-
Genetic Code Overview
Here’s an excerpt from the provided text on the Genetic Code: The **Genetic Code** is a universal set of rules essential for translating genetic information into functional proteins. It operates on a **triplet code** system, where each **codon**, composed of three nucleotides, corresponds to a specific amino acid. This code is **non-overlapping** and **degenerate**, meaning…
-
Immune Response in Plants
Plants, just like animals, have a sophisticated immune system that protects them from pathogens. However, the plant immune response differs from that of animals, as it relies on physical and chemical barriers, as well as specific responses triggered by pathogen detection. The immune response in plants can be classified into basal defense, which is the…
-
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
Gregor Mendel’s groundbreaking research on pea plants led to the formulation of two fundamental laws of inheritance. The Law of Dominance explains how dominant and recessive traits are inherited, while the Law of Segregation elucidates the separation of alleles during meiosis. The Law of Independent Assortment further reveals the independent inheritance of different traits. These…
-
Diffusion
Explore the fascinating process of diffusion, where particles naturally move from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Delve into the principles, factors, and examples of diffusion to understand its significance in various scientific fields and everyday phenomena. Gain insights into how temperature, molecular size, and concentration gradients influence this fundamental process.
-
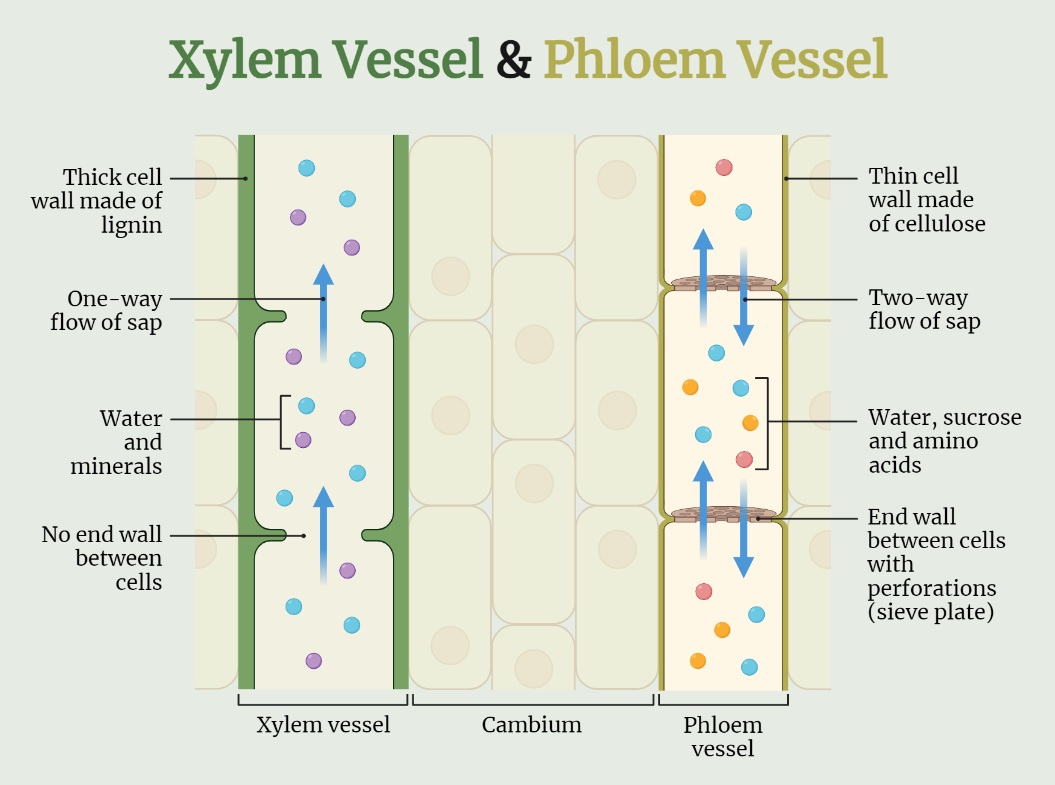
Means of Transport in Plants
