-
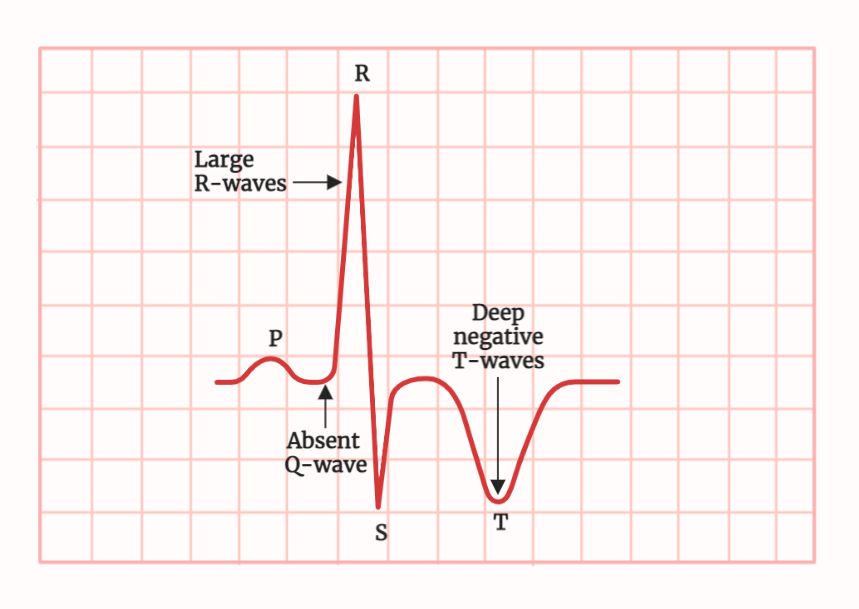
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a widely used diagnostic tool for the evaluation of heart conditions. It is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart and displays it as waves on a graph. The ECG is used to diagnose a variety of heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac…
-

Carbohydrates
The text provides an overview of carbohydrates, which are a class of biomolecules composed of simple sugars linked together through glycosidic bonds. Carbohydrates play crucial roles in energy storage and transport, as well as in structural support and cell-cell recognition. The three main types of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, each with specific functions…
-
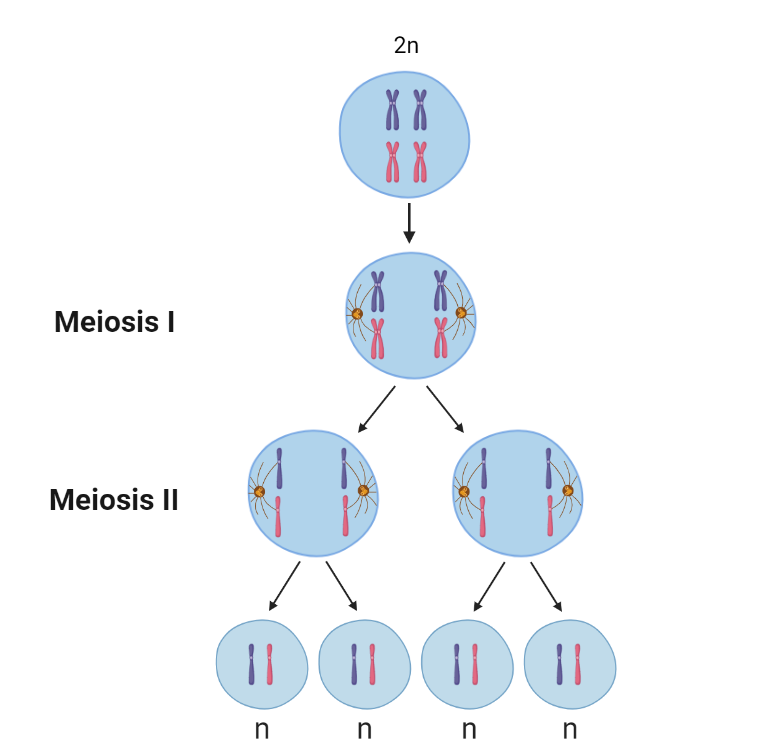
Meiosis: Cell Division
