-

The Living World
The excerpt explores the fascinating realm of the living world, encompassing the vast diversity of organisms and their interactions. From the unity in basic life functions to the hierarchical organization of organisms, the study delves into the significance of cells as the fundamental units of life. It touches upon energy flow, homeostasis, and the profound…
-
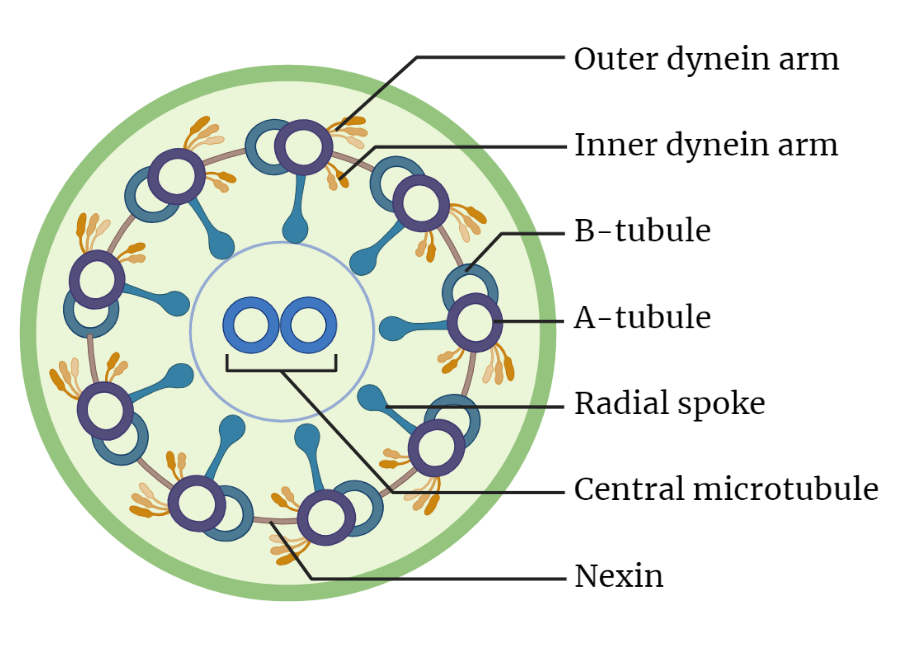
Microtubular arrangement
The 9+2 microtubular arrangement, a fascinating structure found in cilia and flagella, drives the coordinated movement of these hair-like appendages. Comprising 9 doublet microtubules encircling a central pair, this arrangement relies on the motor protein dynein to generate sliding motion, propelling cilia and flagella forward. Essential for cell movement, fluid transport, and sperm motility, understanding…
-
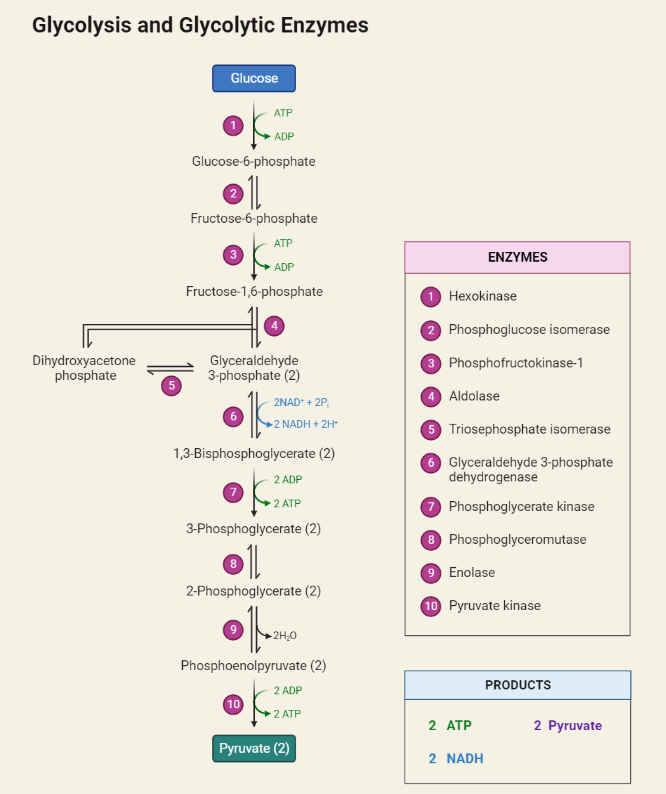
Steps of Glycolysis
The text provides a comprehensive overview of glycolysis, a crucial metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, ATP, and NADH. It explores the process, enzymes involved, and its significance in cellular energy production. Glycolysis’s versatility, occurring in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, makes it fundamental for cell survival and energy generation in various organisms, from…
-

Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic process that occurs in almost all living organisms. It is a critical pathway that provides energy for cells by breaking down glucose to produce ATP. This article will discuss the definition, equation, enzymes, and steps involved in glycolysis. What is Glycolysis? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate,…
-
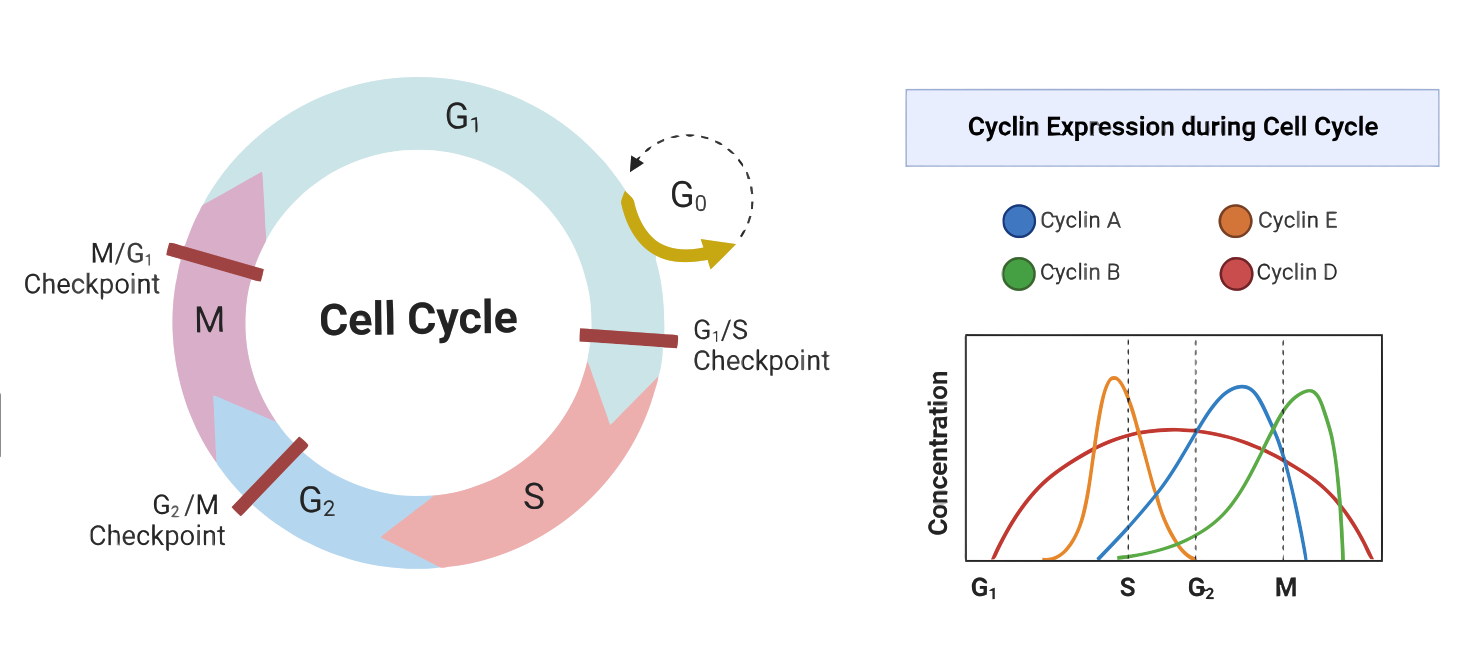
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