Discover the fascinating means of transport in plants, as water, nutrients, and sugars are efficiently distributed through specialized structures like xylem and phloem. From transpiration and active transport to cytokinesis and endocytosis, explore the intricate mechanisms that ensure the plant’s survival and growth by delivering essential resources to various parts of the pla
-
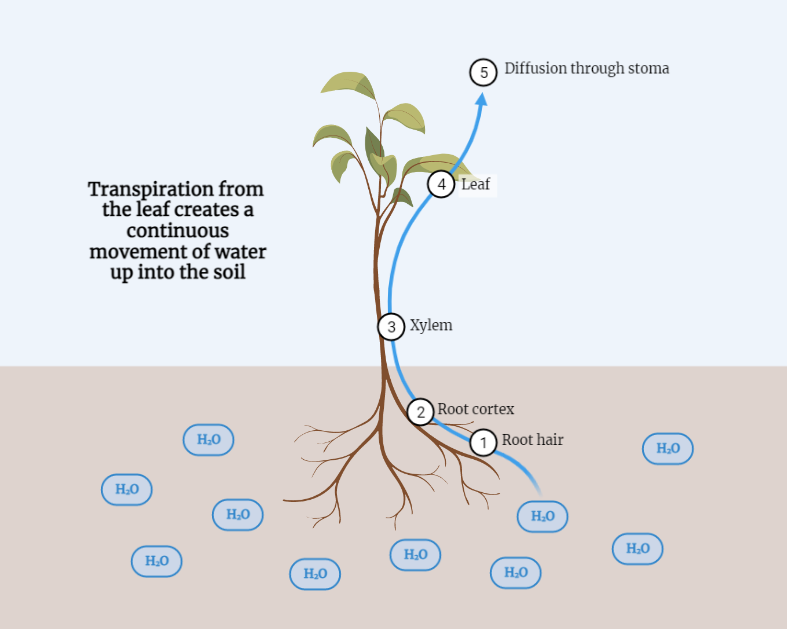
Transportation in Plants
Transportation in plants is a vital process that ensures the distribution of water, nutrients, and organic compounds throughout the plant’s various parts. Through transpiration, water is absorbed by the roots and transported upwards through the xylem vessels, driven by a combination of factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed. Meanwhile, translocation facilitates the movement…
-
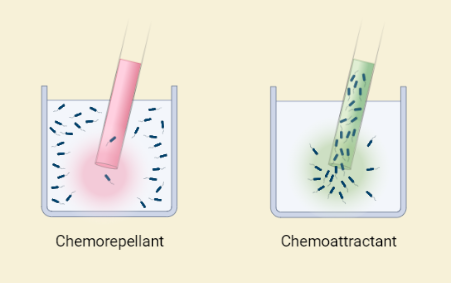
Bacterial Chemotaxis
This article provides an in-depth study of bacterial chemotaxis, which is the ability of bacteria to sense and respond to chemical gradients in their environment. The article discusses the chemotaxis mechanisms, including receptors, signal transduction, the flagellar motor, and adaptation mechanisms, along with their significance for bacterial survival and adaptation to different environments. The article…
-
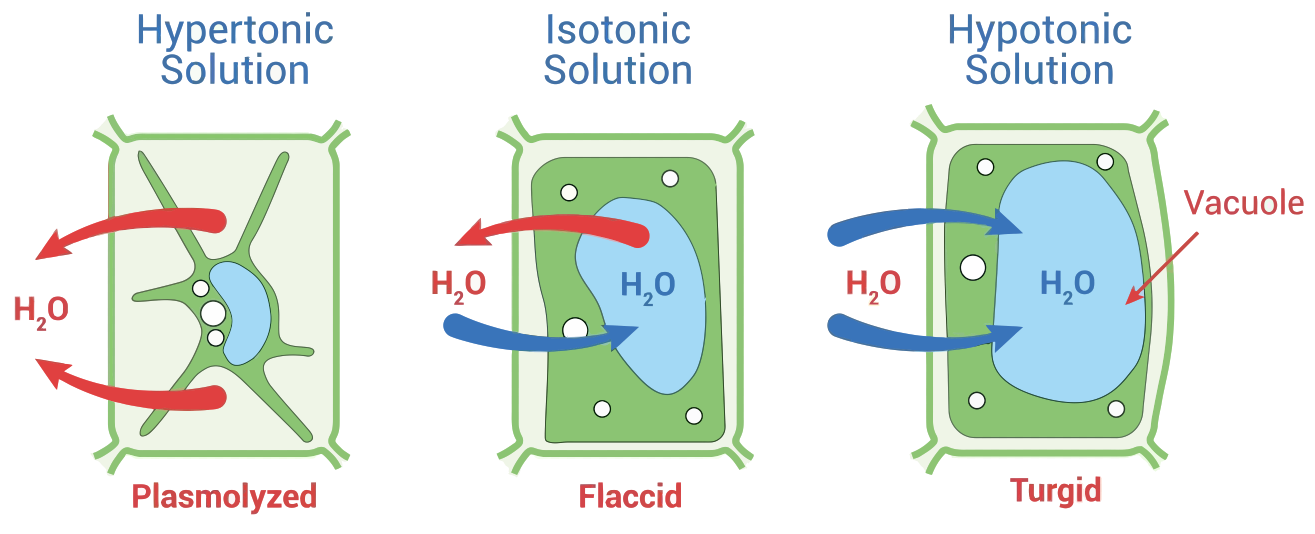
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process by which a plant cell shrinks away from its cell wall when placed in a hypertonic solution. This study note explains the process, types, examples, and the significance of plasmolysis in plant biology and agriculture. Explore the effects of water and solute stress on plants.