The text explains the process of meiosis, which is a type of cell division that produces reproductive cells or gametes. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half and is divided into two rounds of cell division: meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, the chromosomes pair up with their homologous partner, exchange genetic material…
-
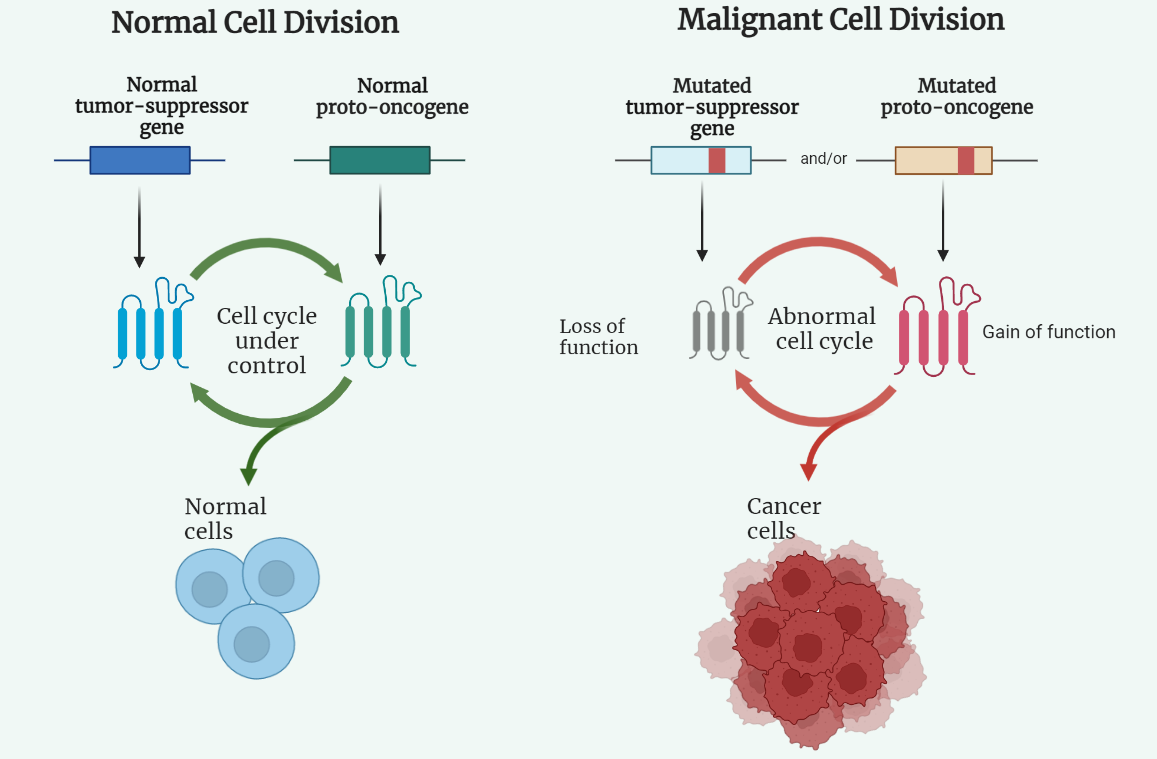
Cancer and cell cycle
The article explains the role of the cell cycle in the development of cancer. The cell cycle is a series of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides into two daughter cells. Disruption in the regulation of the cell cycle can lead to uncontrolled growth and proliferation of cells, causing cancer.…
-
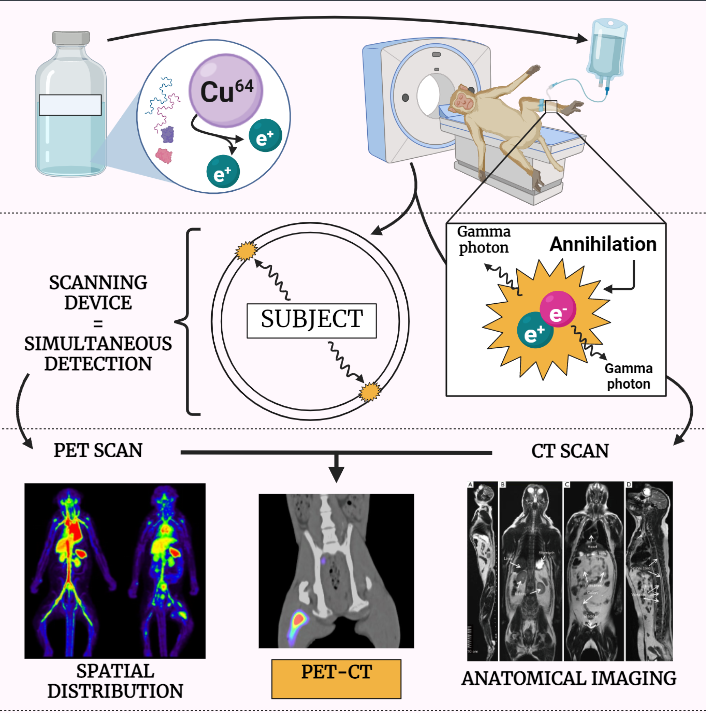
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
The article provides an in-depth study note on Positron Emission Tomography (PET), a non-invasive nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses small amounts of radioactive materials to produce images of the body’s biological