he cell cycle is a crucial process in the growth and development of multicellular organisms, and its regulation is essential for maintaining proper cell function. Dysregulation of the cell cycle can lead to various diseases, including cancer, where cells divide uncontrollably. The regulation of the cell cycle is a complex process that involves a delicate…
-
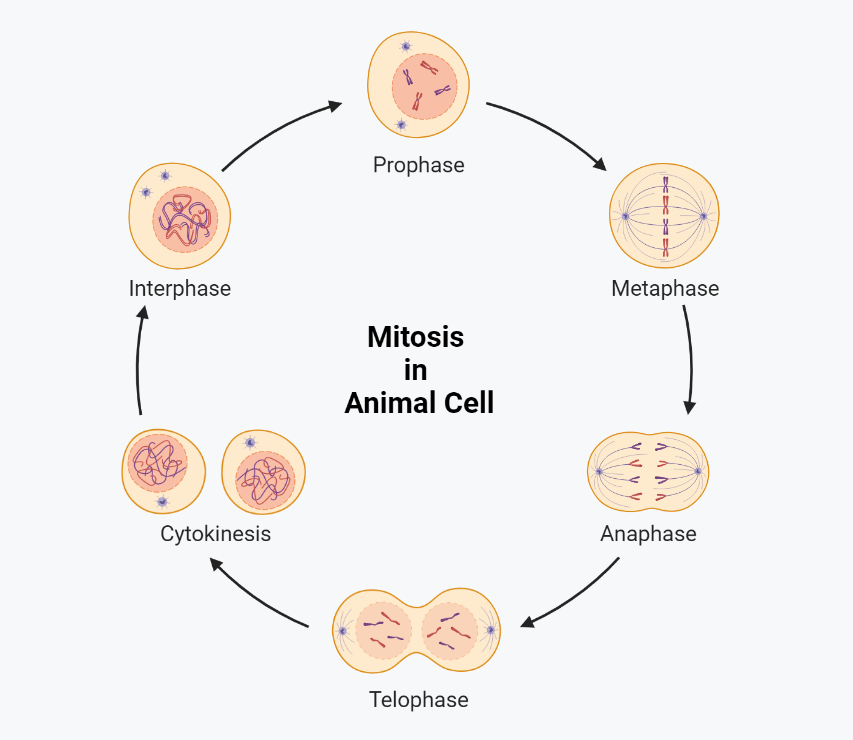
Mitosis: Cell Division
Mitosis cell division is essential for the growth and repair of an organism. Mitosis involves four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, followed by cytokinesis, the final stage where the cell physically divides into two identical daughter cells. The proper execution of mitosis is critical for the accurate replication and segregation of DNA and…
-
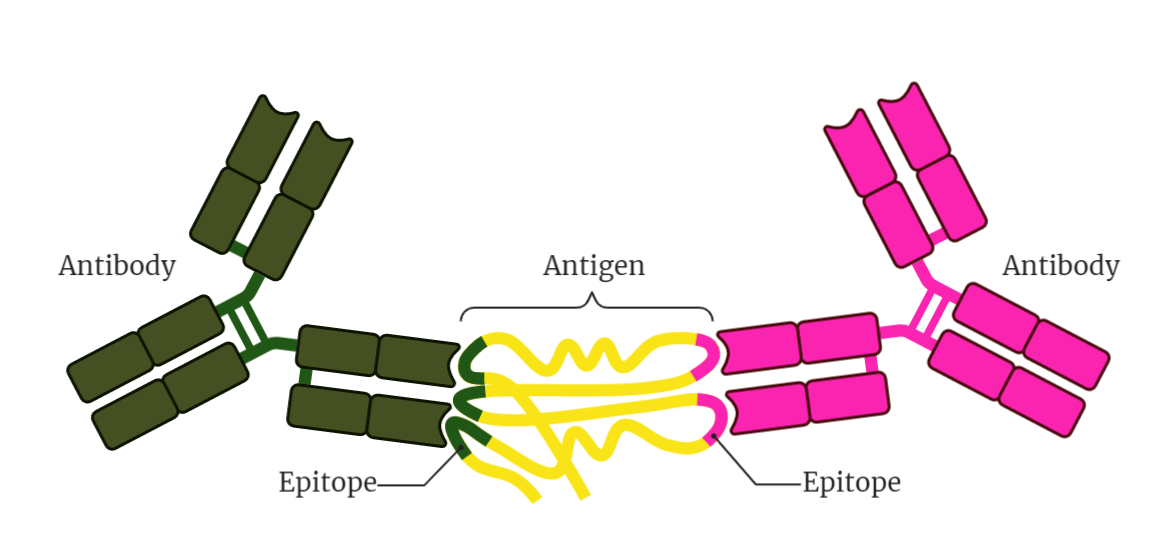
Antigen-Antibody Reaction
The text above provides an overview of antigen-antibody reactions, which play a crucial role in the immune response. It explains the specific binding of an antigen to an antibody through non-covalent bonds and the diversity of antibodies generated by the immune system. The mechanisms of action resulting from antigen-antibody reactions are also discussed, including neutralization,…
-

Micro and macro molecules
Micro and macro molecules are the building blocks of all living organisms. Micro molecules are small and simple in structure, while macro molecules are large and complex. They play crucial roles in metabolic processes, structural organization, and cellular processes. Understanding the properties and functions of these molecules is essential for understanding the complex processes that…
-
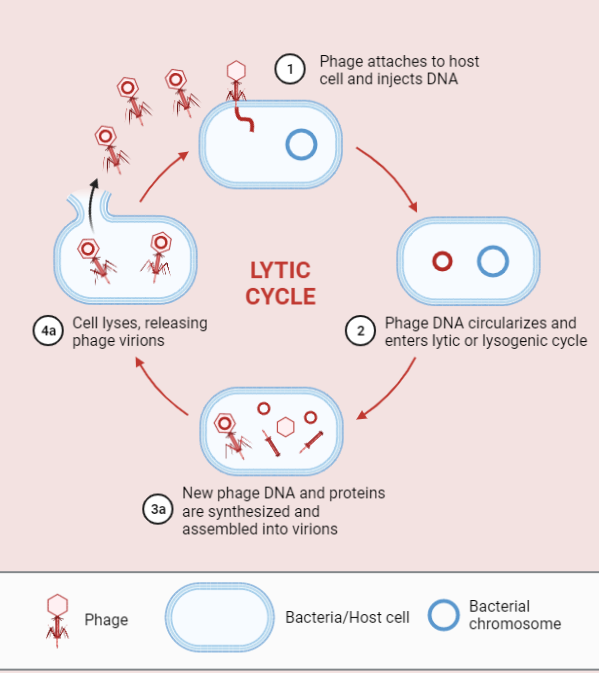
Lytic Cycle
The lytic cycle is a process used by certain viruses to reproduce and spread. It involves the virus infecting a host cell, using the host’s cellular machinery to replicate itself, and causing the host cell to lyse or burst, releasing new viral particles. This cycle can cause significant damage to the host cells and tissues,…
-
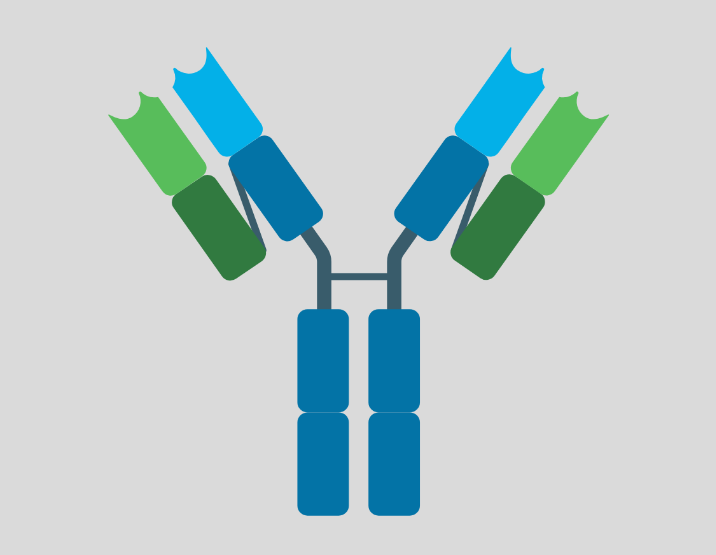
Antibodies