-
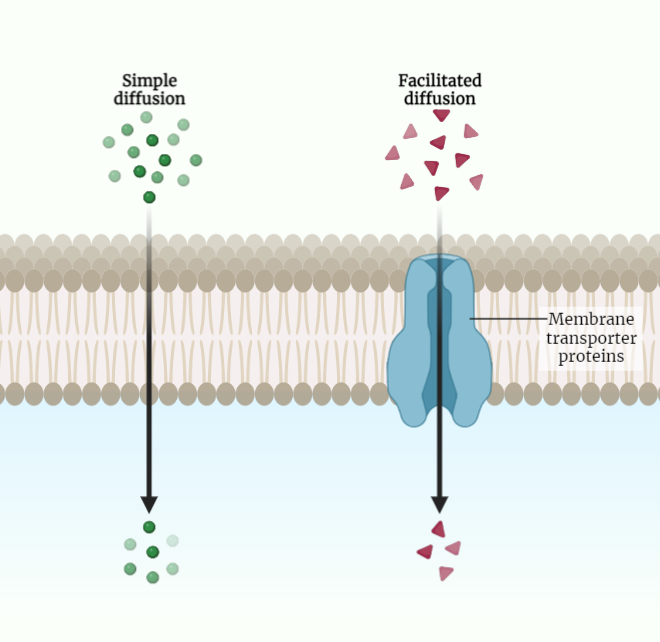
Passive Transport
Passive transport refers to the movement of substances across cell membranes without the use of energy. This study note explores key concepts such as diffusion, osmosis, the role of the cell membrane, concentration gradients, and how passive transport contributes to maintaining cellular homeostasis. Understanding these mechanisms is vital in comprehending the fundamental processes of substance…
-
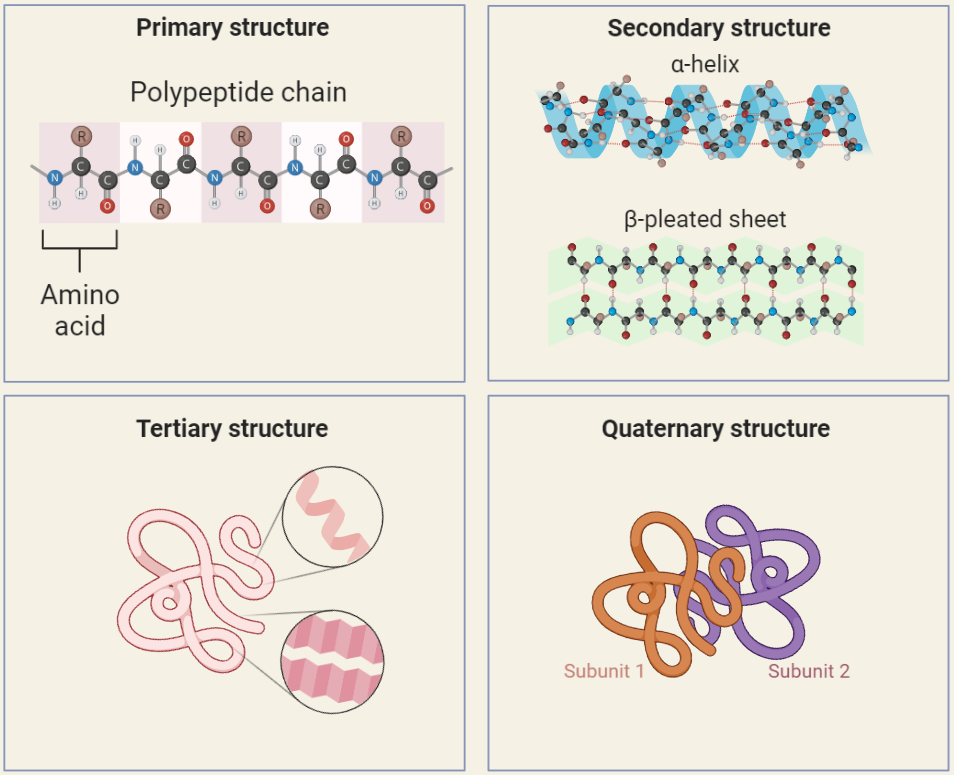
Secondary Structures of Proteins
Protein secondary structure, including alpha helix and beta sheet, plays a vital role in protein function and stability. Explore their characteristics, discover their importance in drug design and protein engineering, and learn about their applications in biotechnology.