processes. It explains the principles of the PET imaging technique, the use of radiotracers, its applications in detecting and diagnosing various diseases, and…
-

Beer-Lambert Law and Spectrophotometry
Discover the principles of the Beer-Lambert Law and its application in spectrophotometry. Explore how this law relates the concentration of a solute to absorbance, and its significance in quantitative analysis, chemical kinetics, environmental monitoring, pharmaceutical analysis, and biochemical assays. Unlock the power of spectrophotometry in understanding chemical substances and their characteristics.
-
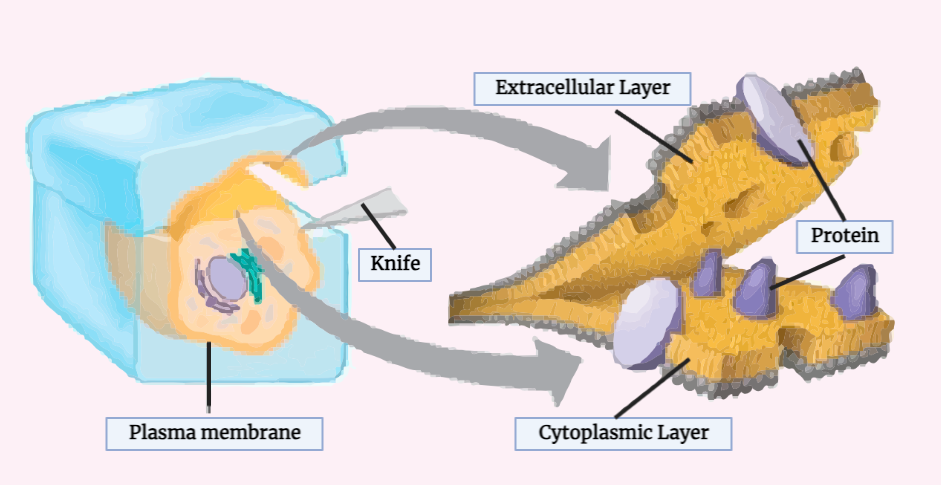
Freeze Fracture Technique
The Freeze Fracture Technique is a powerful method utilized in the study of cell biology and other biological samples. By freezing and breaking a sample, its internal structure is revealed and can be examined under an electron microscope. This technique is commonly applied to investigate cell membranes, organelles, microorganisms, as well as in fields like…