This text provides an overview of antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), which are proteins produced by the immune system in response to foreign antigens. Antibodies are highly specific to a particular antigen and play a crucial role in fighting infections and diseases. The text covers the structure and different classes of antibodies, their mechanisms…
-
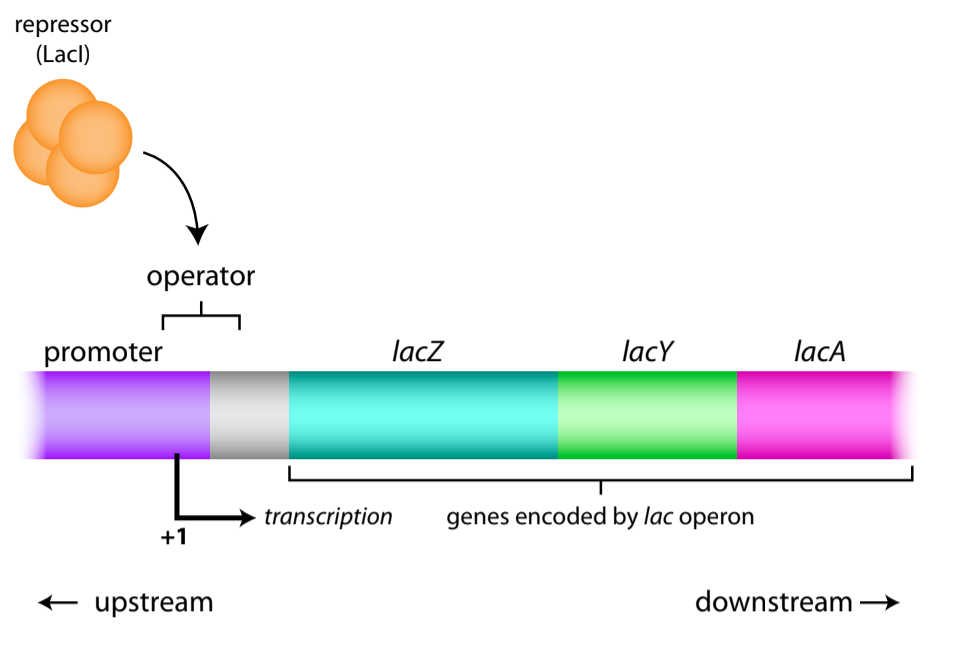
Lac Operon- Gene Regulation in Bacteria
The lac operon, found in E. coli bacteria, is a remarkable genetic system that controls the metabolism of lactose, a sugar commonly present in milk. This operon comprises three crucial structural genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA, responsible for encoding the essential enzymes needed to break down lactose into glucose and galactose. Its significance in the…
-
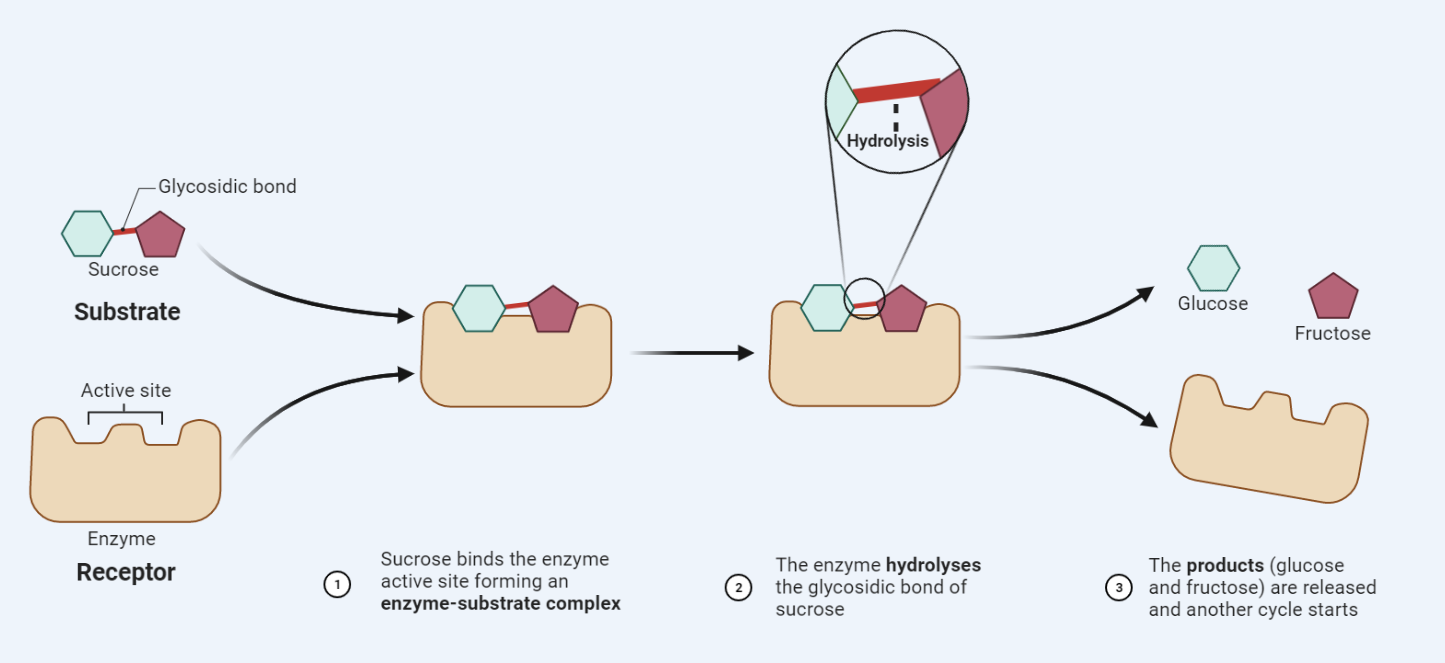
Enzyme-substrate interaction
Enzymes are crucial biomolecules that facilitate specific chemical reactions in living organisms. They do this by binding to specific molecules known as substrates, and this interaction is key to their function. Enzymes can only catalyze specific types of reactions, and this specificity is determined by the unique shape of their active site, which is in…
-
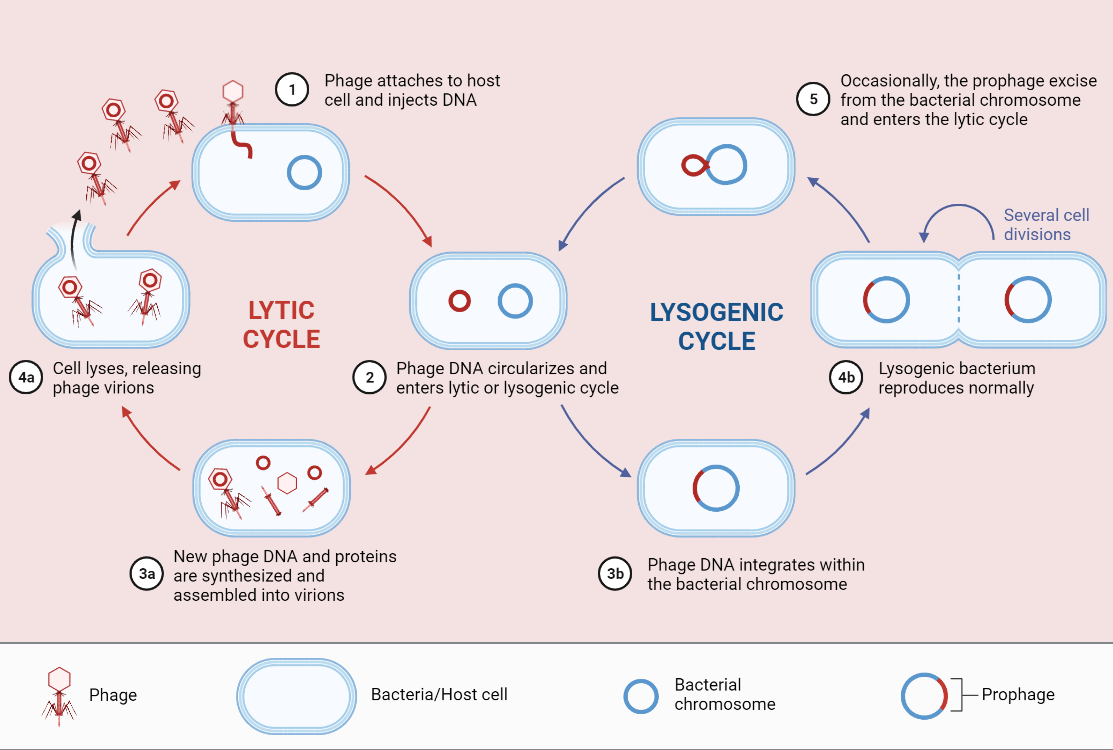
Lysogenic Cycle
The lysogenic cycle is a reproductive cycle used by certain viruses to infect and replicate within a host cell. During this cycle, the virus inserts its genetic material into the host cell’s DNA, becoming a dormant or latent infection. This period of dormancy allows the virus to evade the host immune response and persist within…
-
Antigen
This text provides an overview of antigens, which are molecules capable of inducing a specific immune response. It explains the two main types of antigens, their structure and characteristics, antigen processing and presentation, and how they are recognized by the immune system.
