-
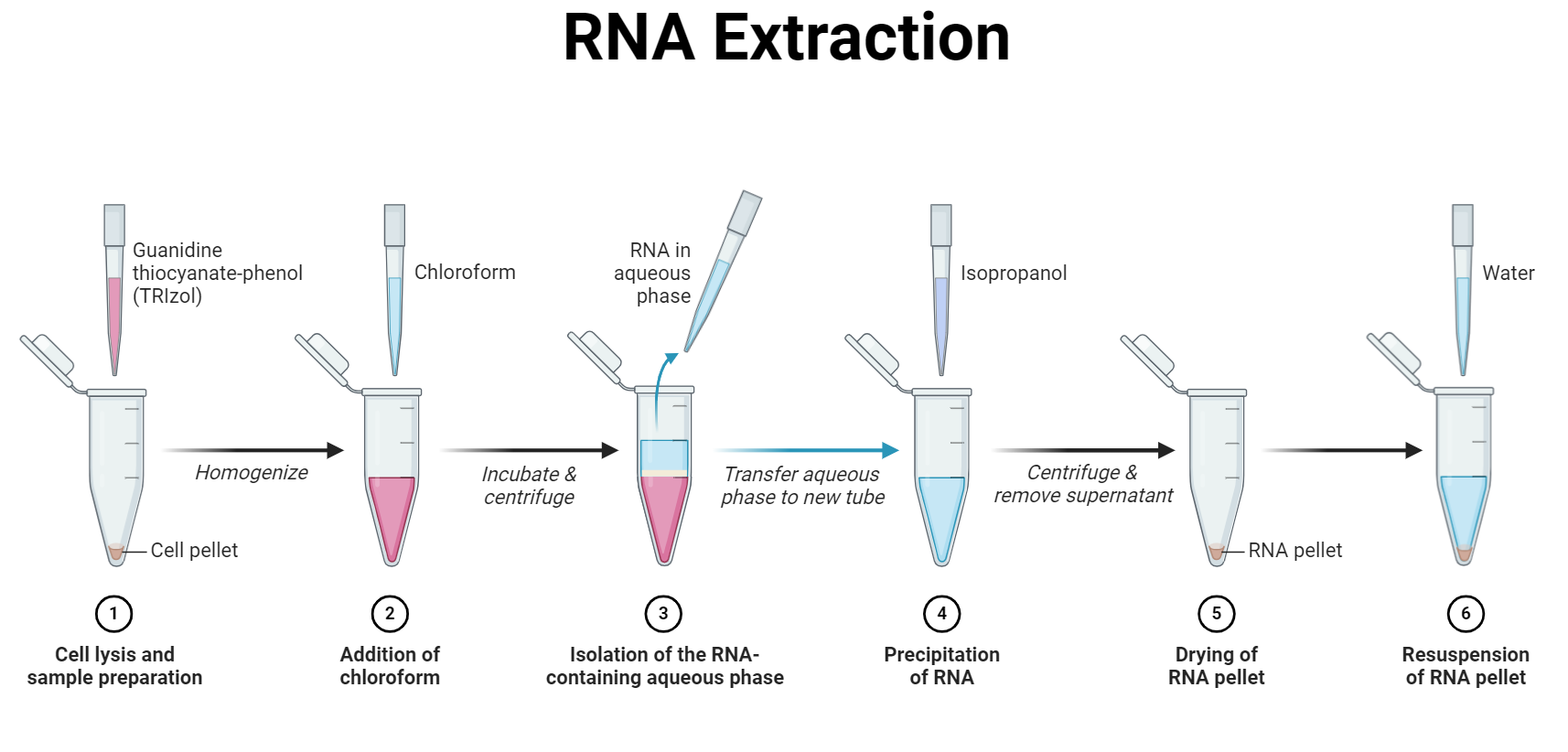
Isolation and Purification of RNA
Pure RNA isolation is essential in molecular biology for gene expression studies and downstream analyses. There are two main strategies: total RNA isolation and mRNA isolation, with total RNA isolation being less laborious. Methods include phenol-chloroform extraction, spin column purification, and magnetic bead-based methods, each having unique advantages. Choose based on sample specifics.
-
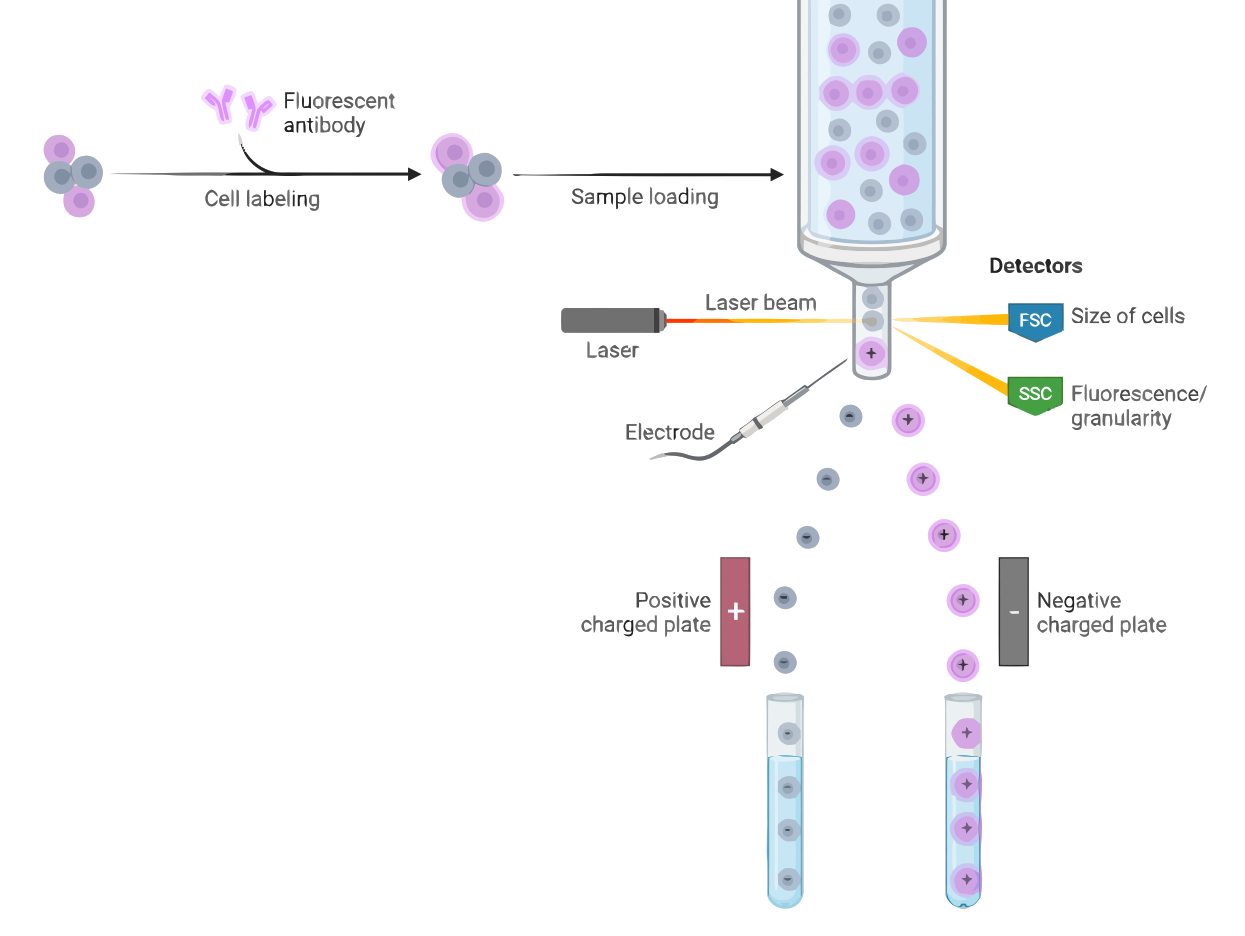
Fluorescence-activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) is a powerful technique used to separate and purify cells or particles based on their fluorescence properties. By using fluorescently-labeled probes that bind to specific cellular or particle markers, such as proteins or nucleic acids, the FACS system measures the fluorescence of each individual cell or particle, allowing for identification and…
-
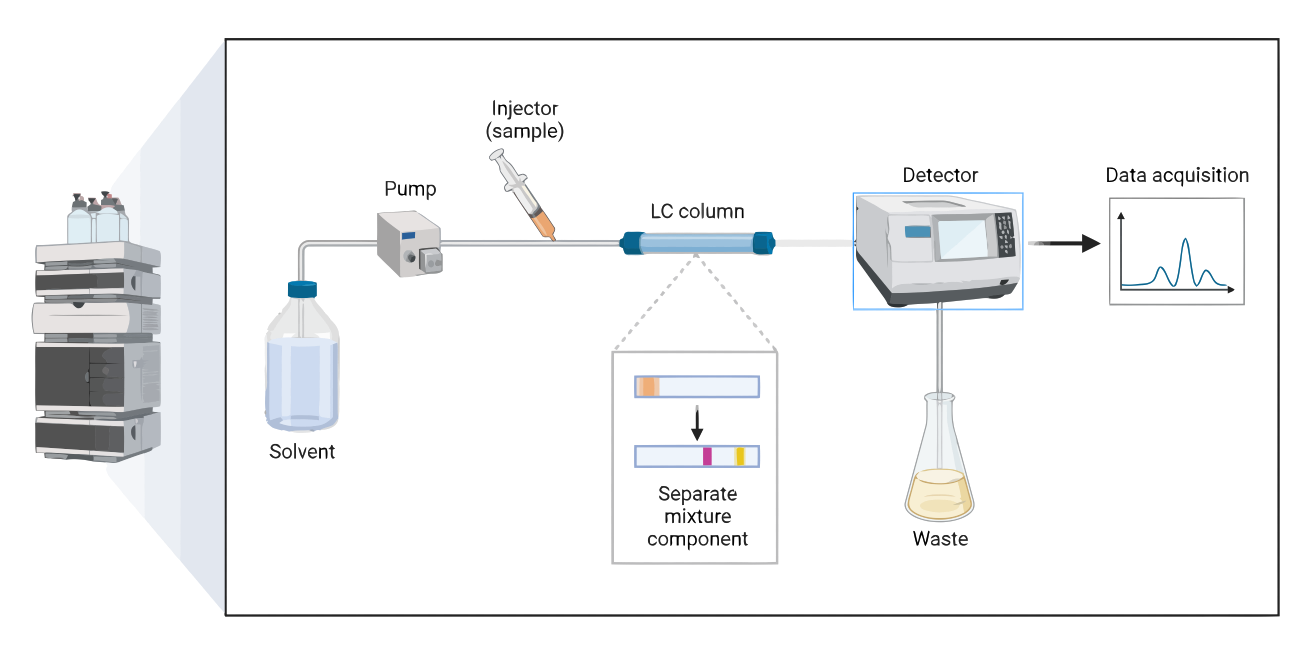
Liquid Chromatography
Liquid chromatography (LC) is a powerful separation technique used in many fields of science, including biology. LC separates a mixture of compounds by passing it through a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The compounds in the mixture interact differently with the two phases, leading to their separation based on their relative affinities for each…
-
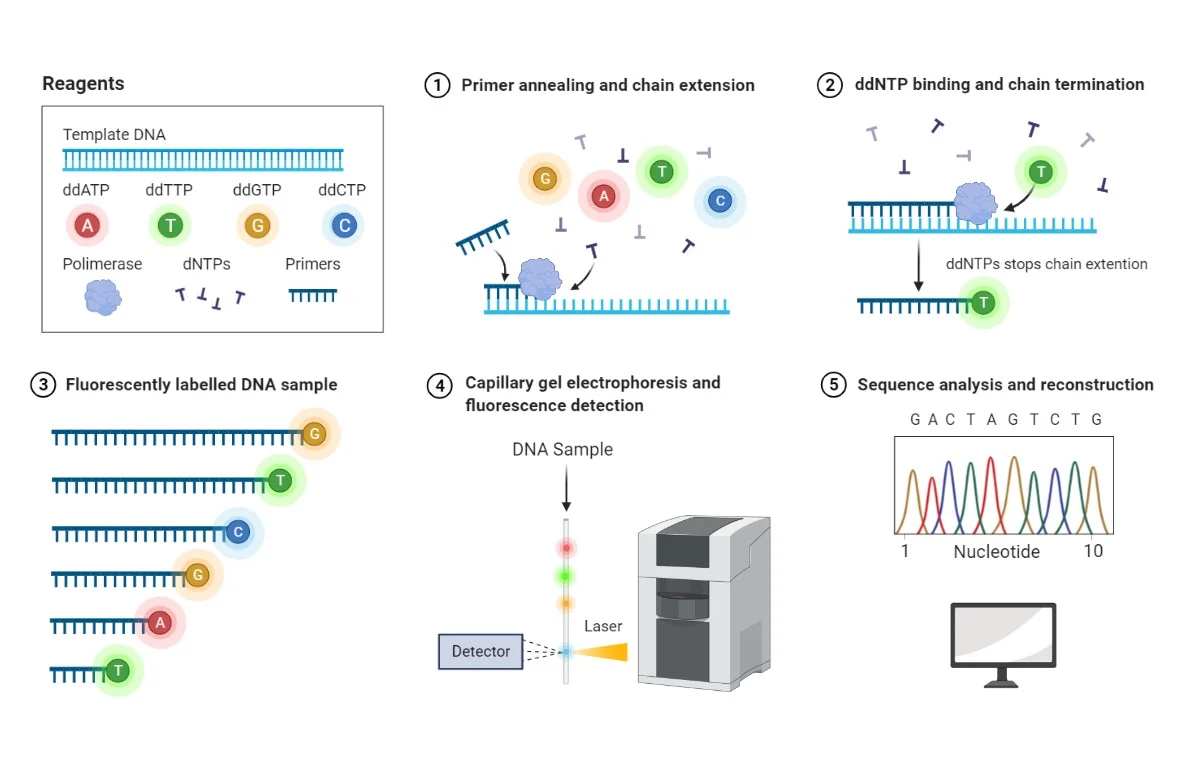
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Introduction: Illumina Sequencing: Roche 454 Sequencing: Ion Torrent Sequencing: Workflow: Applications: Conclusion:
-
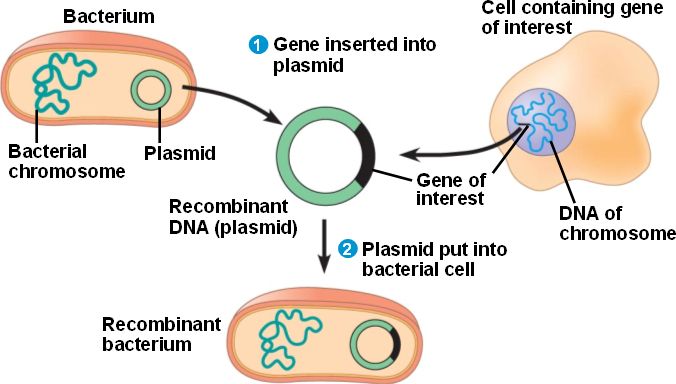
DNA Cloning
Introduction: Restriction Enzyme Cloning: PCR Cloning: Gene Synthesis: Conclusion:
-
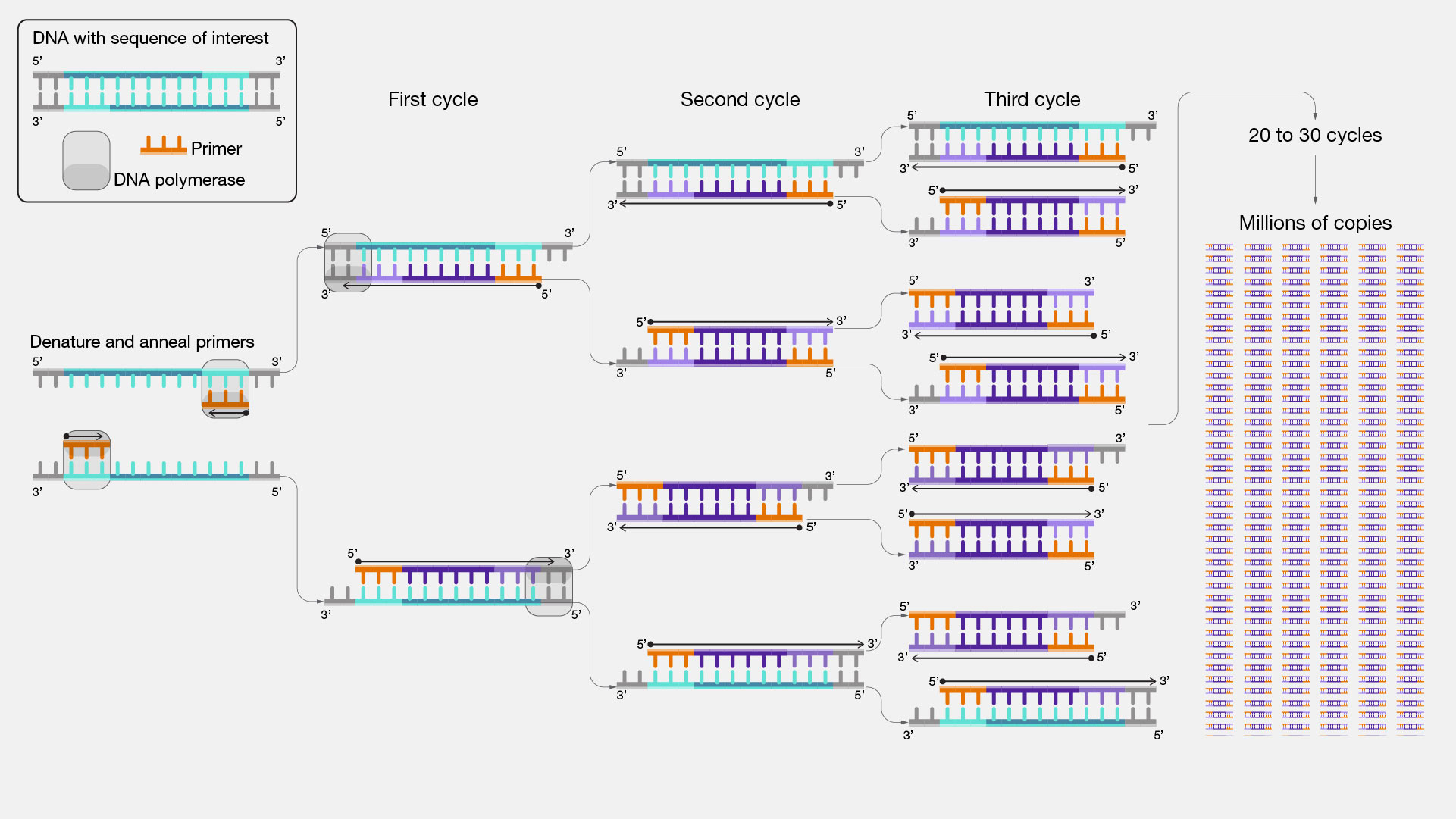
Steps of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
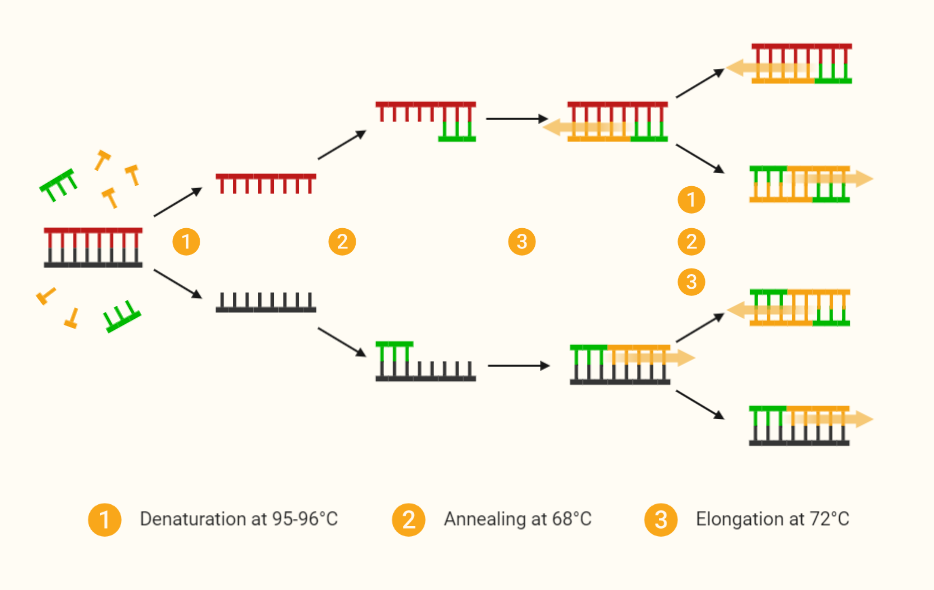
Introduction Principles of PCR Reagents and Equipment used in PCR Applications of PCR Conclusion
-
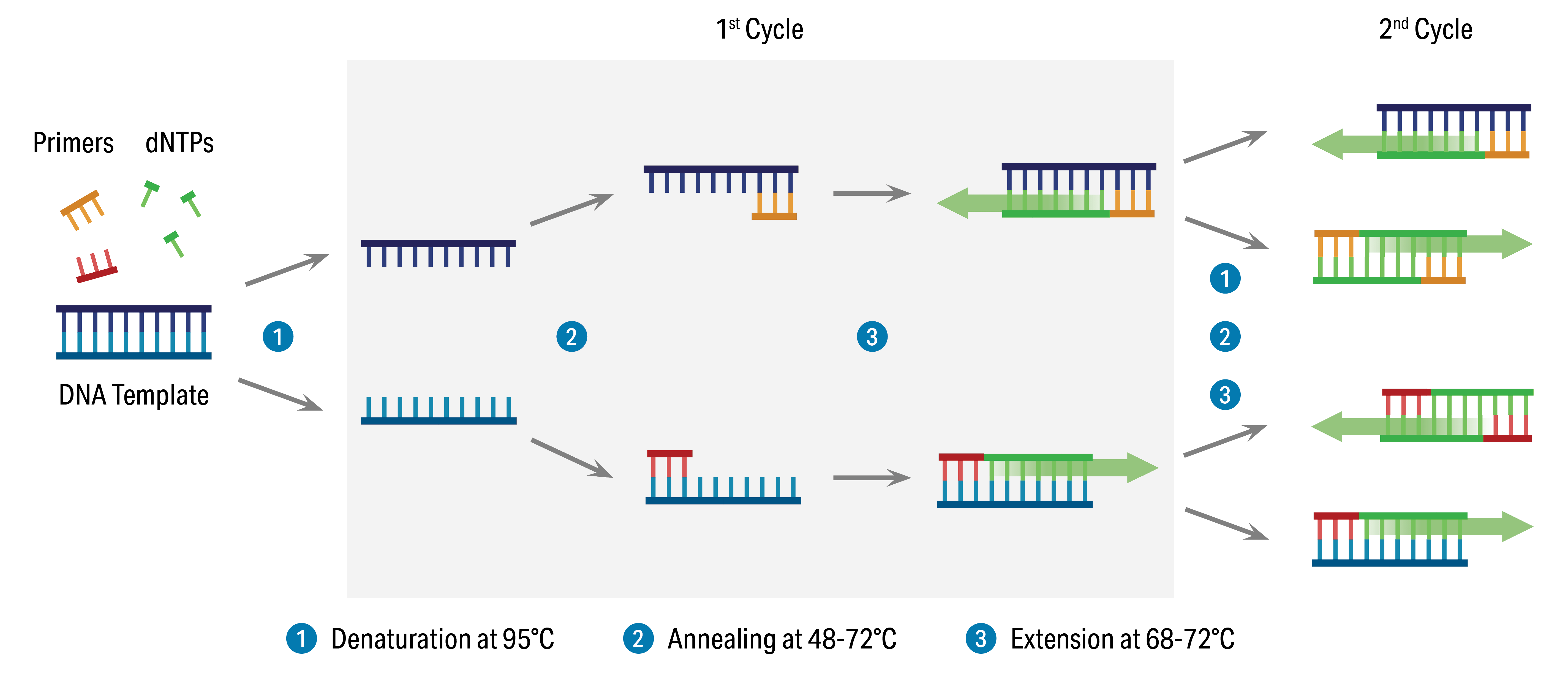
Real-Time PCR