-
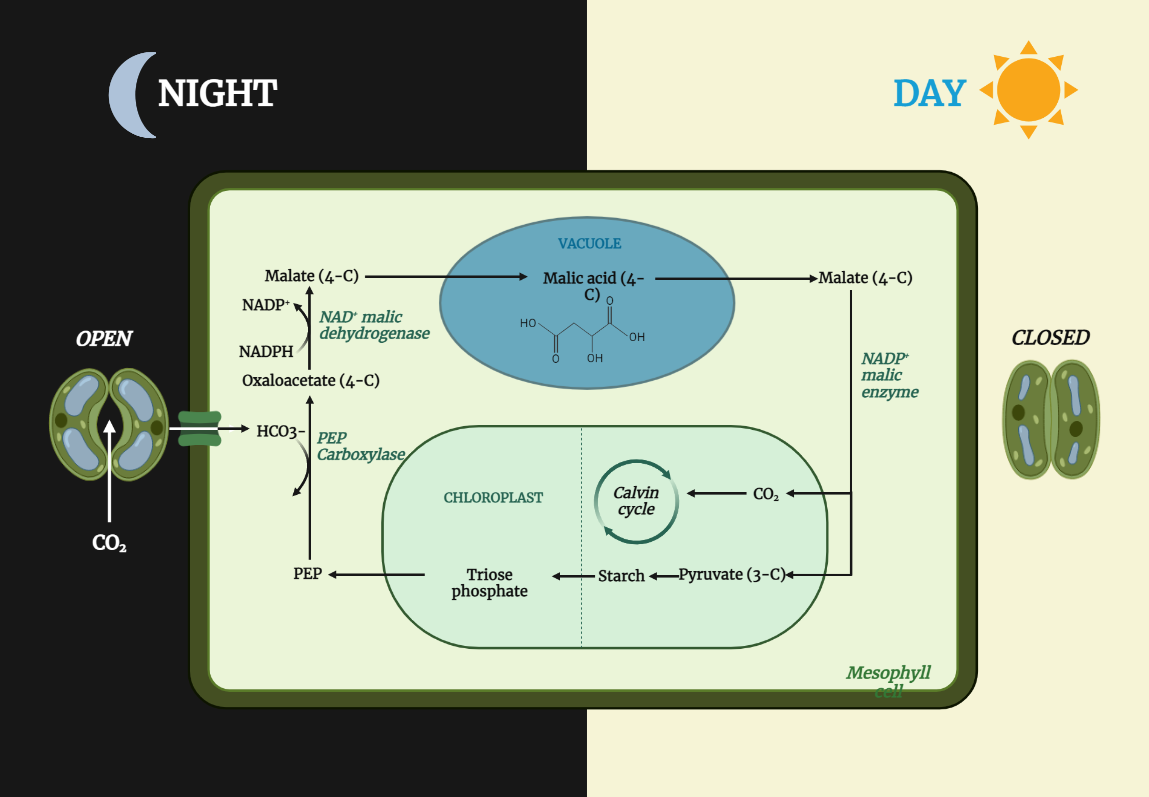
CAM plants
CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) plants have evolved a specialized carbon fixation pathway that allows them to carry out photosynthesis while minimizing water loss, making them well adapted to arid and semi-arid environments. Their ability to store water in their leaves, stems, and roots, along with their thick, waxy leaves and shallow root system, helps them…
-
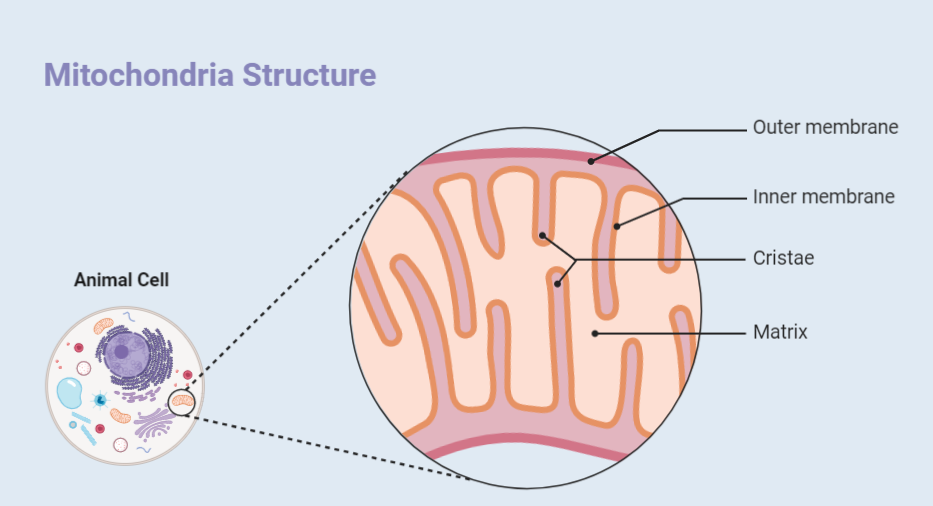
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Due to their essential role in cellular respiration, they are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. Mitochondria have a unique structure consisting of an outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix. They…
-

The Living World
The excerpt explores the fascinating realm of the living world, encompassing the vast diversity of organisms and their interactions. From the unity in basic life functions to the hierarchical organization of organisms, the study delves into the significance of cells as the fundamental units of life. It touches upon energy flow, homeostasis, and the profound…
-
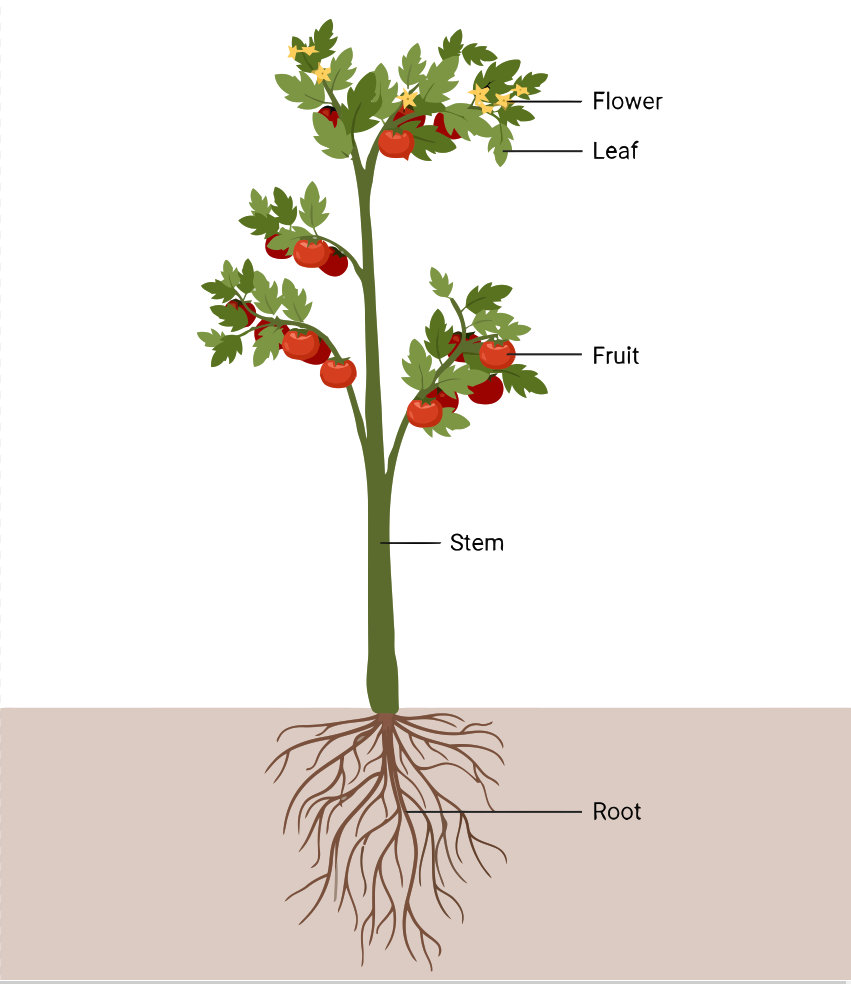
Morphology of Plant