-
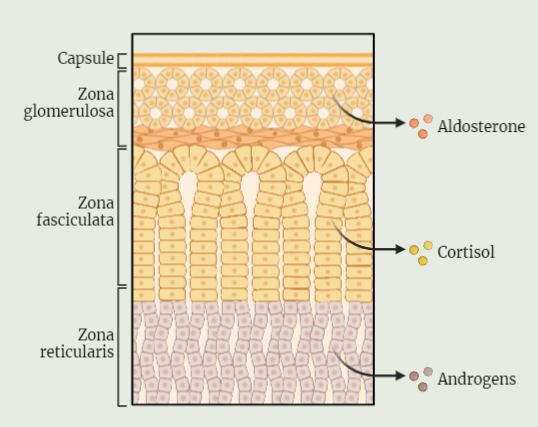
Histology of Adrenal Gland
The adrenal glands, also known as the suprarenal glands, are a vital part of our endocrine system. Positioned on top of each kidney, these small triangular-shaped glands produce and release a variety of hormones that play crucial roles in our body’s functioning. The outer region, called the adrenal cortex, consists of three layers that produce…
-
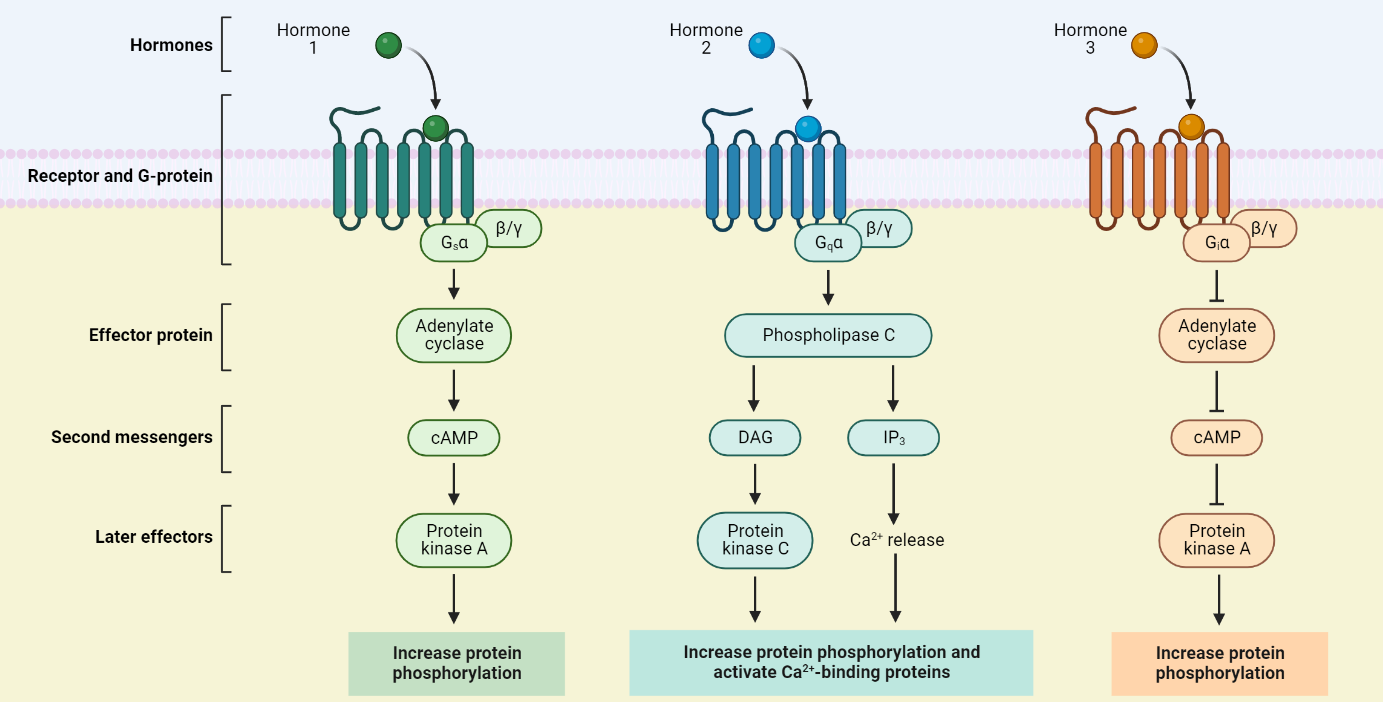
GPCR Signalling Pathway
The G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signalling pathway plays a vital role in transmitting signals from extracellular molecules, such as hormones, to intracellular effectors. This pathway involves a series of steps, including hormone binding to the GPCR, activation of the G protein, signal transduction, termination of the signal, and ultimately leading to a cellular response. The…
-
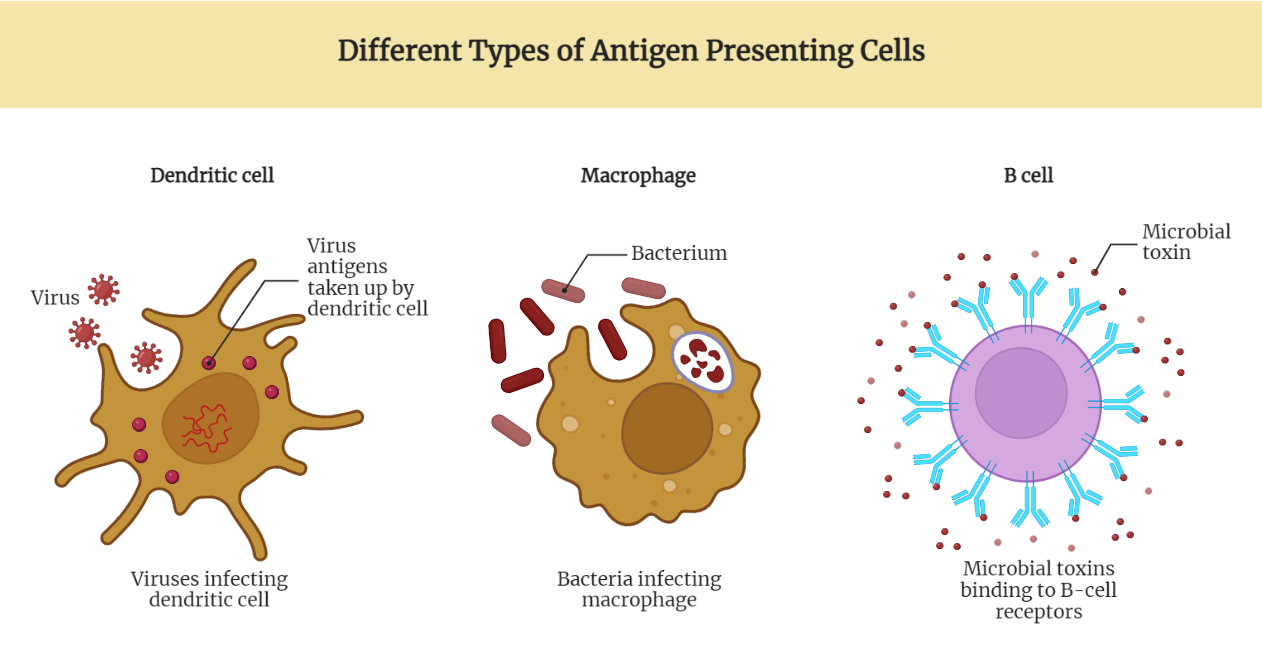
Antigen Presenting Cells
This text provides an overview of antigen presenting cells (APCs), including dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells, and their crucial role in initiating the adaptive immune response. It also discusses the process of maturation of APCs, which enhances their efficiency in presenting antigens to T cells.