Introduction: Real-Time PCR is a powerful and versatile tool used in molecular biology to quantify the amount of specific DNA or RNA in a sample. This technique enables quantification of nucleic acids in real-time by monitoring the accumulation of fluorescence generated during the extension phase of the PCR reaction. Principle: Real-Time PCR is based on…
-
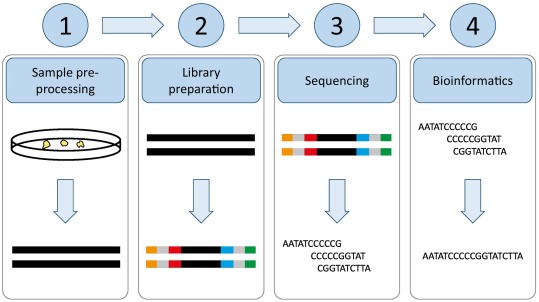
The Steps of Next-Generation Sequencing
Introduction: Steps: Sample Preparation: Library Preparation: Sequencing: Data Analysis: Conclusion:
-
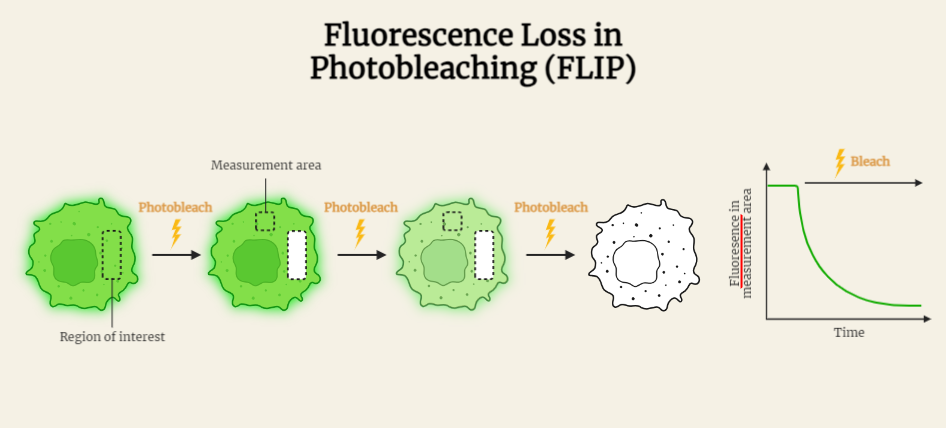
FLIP (Fluorescence Loss in Photobleaching)
Discover the power of Fluorescence Loss in Photobleaching (FLIP), a technique used to investigate molecular dynamics within cells. Explore its applications in protein and membrane dynamics, protein-protein interactions, intracellular transport, and subcellular compartmentalization. FLIP provides valuable spatial and temporal information, allowing researchers to study biological processes in their natural state. Embrace the versatility of FLIP…
-
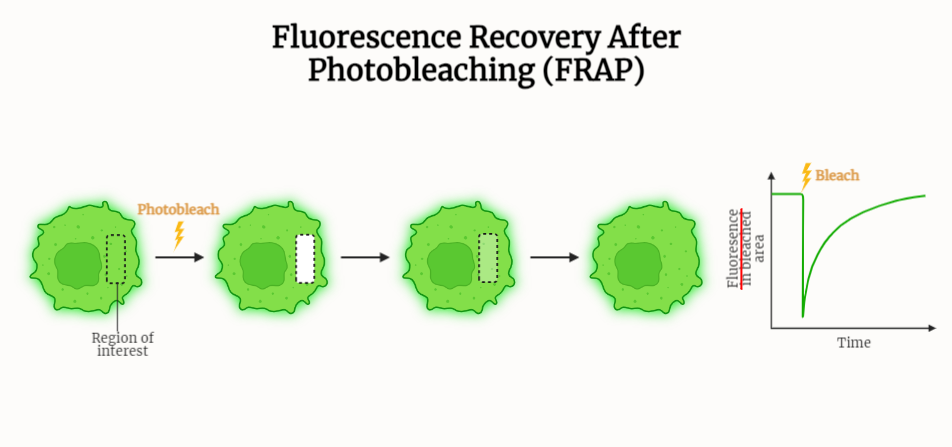
FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching)
Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) is a powerful technique widely employed in the study of biomolecules within biological systems. By selectively bleaching a small region of a sample and monitoring the subsequent fluorescence recovery, FRAP enables the investigation of molecular mobility. Its applications encompass protein dynamics, intracellular organelle movements, cytoskeleton organization, membrane dynamics, intracellular transport,…
-

Gene Therapy: A study note
Gene therapy is a groundbreaking medical approach that holds tremendous potential for revolutionizing disease treatment. By altering the genetic material within cells, gene therapy aims to correct abnormal genes or introduce therapeutic genes to combat a wide range of conditions. This study note provides a comprehensive overview of gene therapy, exploring its principles, techniques, applications,…
-
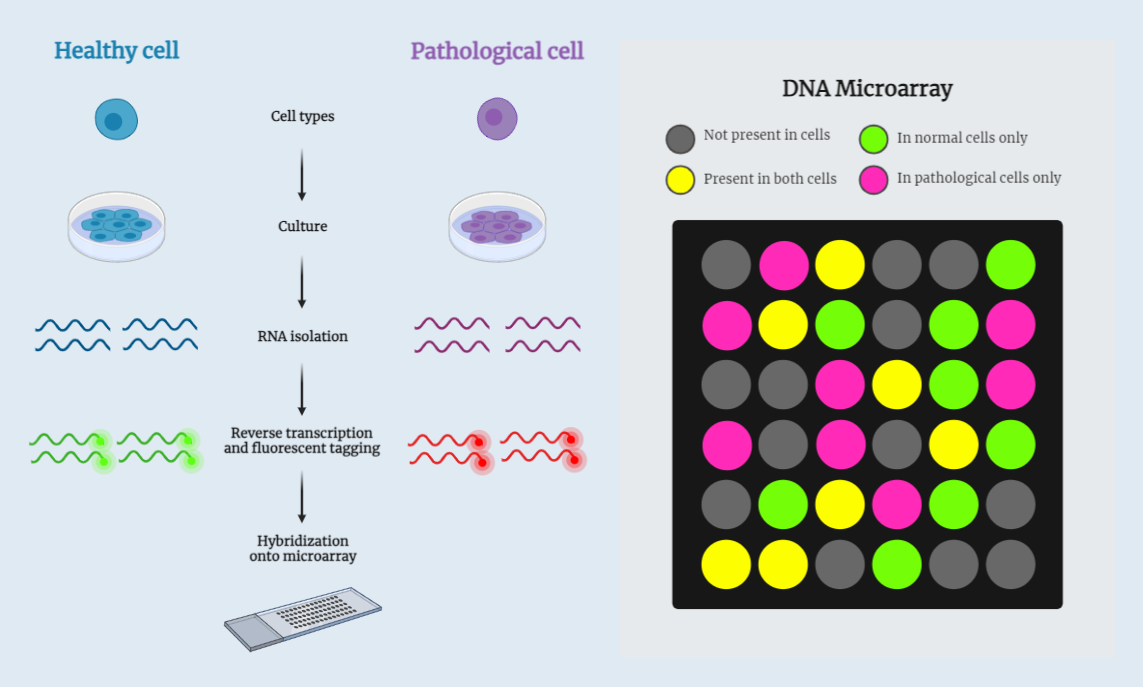
DNA Microarray Technique
DNA microarray is a powerful technique used to study gene expression levels in a high-throughput manner. It involves hybridizing labeled target sequences to DNA probes on a microarray, allowing researchers to detect and quantify specific nucleic acid sequences. This study note explores the principles, procedure, applications, and limitations of DNA microarray, highlighting its role in…