The study of plant morphology is the study of the structure and form of plants. It encompasses the organization of plant tissues, the structure and function of roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, and the processes of photosynthesis and reproduction. Understanding plant morphology is essential for comprehending the interactions between plants and their environment, as well…
-
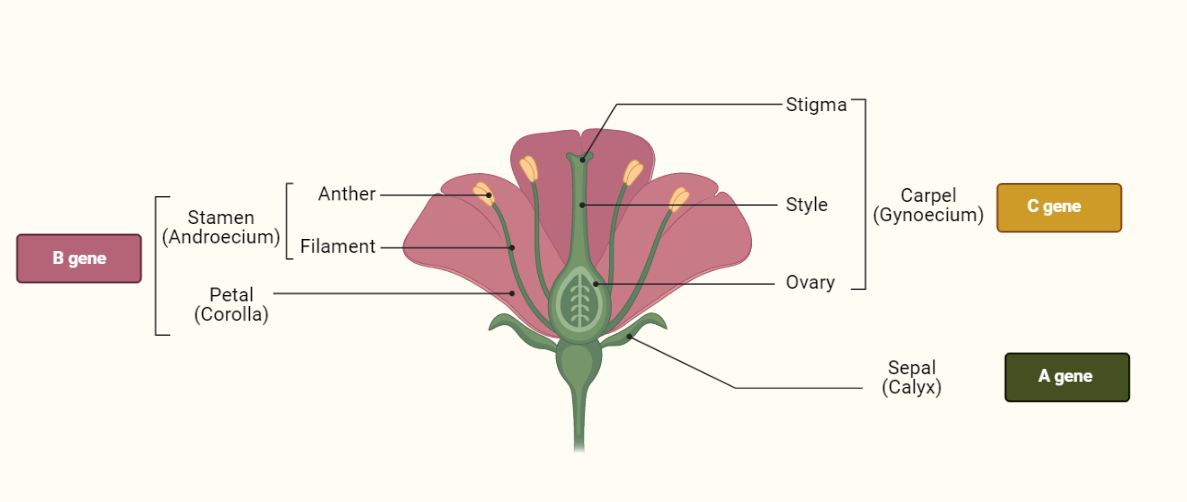
ABC Model of Flowering
The ABC model of flowering is a genetic and molecular framework that explains how plants transition from vegetative growth to reproductive development. The model proposes that three groups of genes, referred to as A, B, and C genes, work together to regulate this process. A genes are responsible for initiating the flowering process independently of…
-
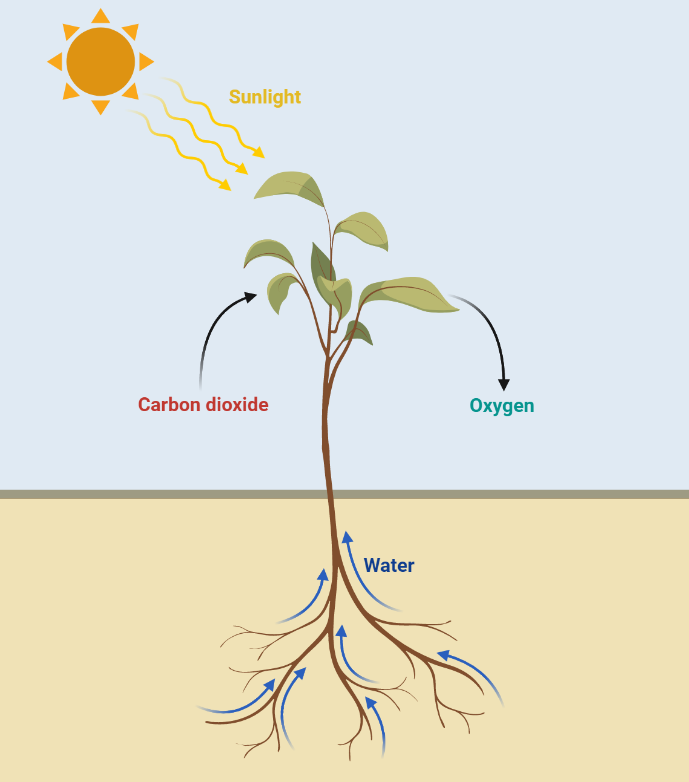
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that occurs in green plants and other photosynthetic organisms. It is the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose and other organic compounds. This energy is then used to fuel the metabolic processes of the organism. Photosynthesis is vital to the survival…
-
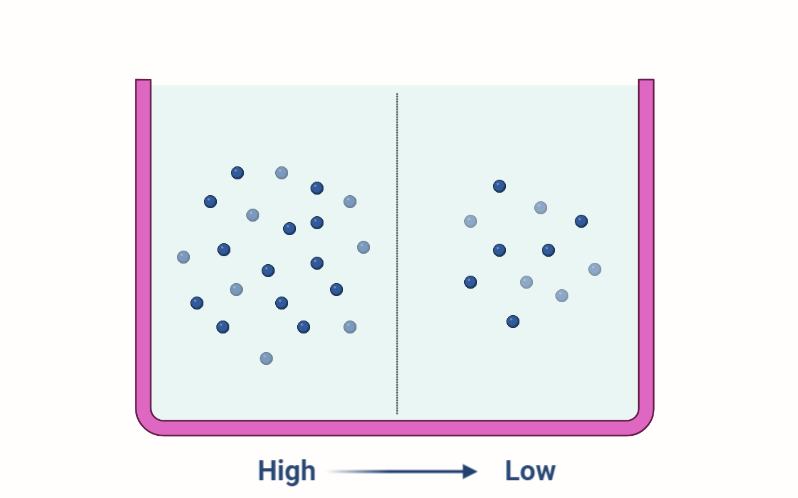
Osmosis