-
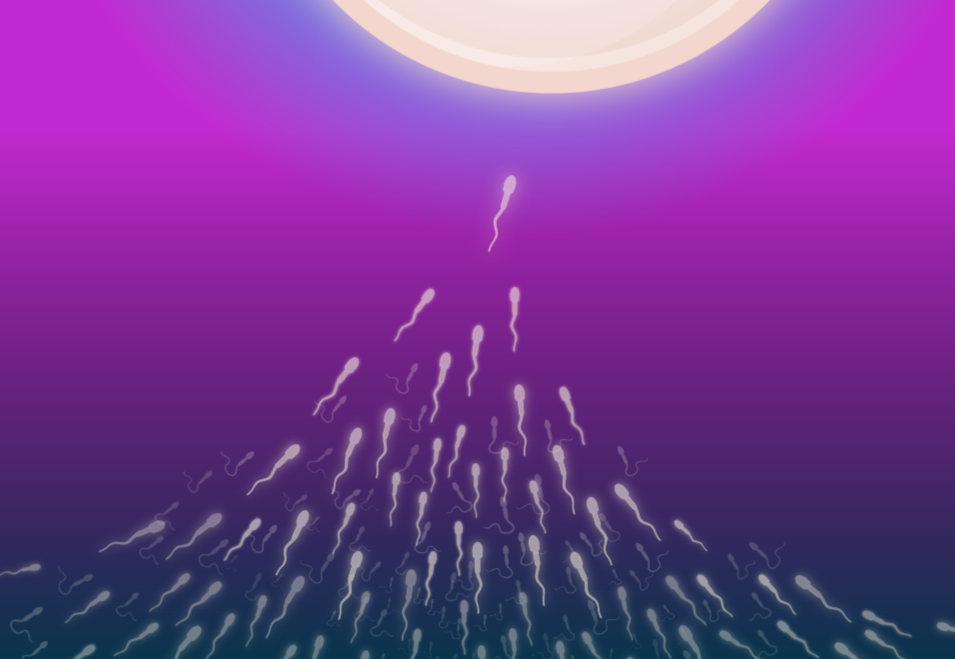

Molecular Events of Amphibian Fertilization
Fertilization in amphibians is a fascinating process that involves a unique set of molecular events governing the successful fusion of male and female gametes. Unlike mammals, amphibians employ external fertilization, where the male releases sperm into the surrounding water, and the female lays her eggs. This process requires intricate cellular interactions, starting with chemotaxis and…
-
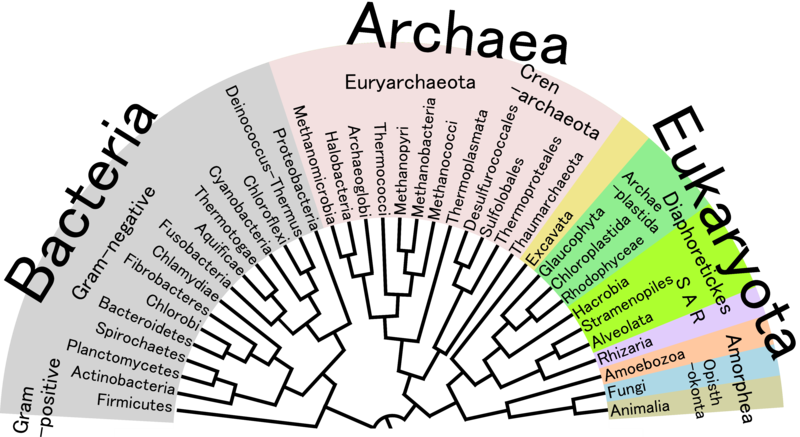
Classification, Systematics, and Taxonomy
Introduction Classification Taxonomy Systematics Types of Classification Hierarchy of Taxa Examples Conclusion
-
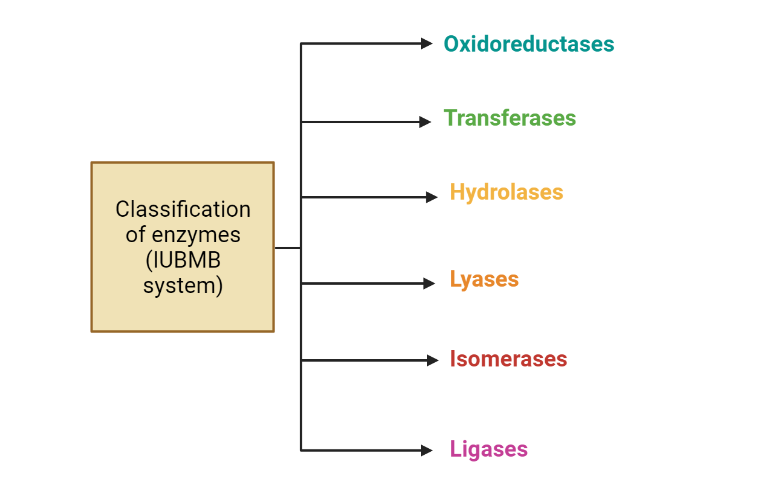
Enzymes : classification
Enzymes are incredibly important biomolecules that play a crucial role in the proper functioning of living organisms. They catalyze specific chemical reactions, making it possible for various biological processes such as metabolism, DNA replication, and cell signaling to occur efficiently. The structure of enzymes is complex, with different levels of organization, including the primary, secondary,…
-
Post transcriptional processing
Post-transcriptional processing refers to the set of modifications and events that occur to the RNA molecule after transcription, but before translation. These modifications are important for the stability, localization, and translation of the RNA molecule. Capping, polyadenylation, splicing, RNA editing, RNA localization, and RNA stability are all important aspects of post-transcriptional processing.