-
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique in molecular biology for separating and analyzing DNA, RNA, and proteins. It plays a crucial role in various applications such as DNA analysis, protein characterization, and clinical diagnostics. This study note provides an in-depth understanding of the principles, procedure, and applications of gel electrophoresis, making it a valuable…
-
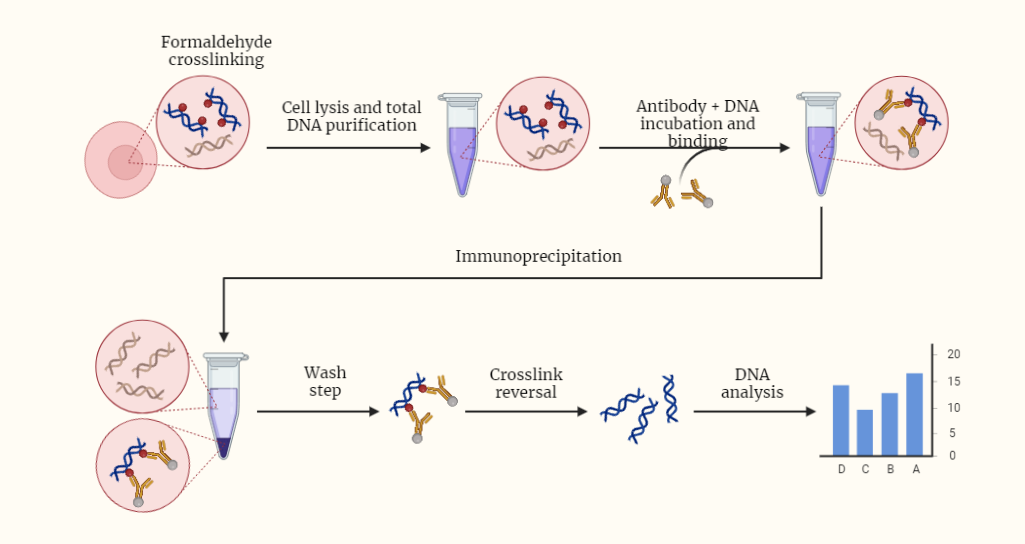
ChIP (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation)
ChIP (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation) is a powerful molecular biology technique used to study protein-DNA interactions in cells. This article explores the principles, procedure, applications, and limitations of ChIP, providing insights into its significance in gene expression regulation and chromatin structure. Discover how ChIP has revolutionized research in genetics, epigenetics, and cancer research, while also exploring newer…
-
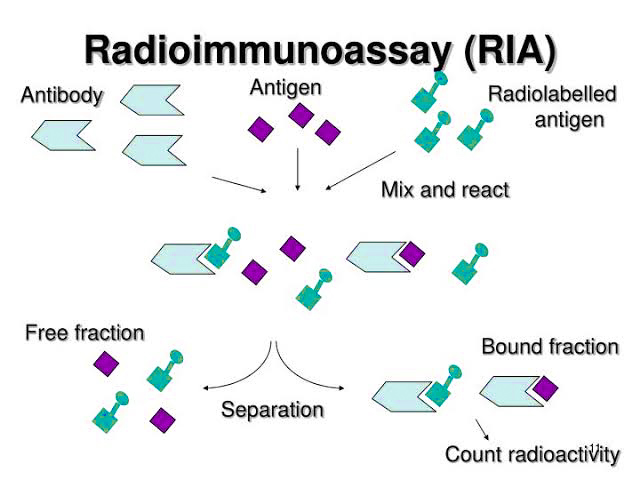
RIA (Radioimmunoassay)
Discover the powerful technique of Radioimmunoassay (RIA) used in immunological and biomedical research. Explore the principles, types, reagents, and procedure involved in RIA. Uncover the advantages of its sensitivity, specificity, and versatility, while acknowledging limitations such as radiation hazards. Delve into the wide-ranging applications of RIA in medical research, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. Embrace RIA…
-
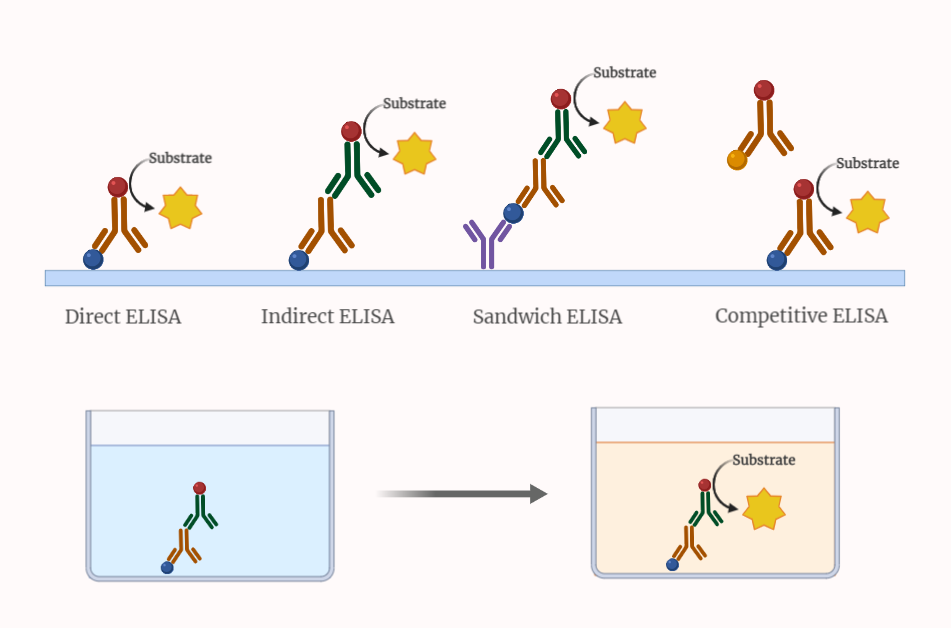
ELISA
ELISA, or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a widely used technique for detecting and quantifying proteins and antibodies in research and diagnostics. This excerpt provides an overview of ELISA, including its types, procedure, advantages, limitations, and applications in various fields. Explore the power of ELISA in protein and antibody detection for a wide range of scientific…
-

Spectroscopy and Beer-Lambert’s Law