Osmosis is a process that occurs naturally in all living things, including plants and animals. It is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This movement of water molecules helps maintain the balance…
-

CAM Pathway
The CAM pathway is a unique mechanism for carbon fixation in plants that allows them to carry out photosynthesis in arid environments with minimal water loss. By fixing carbon dioxide at night and storing it as malic acid, CAM plants are able to use it during the day to carry out photosynthesis without losing water.…
-
C4 Plants
C4 plants have evolved a unique mechanism for carbon fixation that allows them to efficiently produce glucose in hot and dry environments. This mechanism, known as the C4 pathway, involves the spatial separation of carbon dioxide fixation and the Calvin cycle. The C4 pathway provides several ecological advantages to plants, including increased water use efficiency…
-
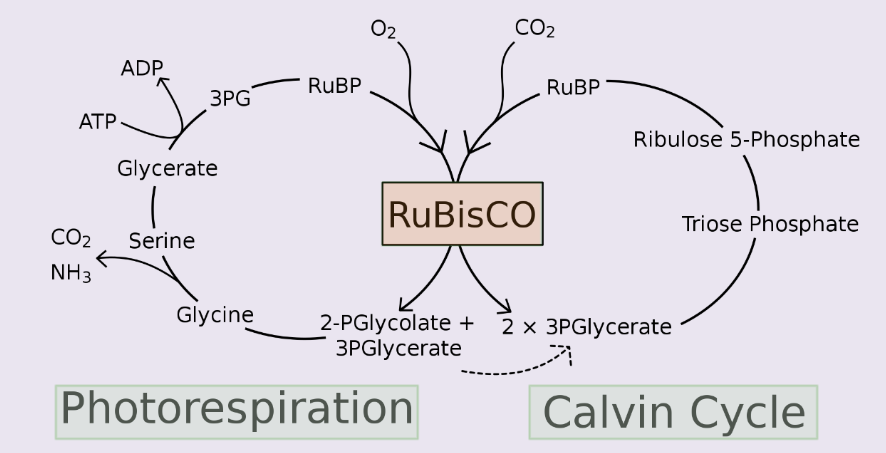
Photorespiration
Photorespiration is a complex process that takes place in plants when the concentration of CO2 inside the leaves decreases. This process reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis and ultimately leads to decreased plant growth and yield. In this chapter, we provide an in-depth overview of photorespiration, its biochemistry, regulation, and its impact on plant growth and…