-
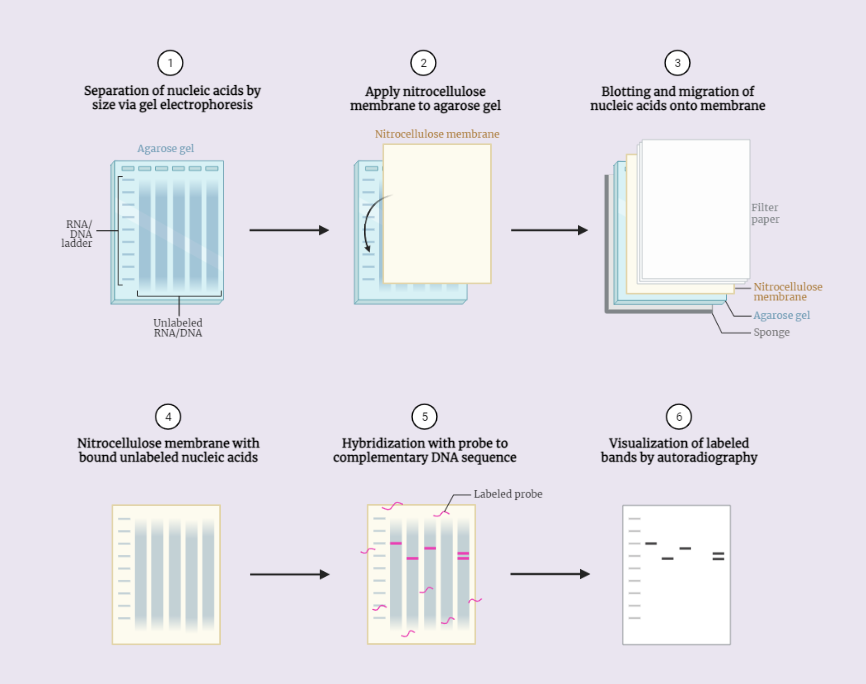
Northern blotting
Northern blotting is a technique used in molecular biology and medical research to analyze and detect specific RNA sequences. It involves the separation of RNA by electrophoresis and detection through hybridization. This powerful method has applications in genetics, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, providing valuable insights into diseases and genetic disorders. Discover more about the principles,…
-

Southern blotting
Southern blotting is a powerful technique used in molecular biology and genetics to analyze and identify specific DNA sequences. It involves the separation of DNA by electrophoresis and detection by hybridization. With applications in medical research, genetic engineering, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, Southern blotting plays a crucial role in understanding DNA-related phenomena. Discover the principles,…