Spectroscopy, a fascinating scientific technique, delves into the captivating interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation. By analyzing how substances interact with light at different wavelengths, spectroscopy provides crucial insights into the composition, structure, and behavior of materials. One of the fundamental principles in spectroscopy is the Beer-Lambert’s Law, a cornerstone in quantitative analysis. This law…
-

DNA Footprinting
The DNA footprinting technique is used to study the interactions between DNA and proteins. This allows researchers to identify which regions of DNA are bound by specific proteins and how they interact with DNA. DNA footprinting has various methods like chemical, thermal, and electrophoretic mobility shift assays, which are used to map protein-DNA interactions, study…
-
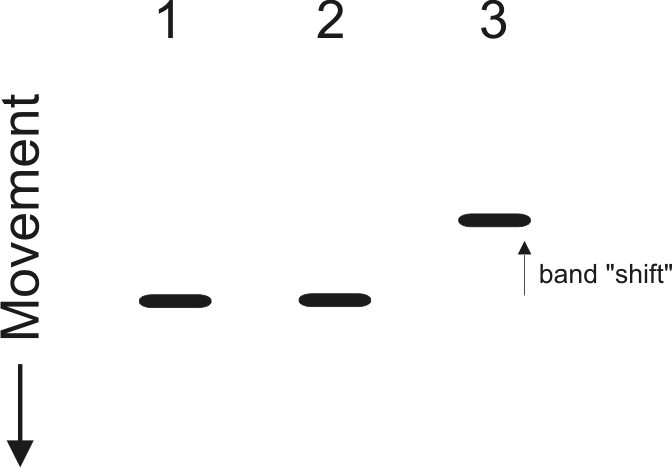
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay: EMSA
The text describes Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA), a molecular biology technique used to study protein-DNA interactions. EMSA is based on the principle that proteins can bind to specific regions of DNA and alter its conformation, affecting the mobility of the DNA in an electric field. This technique is used to study transcription regulation, DNA…
-
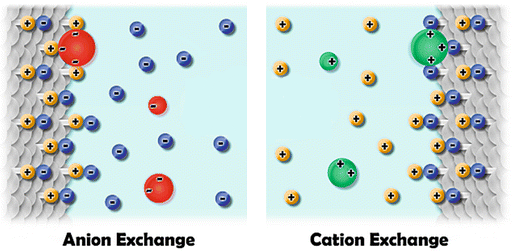
Ion Exchange Chromatography
Introduction Ion exchange chromatography (IEC) is a type of liquid chromatography that separates molecules based on their charge. It is a widely used technique in biochemistry and analytical chemistry for the purification and isolation of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules. Principles of Ion Exchange Chromatography IEC utilizes a stationary phase, which…
-
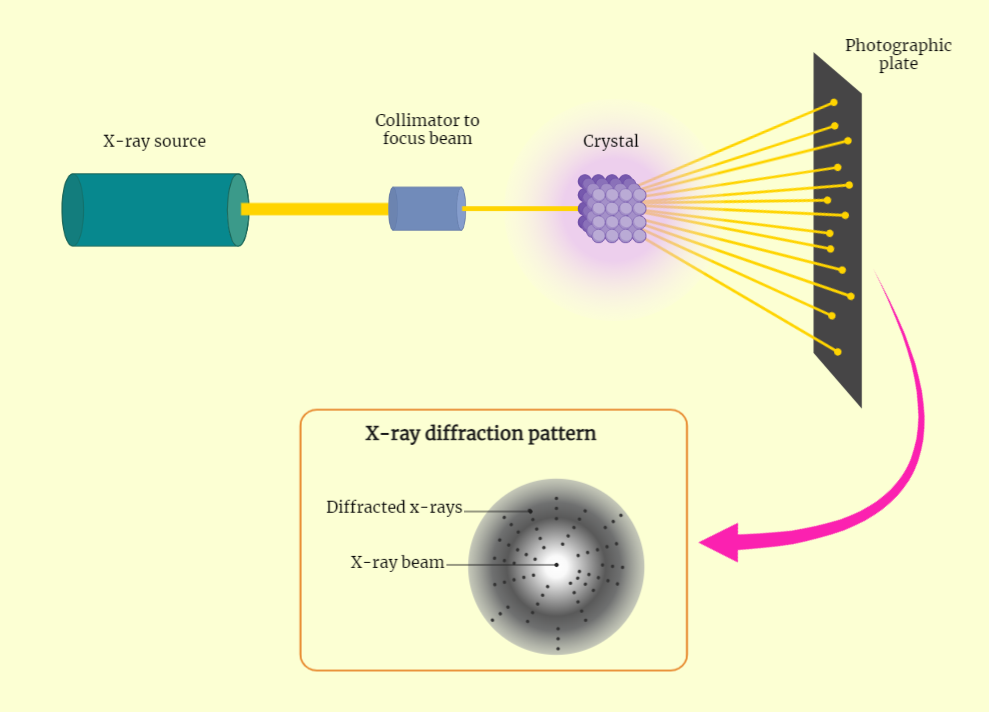
X-ray Diffraction Technique
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique is a powerful tool for studying the structure of crystalline materials. It works by shining X-rays on a crystalline material and detecting the diffracted X-rays on a detector, creating a pattern of diffraction peaks. The angle and intensity of these peaks can be used to determine the crystal structure, unit…
-
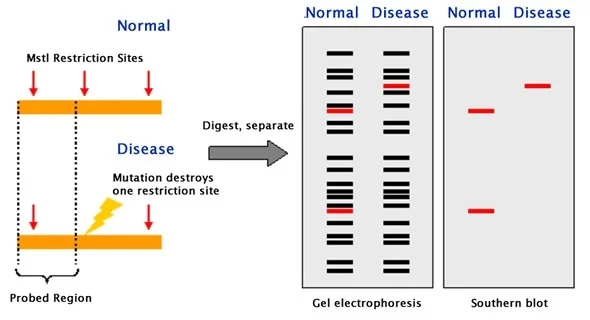
RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism)