-
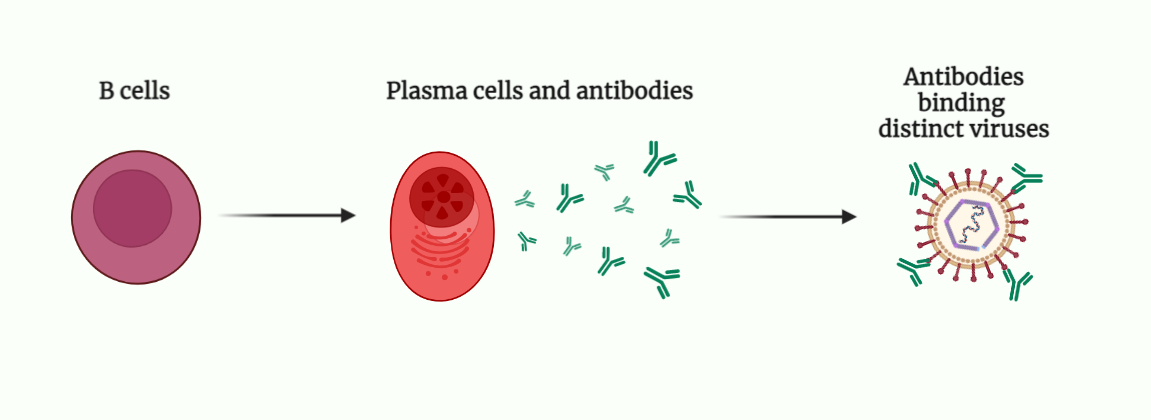
Humoral Immune Response
The humoral immune response, also known as antibody-mediated immunity, is one of the two branches of the adaptive immune response. It involves the production of antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), by B cells in response to an antigen. The purpose of the humoral immune response is to neutralize and remove antigens from the body.…
-
The Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Function
The Golgi apparatus, a crucial organelle in eukaryotic cells, plays a vital role in processing, sorting, and transporting proteins and lipids. Comprising stacked cisternae with distinct regions, it employs a myriad of enzymes for modifications. This dynamic structure ensures proper cellular function by facilitating the formation of lysosomes, secretory vesicles, and the extracellular matrix. Understanding…
-
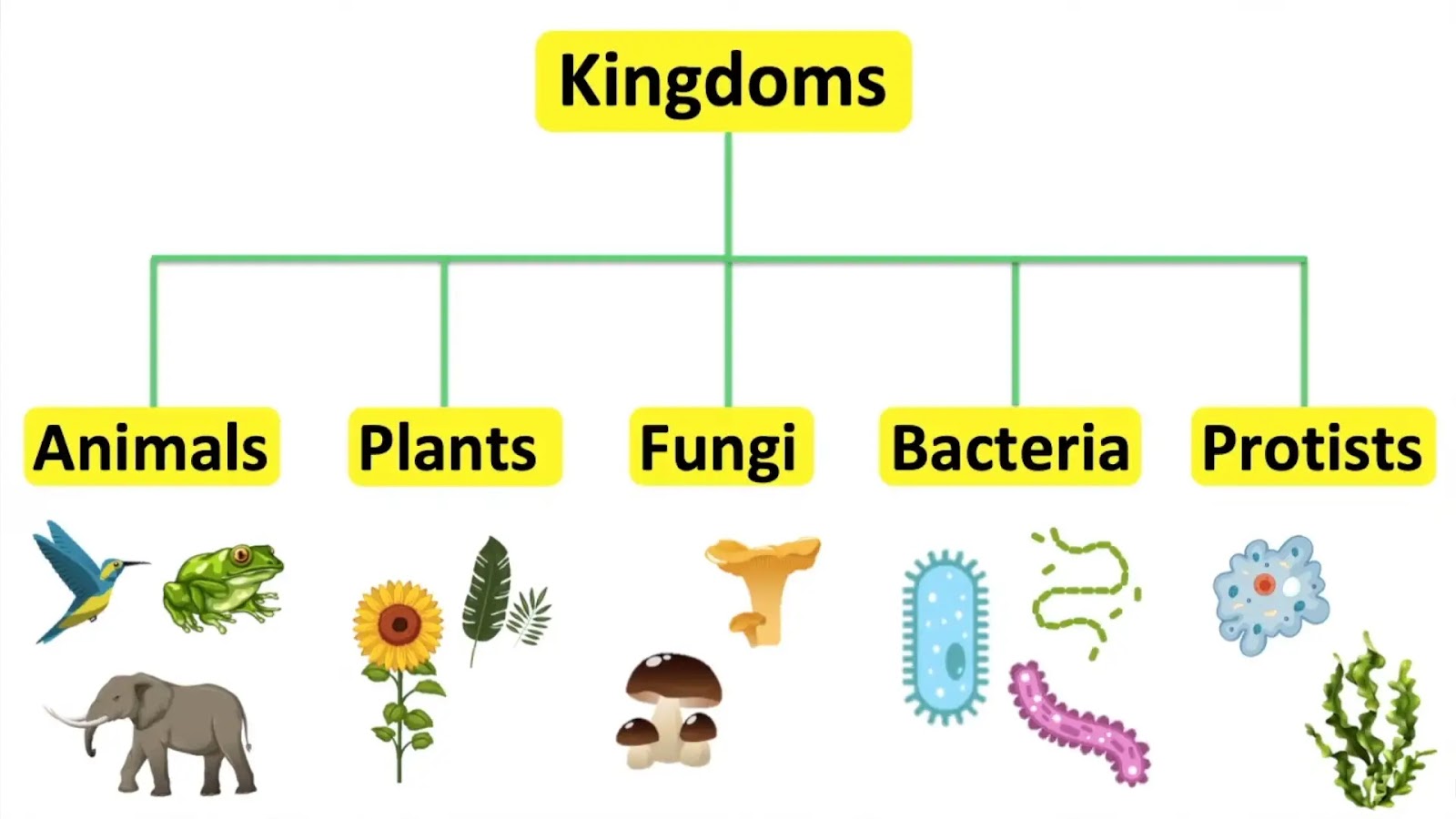
Five Kingdom Classification of Whittaker
Introduction Kingdom Monera Kingdom Protista Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Animalia Conclusion
-
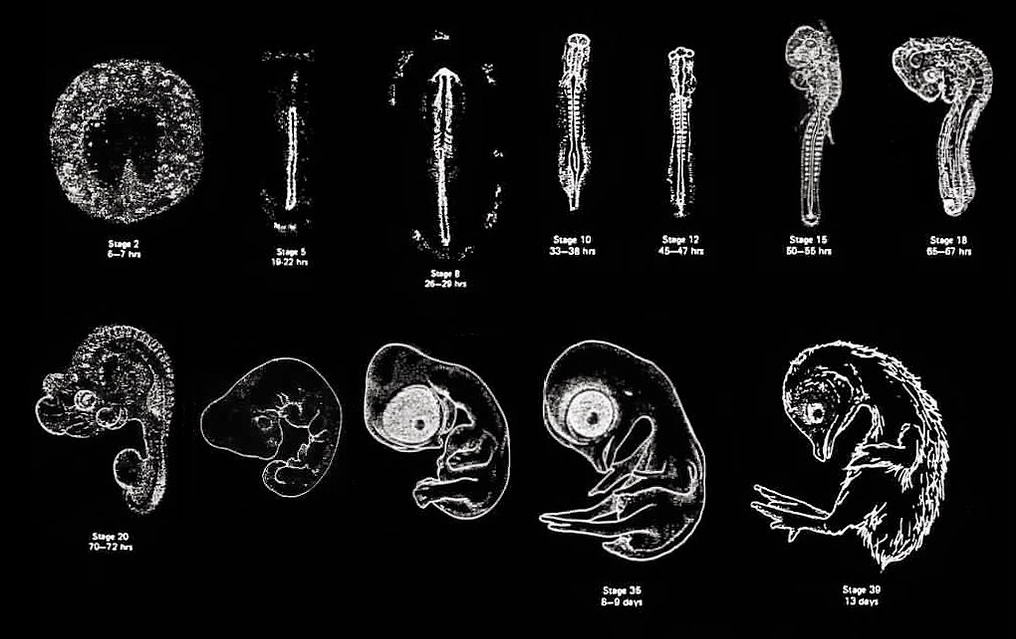
Chick embryo development
Chick embryo development is a fascinating and complex process that involves a series of morphological changes from fertilization to hatching. Chick embryos are an excellent model organism for studying development due to their accessibility and similarity to human development. The development of a chick embryo involves six major steps: fertilization, cleavage, gastrulation, neurulation, organogenesis, and…
-
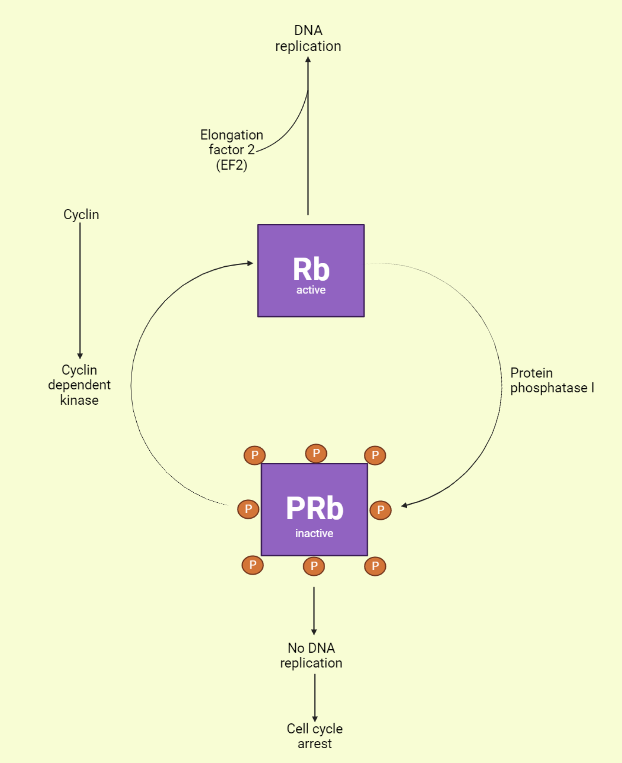
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare type of cancer that affects the retina of the eye and is caused by mutations in the retinoblastoma (RB) gene. The RB gene plays a critical role in the regulation of cell growth and division, acting as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the activity of other proteins that are important for…