-
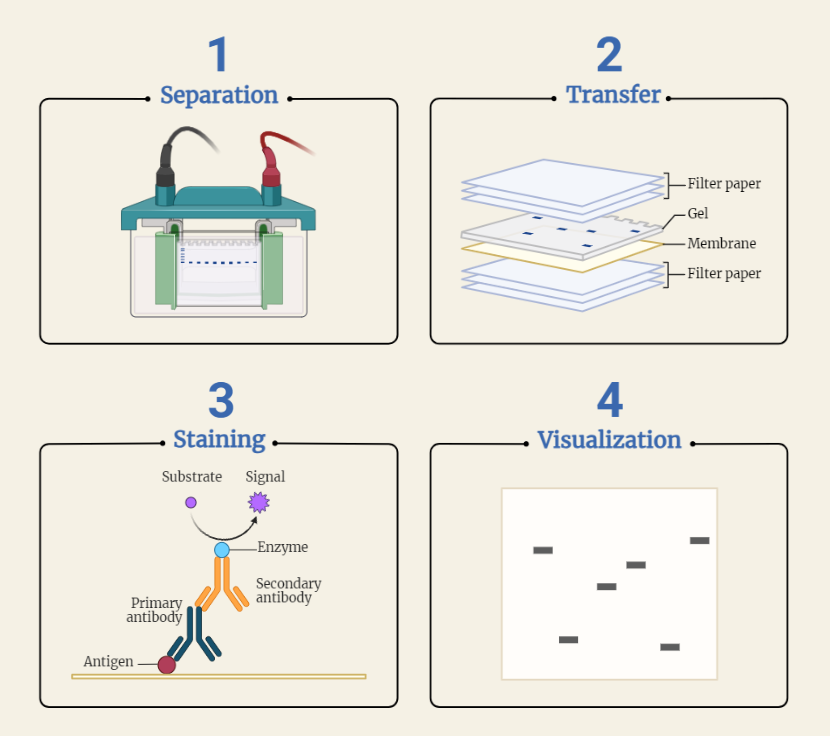
Western blotting
Discover the powerful technique of Western blotting, used in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medical research. Explore its principle of protein separation and antibody binding for protein analysis and identification. Uncover its wide-ranging applications in disease research, biotechnology, diagnostics, quality control, and environmental monitoring. Embrace Western blotting as a crucial tool for advancing scientific understanding and…
-
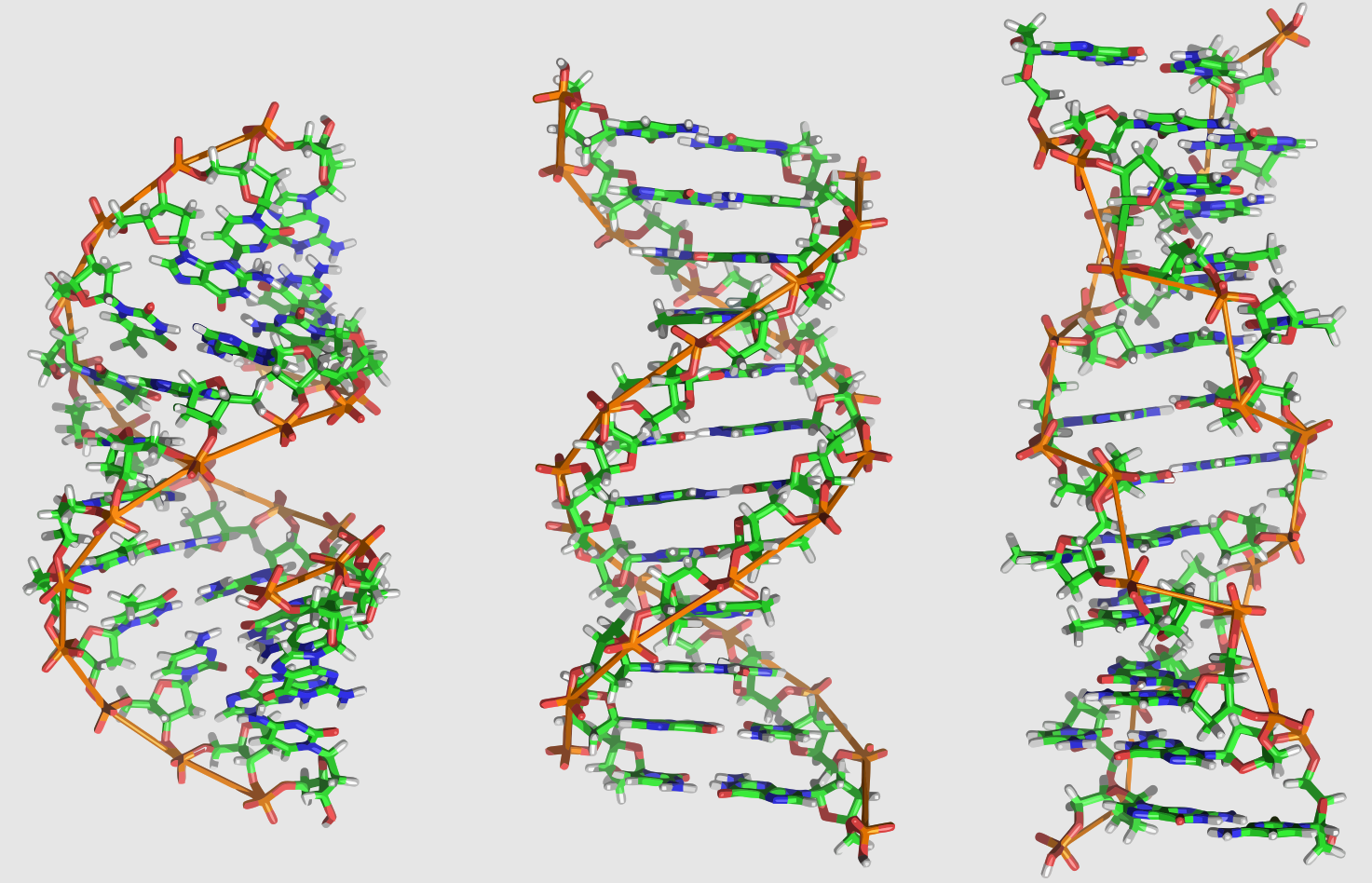
DNA Helix Variations
Explore the fascinating world of DNA structures with distinct characteristics and functions. Discover the diverse forms of A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA, each with their unique helix shapes, base pairs per turn, and pitches. While A-DNA boasts a narrower and regular structure with 11 base pairs per turn and a pitch of 3.4 nm, B-DNA presents…