The excerpt introduces RFLP, a molecular biology method for detecting DNA sequence variations. It explains the principle of restriction enzymes cutting specific DNA sequences and generating restriction fragments. The procedure involves DNA isolation, digestion, gel electrophoresis, and hybridization with labeled probes. RFLP’s applications span genetics, forensic science, and medical diagnostics. Despite its replacement by newer…
-
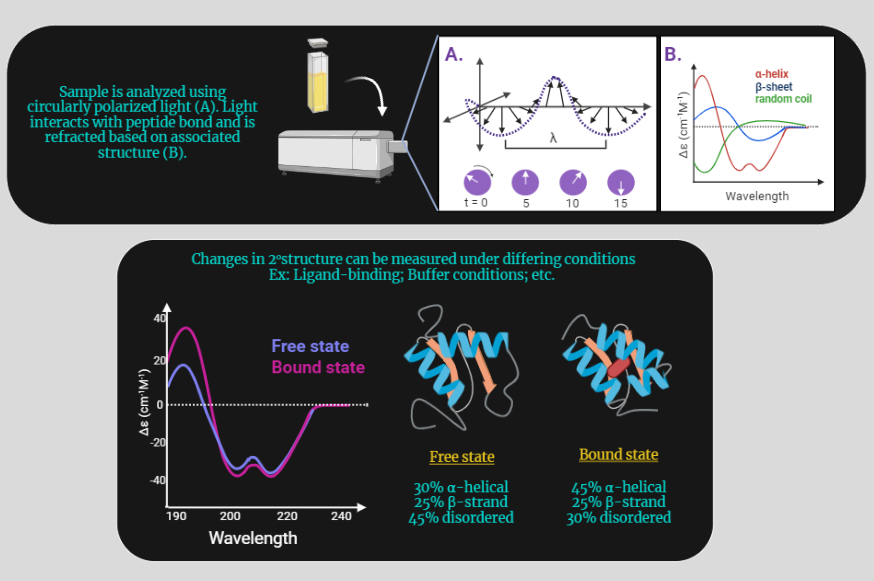
Circular Dichroism (CD) Technique
Circular dichroism (CD) is a powerful spectroscopic technique used to study the structure and properties of chiral molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. It is based on the differential absorption of left and right circularly polarized light by chiral molecules, which can provide information on their secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. In this…
-
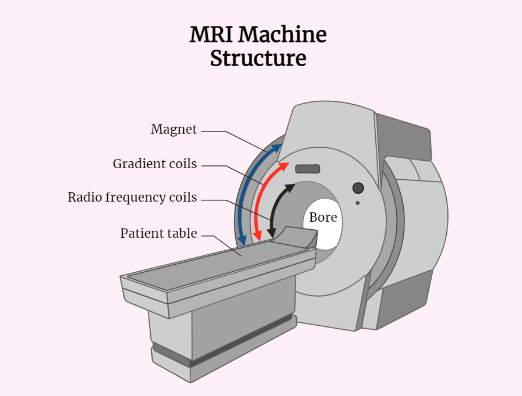
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that creates detailed images of the internal structures of the body using magnetic fields and radio waves. MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that provides high-quality images of soft tissues, organs, and bones without exposing patients to harmful radiation. The basic principle of MRI is to…
-
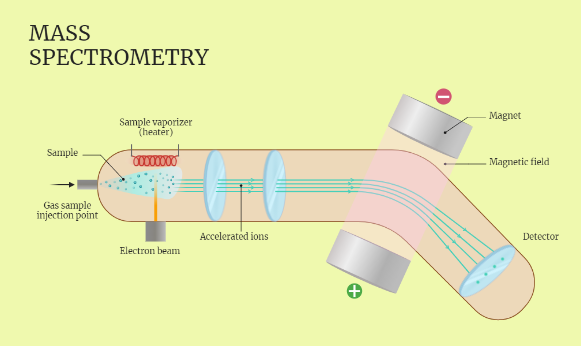
Mass Spectrometry (MS) Technique
The article discusses the principles, techniques, and applications of Mass Spectrometry (MS) from a biophysics perspective. It explains how MS is used to study the structure, dynamics, and interactions of biomolecules and how it can be applied to a wide range of biomolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and small molecules. The article also discusses…
-
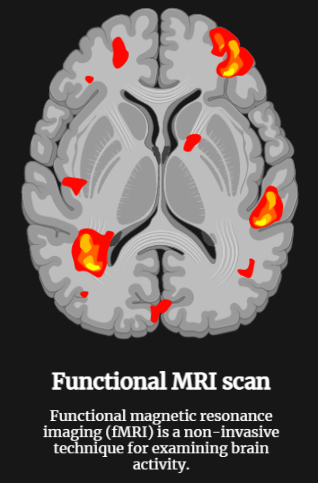
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is a powerful medical imaging technique used to study brain function. It measures changes in blood flow in the brain using MRI technology, which can be used to infer changes in neural activity. fMRI is commonly used in neuroscience, psychology, and psychiatry to investigate a wide range of questions related…
-