-
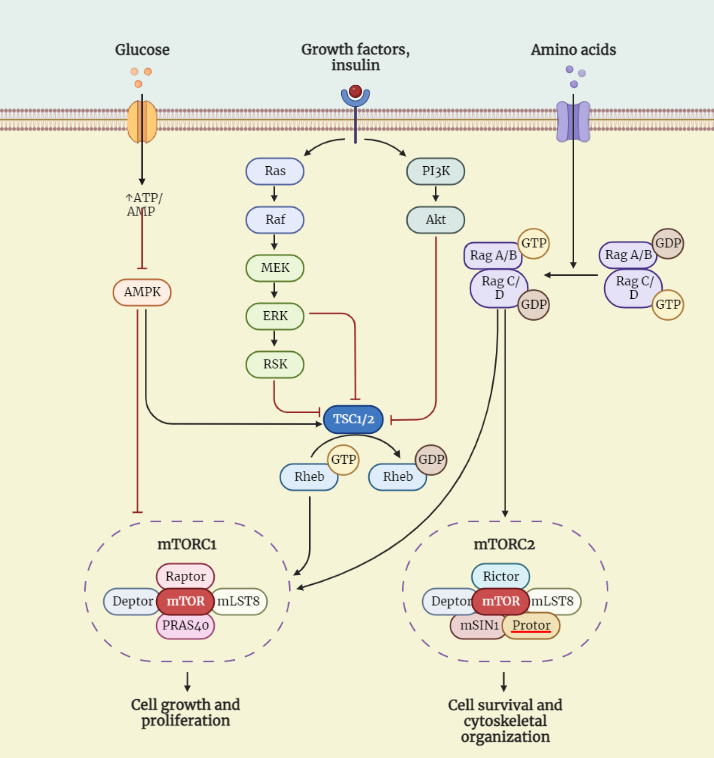
Insulin Signaling
The Insulin Signaling Study Notes explain the complex process of how the hormone insulin regulates glucose metabolism in cells. The notes cover the interaction of insulin with its receptors, downstream signaling pathways, insulin resistance, and the significance of understanding insulin signaling in various diseases. These notes are essential for students studying physiology, biochemistry, and endocrinology,…
-
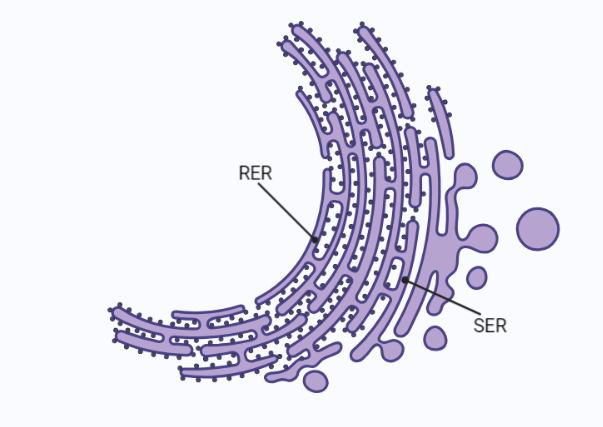
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a vital organelle in eukaryotic cells, playing multiple crucial roles. From protein synthesis, folding, and modification to lipid metabolism and calcium storage, the ER ensures the cell’s proper functioning. The Rough ER, adorned with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins, while the Smooth ER is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification. Additionally, the…
-
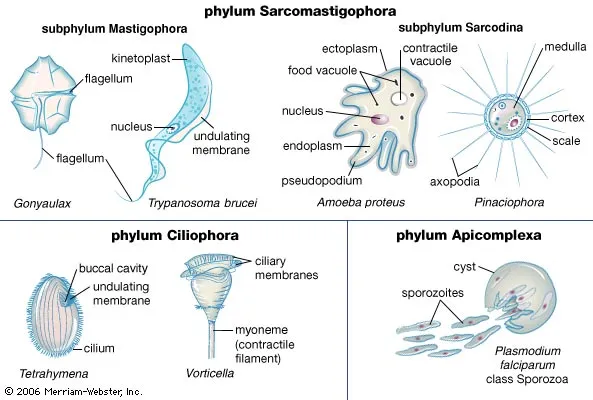
Classification of Protozoa (According to Levine et. al., 1980)
Introduction General Characteristics of Protozoa Classification of Protozoa Phylum Sarcomastigophora Phylum Mastigophora Phylum Opalinata Phylum Ciliophora Phylum Apicomplexa Phylum Microspora and Myxozoa Phylum Acanthamoeba Conclusion
-
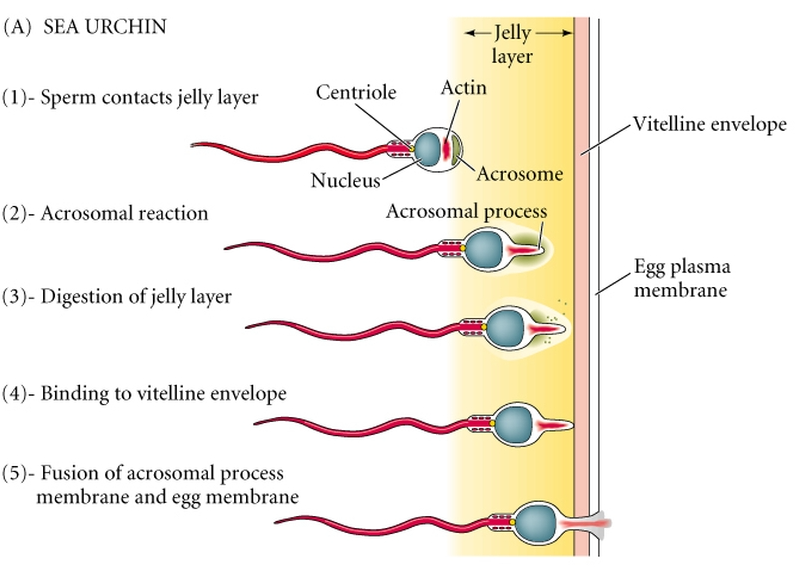
Fertilization in Sea Urchin
Fertilization in sea urchins is a complex process that involves a series of steps, beginning with the release of sperm and eggs and culminating in the formation of a zygote. The release of gametes is often triggered by environmental cues, and upon contact, the sperm undergoes a series of changes, including the release of enzymes…
-
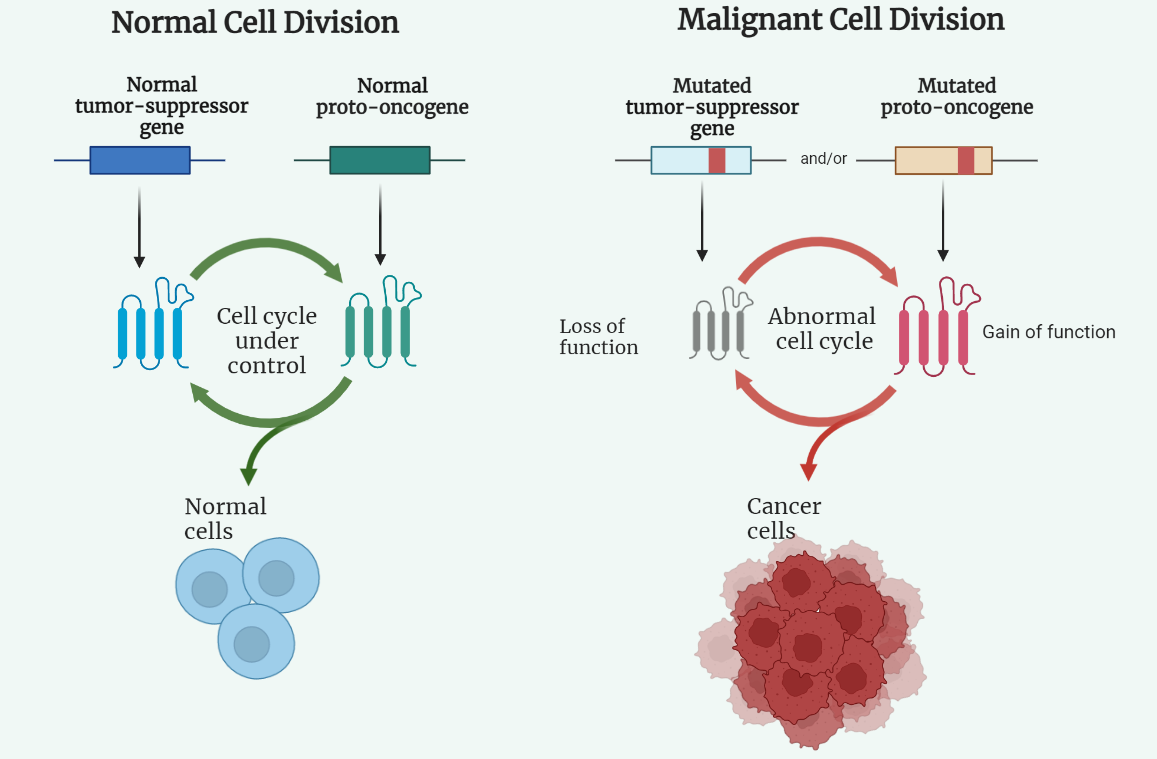
Oncogenes and Tumor suppressor genes