-
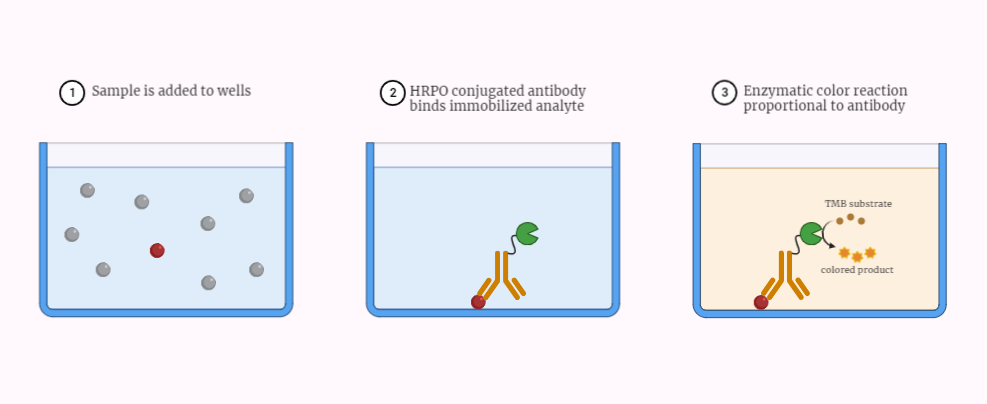
Types of ELISA
Delve into the world of ELISA methods for precise antigen and antibody detection. Uncover the procedures and explore their diverse applications in the field of diagnostics. Learn about direct, indirect, and sandwich ELISA, and how they contribute to accurate detection and analysis in various scientific disciplines.
-
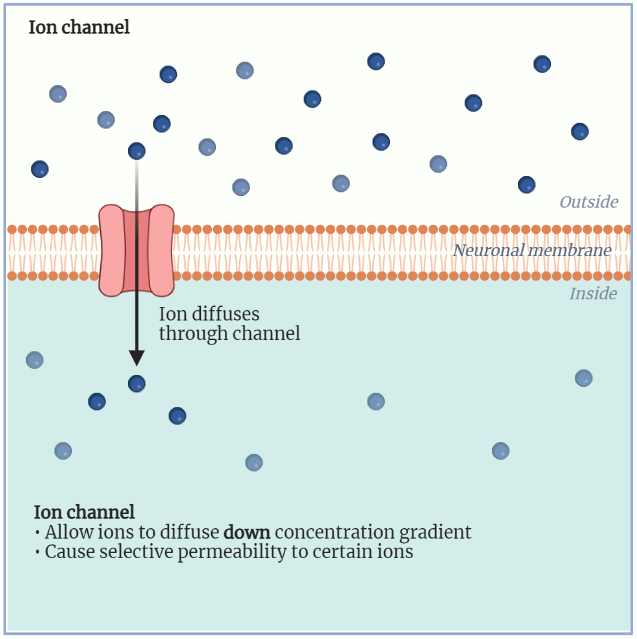
Ion Channels
Ion channels are vital membrane proteins that regulate the passage of ions, influencing cell physiology and essential processes like nerve impulses and muscle contraction. They can be categorized based on ion selectivity, gating mechanisms, and regulatory processes. Examples include voltage-gated channels that respond to membrane potential changes and ligand-gated channels activated by specific molecules. Cyclic…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