Restriction Endonucleases
Restriction endonucleases, the DNA-cutting enzymes, are indispensable in molecular biology research. Classified into four types based on recognition sites, Type II enzymes stand out as the most widely used. They cleave DNA at specific sequences, generating fragments with blunt or sticky ends. Despite their complexity, Type I and III enzymes have limited use due to…
-
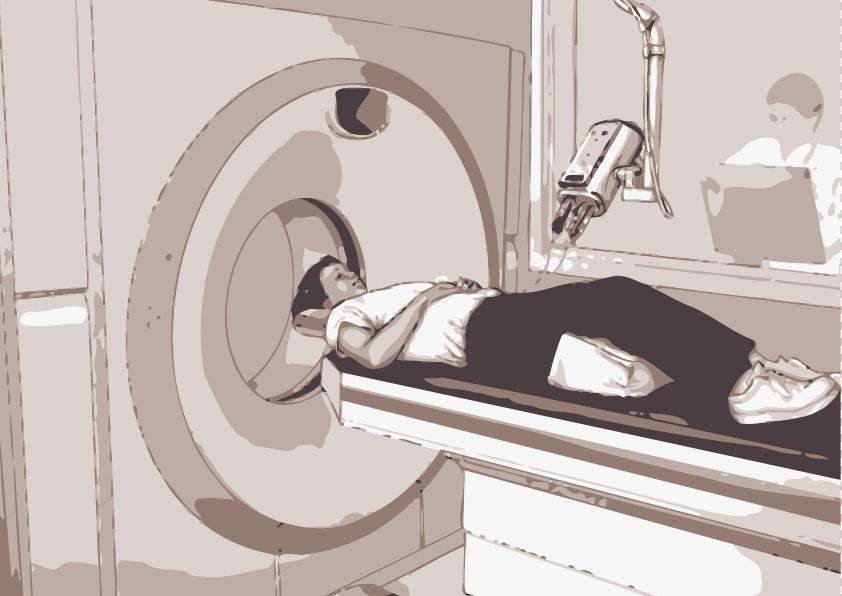
CT Scan Technique
CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a widely used medical imaging technique that produces detailed, cross-sectional images of the body using x-rays and computer technology. The technique uses x-ray detectors, reconstruction algorithms and dose management techniques to minimize the radiation dose to the patient while producing high-quality images. Specialized CT scans such as CT angiography, CT…
-
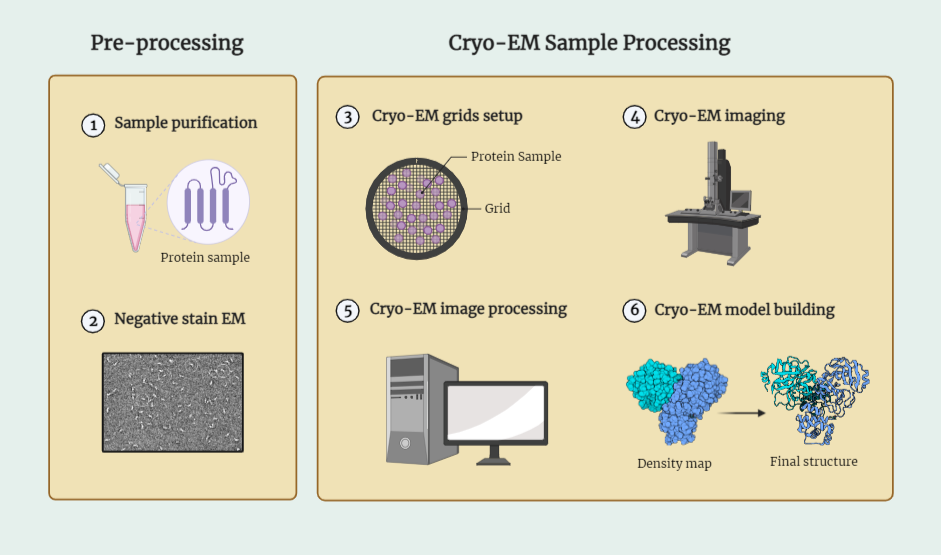
Cryo Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)
Cryo-EM is a cutting-edge imaging technique used for studying the structure of biological macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. By using a cryogenic electron microscope, researchers can capture high-resolution images of frozen, hydrated samples, preserving their native state and avoiding radiation damage. The sample preparation is a crucial step that involves rapid freezing of…
-
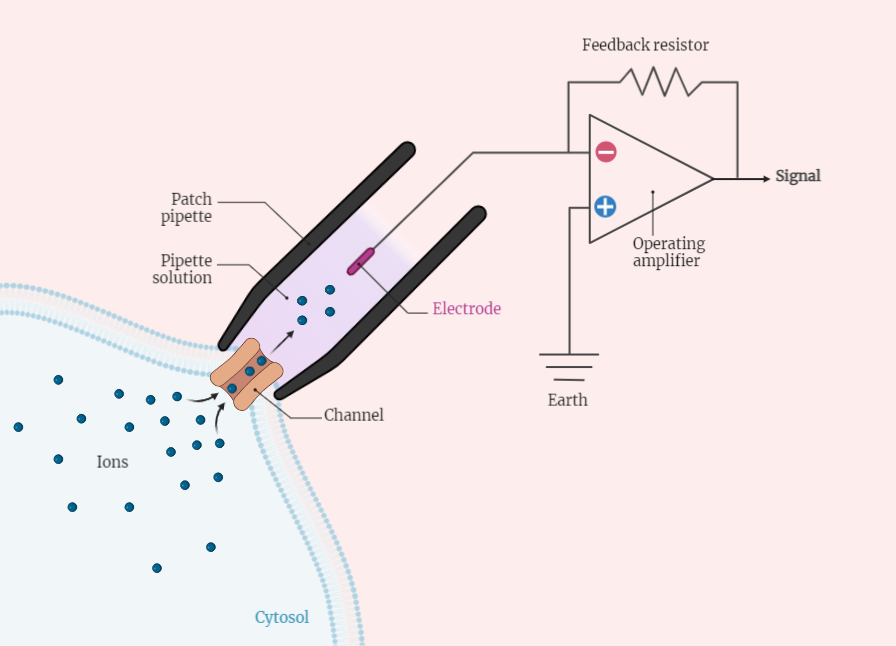
Patch Clamp Technique
The patch clamp technique is a widely used electrophysiological method for studying ion channels in cell membranes. This technique involves using a micropipette to form a gigaohm seal with a cell membrane, allowing for the manipulation of the electrical potential across the membrane. There are four main types of patch clamp, each with their own…
-
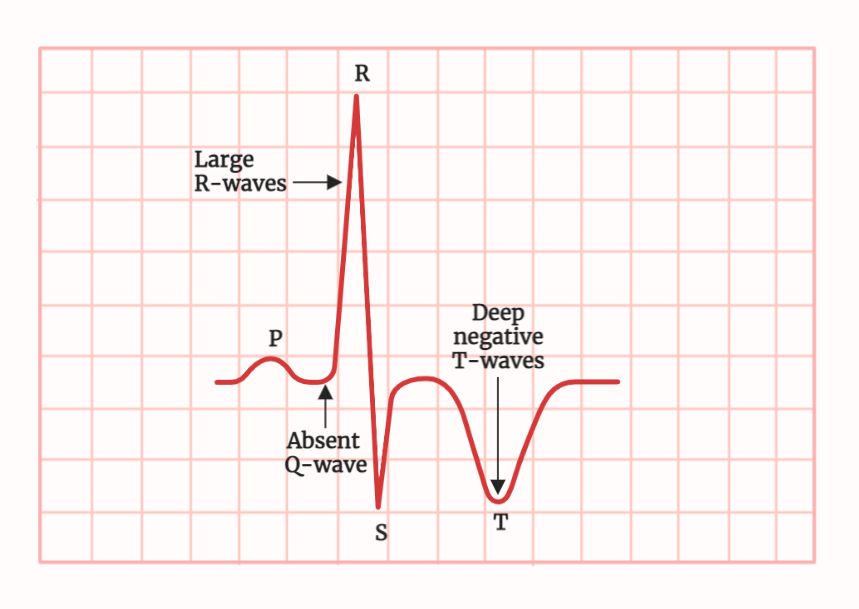
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a widely used diagnostic tool for the evaluation of heart conditions. It is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart and displays it as waves on a graph. The ECG is used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac…
-
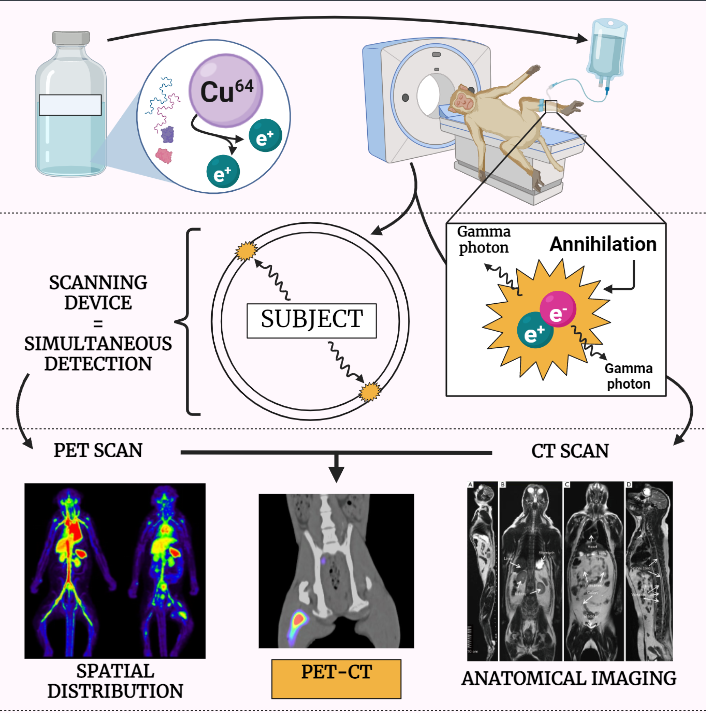
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