-
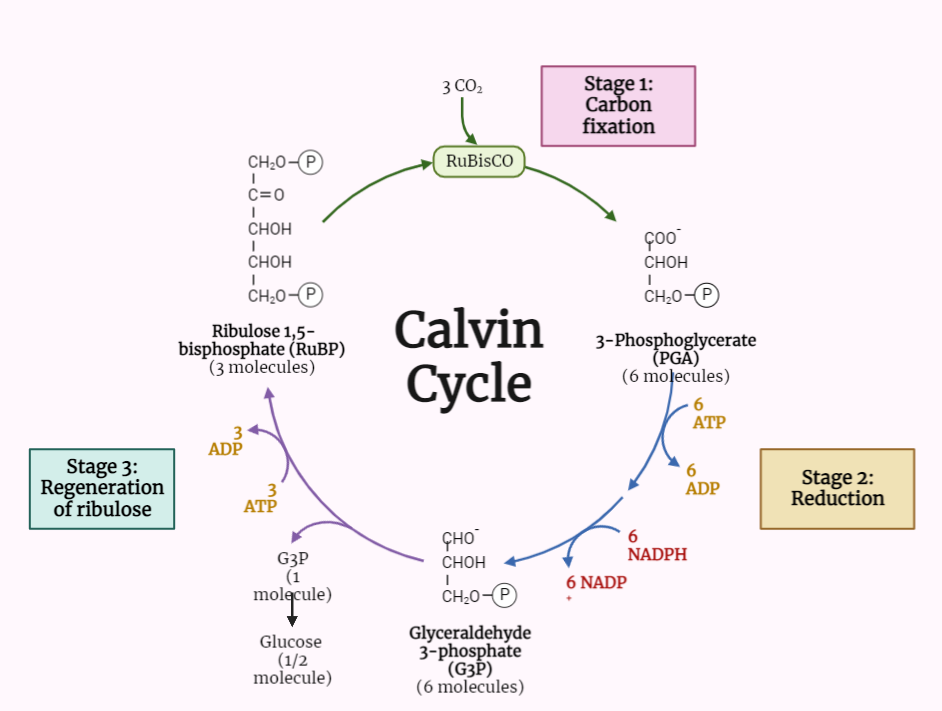
Calvin-Benson Cycle
The Calvin-Benson cycle is a fundamental process in photosynthesis, the metabolic pathway by which autotrophs, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This cycle takes place in the chloroplasts of these organisms and is responsible for fixing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into…
-
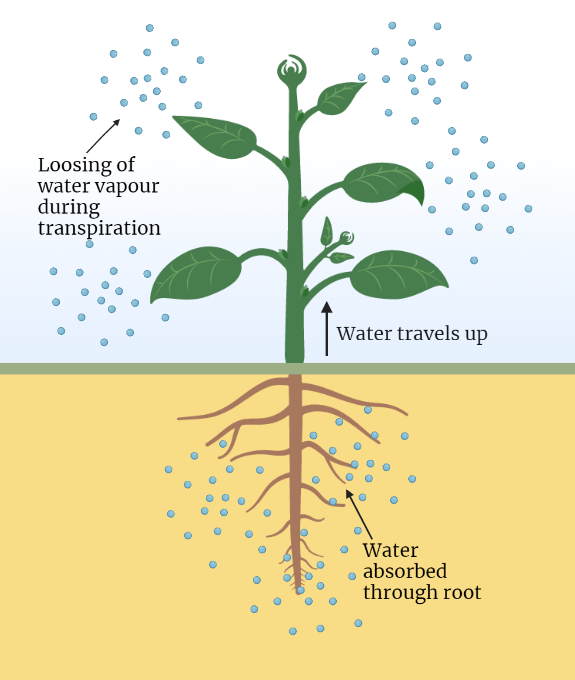
Water Potential
Water potential is a fundamental concept in the study of plant physiology and is also important in the understanding of the movement of water in living organisms. It is a measure of the potential energy of water in a system and is affected by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and solute concentration. Water potential has…
-

Light Signaling in Plants
The article discusses the importance of light signaling in plants and its role in regulating various physiological and developmental processes. It covers topics such as phototropism, photomorphogenesis, photoperiodism, and the light-dependent and independent reactions of photosynthesis. The article provides a brief overview of each topic, explaining their significance in plant growth and survival.
-
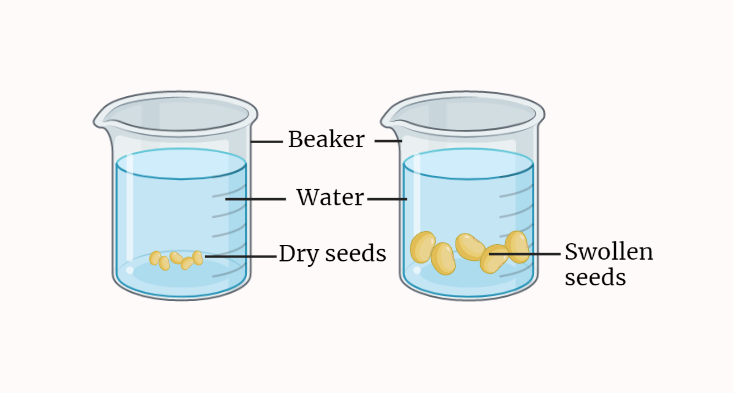
Imbibition
Imbibition is a fascinating process observed in both plants and materials science. It involves the absorption of liquid by solids, resulting in interesting phenomena such as seed germination, polymer swelling, and capillary action. Understanding imbibition provides insights into various natural and synthetic systems, contributing to advancements in agriculture, materials engineering, and more.
-

Transpiration
In this chapter, we delve into the fascinating world of transpiration in plants. We explore the intricate mechanism behind this process, including the role of stomata and the water cycle. Discover how plants adapt to various environmental factors and examine the contrasting strategies of xerophytes and hydrophytes. Gain insight into the ecological impact of transpiration…
-

Facilitated Diffusion
Discover the intricacies of facilitated diffusion, a vital mechanism that allows specific molecules to cross cell membranes with the help of specialized proteins. Explore the principles, proteins involved, and examples of this selective transport process. Gain insights into how facilitated diffusion contributes to cellular homeostasis and essential molecule transport.
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




