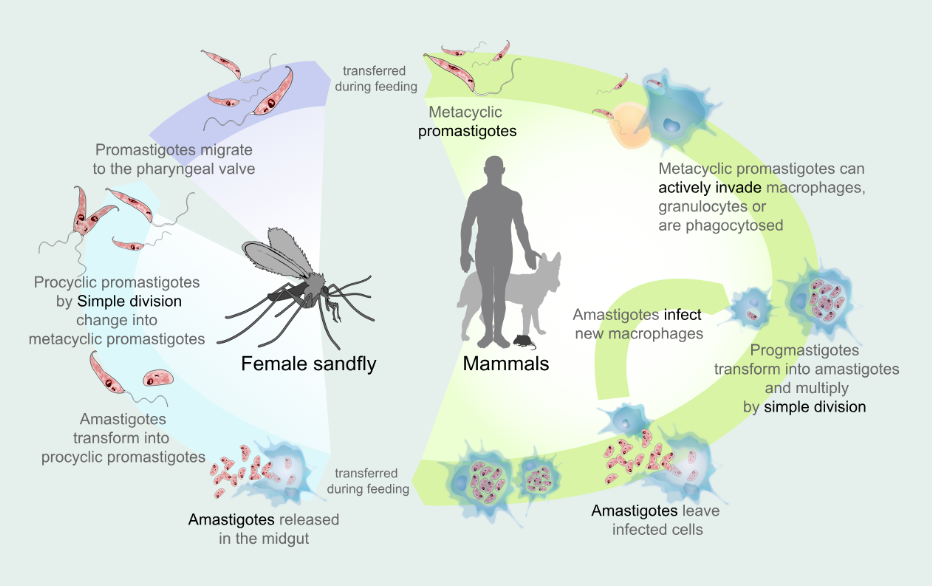
Leishmania donovani
Leishmania donovani is a parasitic protozoan responsible for visceral leishmaniasis, a severe and deadly disease. Explore its morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations in this comprehensive study. Understanding this parasite is crucial for effective treatment and prevention strategies.
-
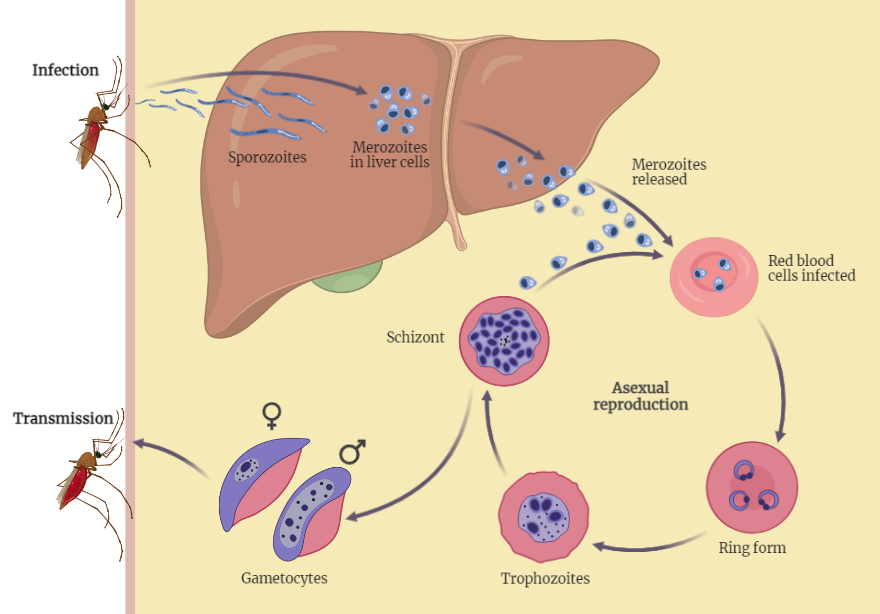
Plasmodium falciparum
Dive into a detailed study on Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest malaria parasite. Explore its morphology, complex life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations. Gain insights into this global health threat to enhance treatment and prevention strategies.
-
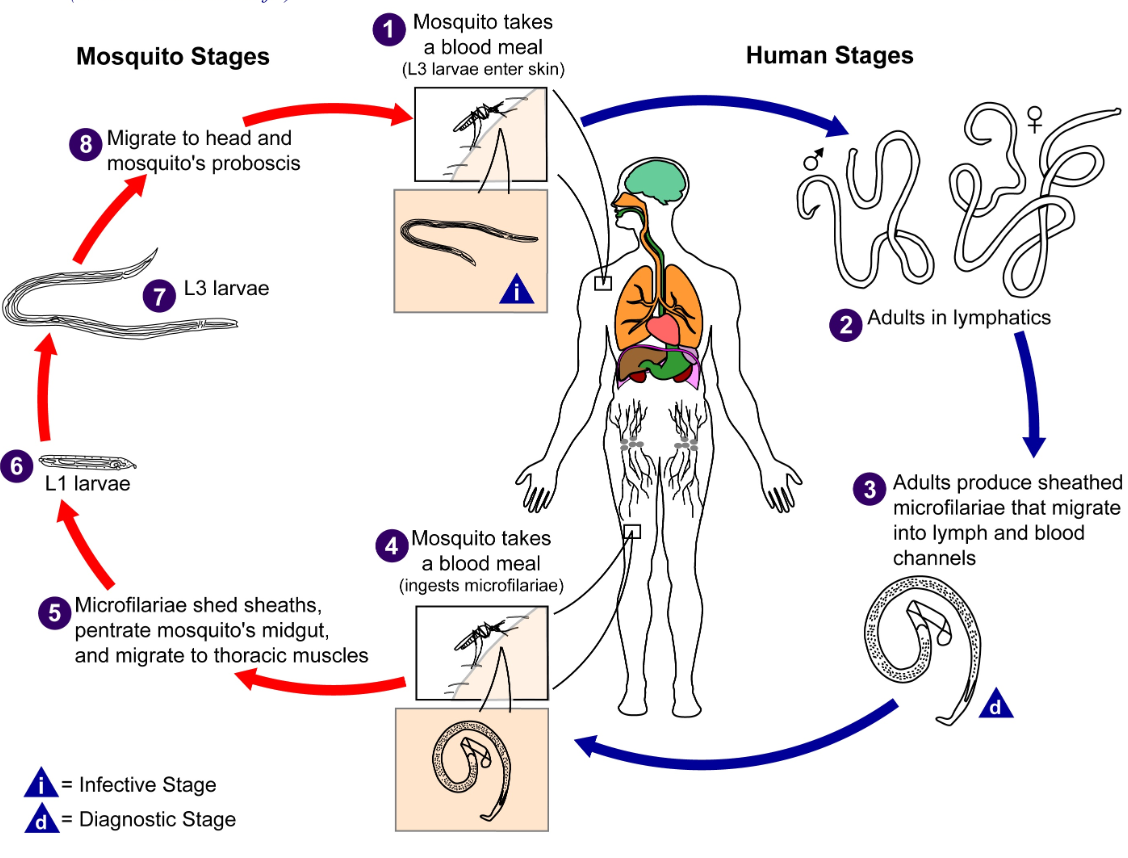
Wuchereria bancrofti
Delve into a detailed study on Wuchereria bancrofti, a parasitic nematode causing lymphatic filariasis. Explore its morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations such as elephantiasis. Gain insights into this debilitating disease to enhance treatment and prevention strategies.
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