The article provides an in-depth study note on Positron Emission Tomography (PET), a non-invasive nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses small amounts of radioactive materials to produce images of the body’s biological processes. It explains the principles of the PET imaging technique, the use of radiotracers, its applications in detecting and diagnosing various diseases, and…
-
Post transcriptional processing
Post-transcriptional processing refers to the set of modifications and events that occur to the RNA molecule after transcription, but before translation. These modifications are important for the stability, localization, and translation of the RNA molecule. Capping, polyadenylation, splicing, RNA editing, RNA localization, and RNA stability are all important aspects of post-transcriptional processing.
-
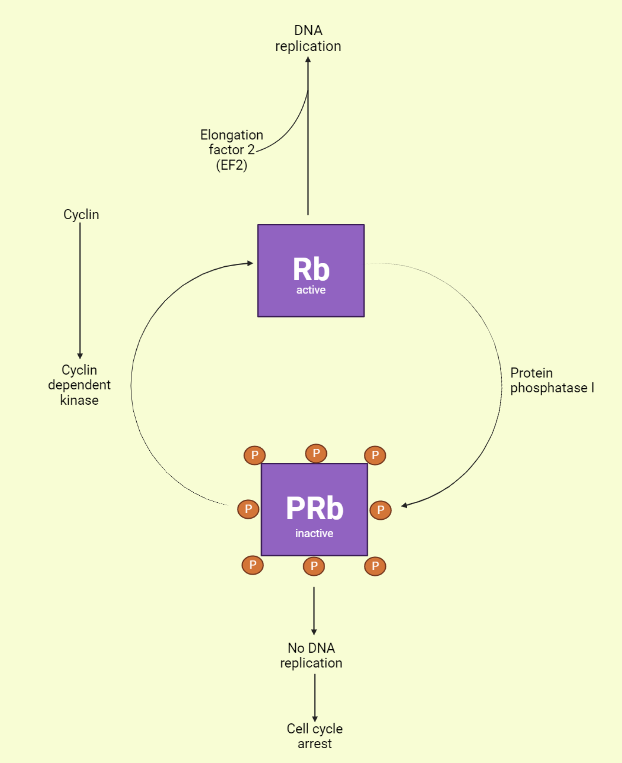
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare type of cancer that affects the retina of the eye and is caused by mutations in the retinoblastoma (RB) gene. The RB gene plays a critical role in the regulation of cell growth and division, acting as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the activity of other proteins that are important for…
-
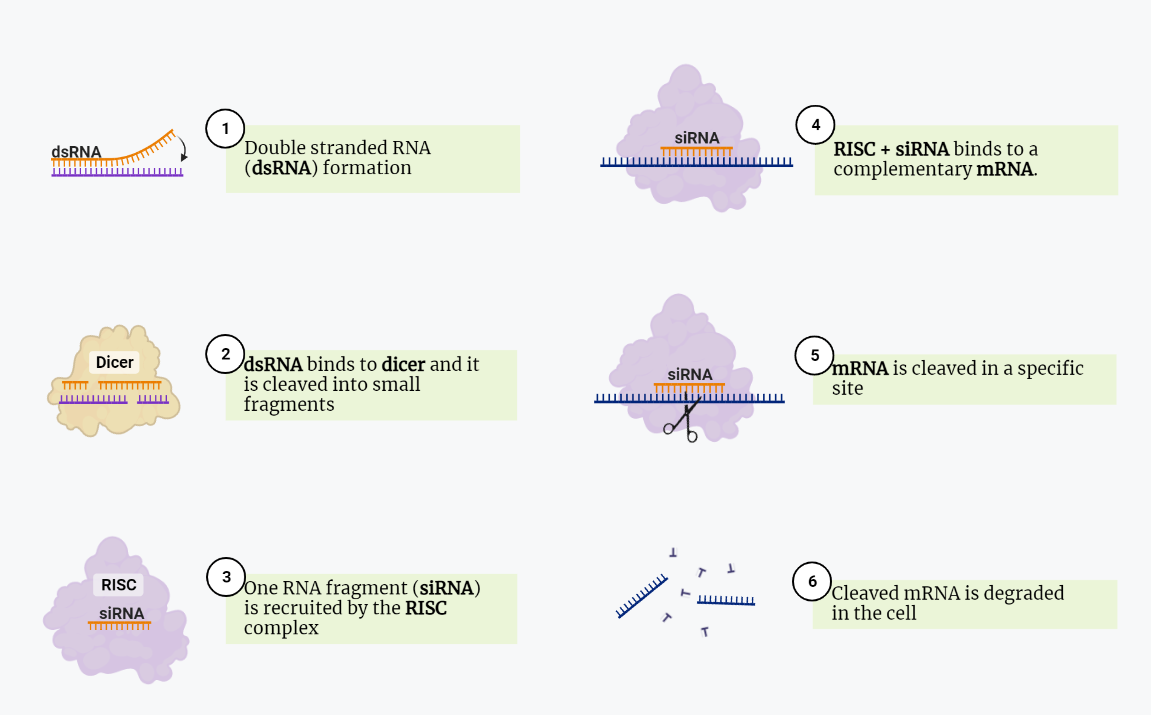
RNA Interference (RNAi)
The article provides an introduction to RNA interference (RNAi), a process by which the expression of specific genes is regulated at the post-transcriptional level. It explains the biochemistry of siRNA and shRNA, the mechanism of action, and the downstream effects of RNAi. The article also discusses the role of RNAi in cancer treatment and defense…
-
DNA Fingerprinting
The article discusses DNA fingerprinting, a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA pattern. It explains the principle of DNA fingerprinting, the methods used, and its various applications such as criminal investigations, paternity testing, and medical research. The advantages and disadvantages of DNA fingerprinting are also discussed along with the ethical and…
-
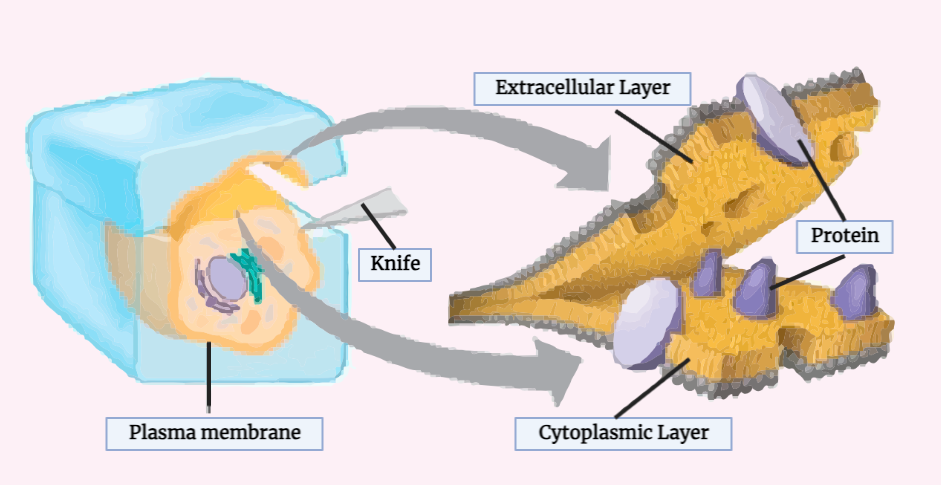
Freeze Fracture Technique
The Freeze Fracture Technique is a powerful method utilized in the study of cell biology and other biological samples. By freezing and breaking a sample, its internal structure is revealed and can be examined under an electron microscope. This technique is commonly applied to investigate cell membranes, organelles, microorganisms, as well as in fields like…
-
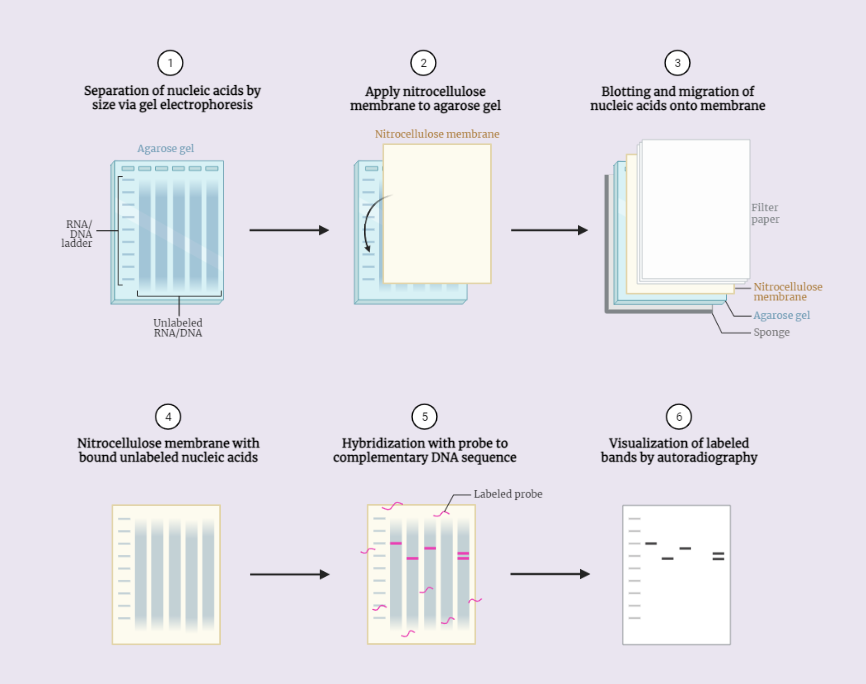
Northern blotting
Northern blotting is a technique used in molecular biology and medical research to analyze and detect specific RNA sequences. It involves the separation of RNA by electrophoresis and detection through hybridization. This powerful method has applications in genetics, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, providing valuable insights into diseases and genetic disorders. Discover more about the principles,…
-

Southern blotting
Southern blotting is a powerful technique used in molecular biology and genetics to analyze and identify specific DNA sequences. It involves the separation of DNA by electrophoresis and detection by hybridization. With applications in medical research, genetic engineering, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, Southern blotting plays a crucial role in understanding DNA-related phenomena. Discover the principles,…
-
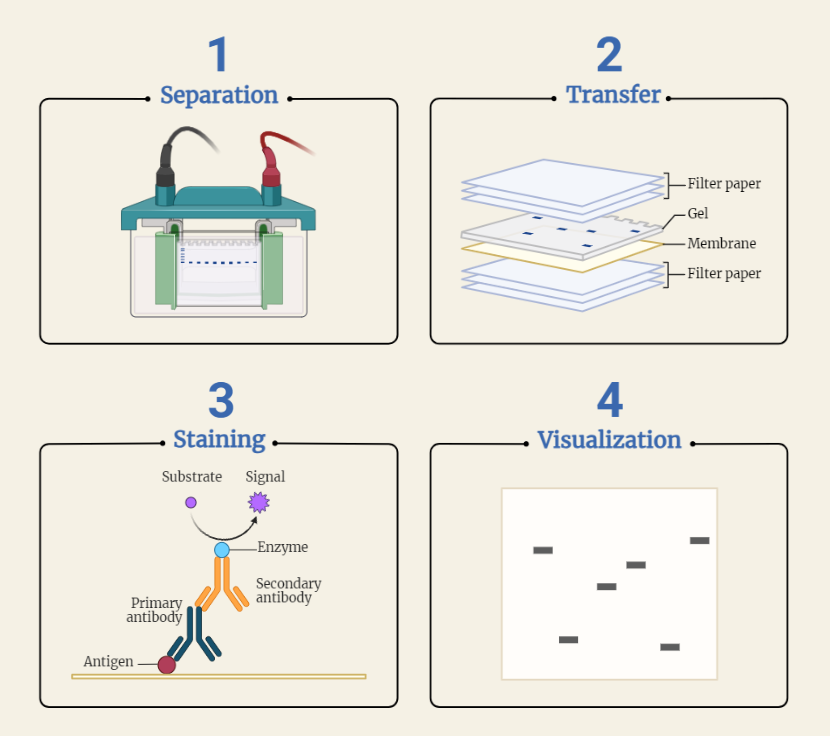
Western blotting
Discover the powerful technique of Western blotting, used in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medical research. Explore its principle of protein separation and antibody binding for protein analysis and identification. Uncover its wide-ranging applications in disease research, biotechnology, diagnostics, quality control, and environmental monitoring. Embrace Western blotting as a crucial tool for advancing scientific understanding and…
-
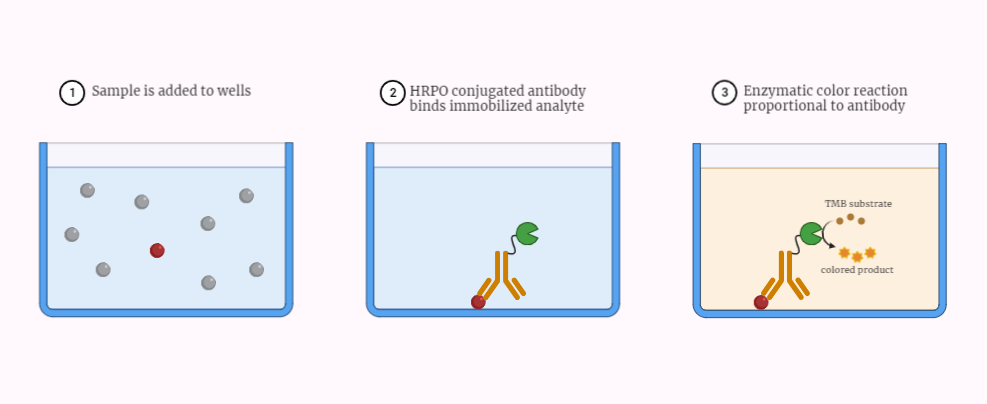
Types of ELISA
Delve into the world of ELISA methods for precise antigen and antibody detection. Uncover the procedures and explore their diverse applications in the field of diagnostics. Learn about direct, indirect, and sandwich ELISA, and how they contribute to accurate detection and analysis in various scientific disciplines.
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