The molecular genetics of cancer involves the study of the genetic and molecular changes that occur in cells as they become cancerous. This field of study has led to the identification of two important classes of genes involved in the development of cancer: oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Oncogenes promote cell growth and proliferation, while…
-
Lysozomes
Lysozomes, the essential organelles in eukaryotic cells, play a pivotal role in cellular material degradation. Enclosed within a lipid bilayer, these spherical structures house hydrolytic enzymes responsible for breaking down bacteria, old organelles, and other cellular components. Additionally, lysozomes contribute to autophagy, cellular protection against harmful agents, and lipid metabolism. Formation from the Golgi apparatus…
-
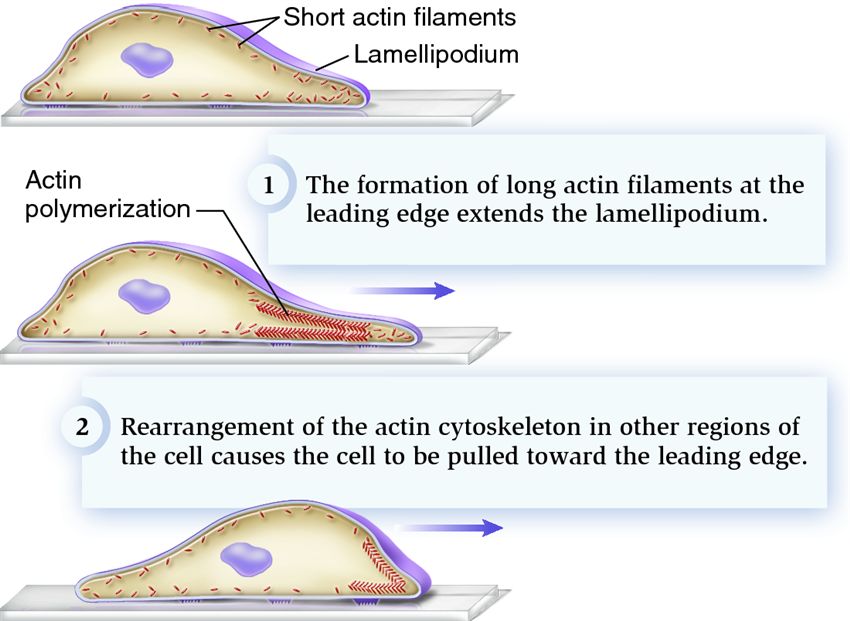
Molecular Basis of Locomotion in Amoeba
Introduction Actin Cytoskeleton Membrane Protrusion and Retraction Conclusion
-

Vitamins
Vitamins are essential micronutrients that the body needs in small amounts to maintain good health. They are required for various functions in the body, such as growth and development, metabolism, and maintaining the immune system. There are two types of vitamins: fat-soluble and water-soluble. Fat-soluble vitamins include vitamin A, D, E, and K, while water-soluble…
-
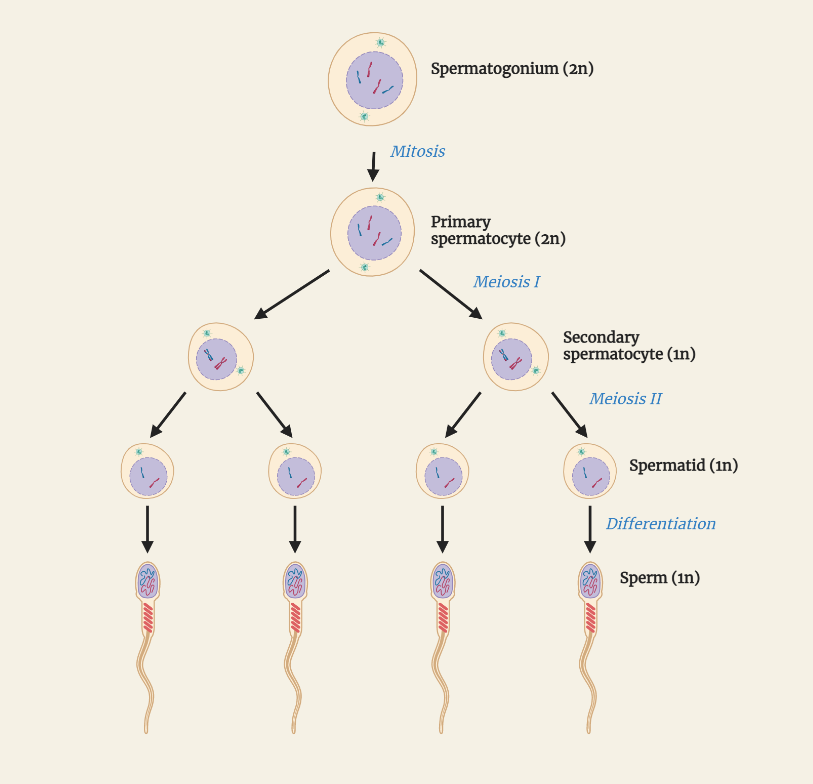
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell formation and development, which occurs in the testes of males and is regulated by a delicate balance of hormones. It is a complex process that involves four main phases: the mitotic phase, meiotic phase, morphological maturation phase, and maturation phase. Each phase is characterized by specific events that…
-
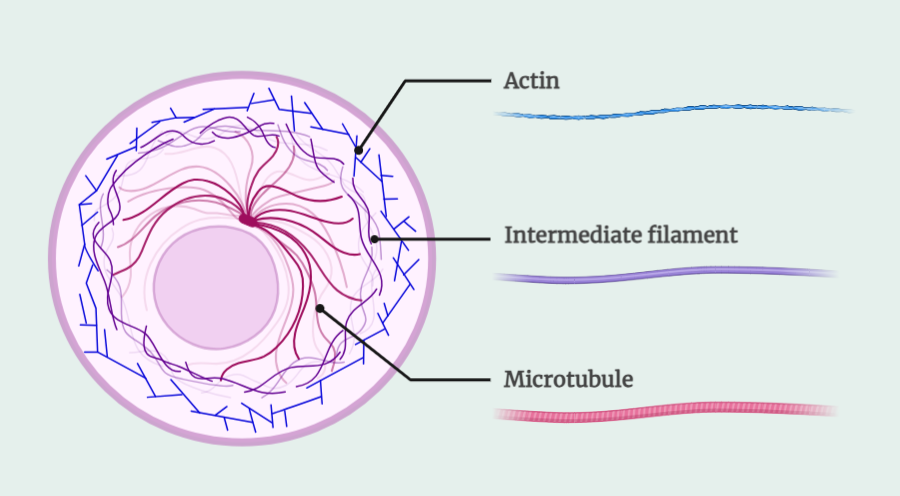
The cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton, a complex network of protein filaments, serves as the architectural backbone of eukaryotic cells. Comprised of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, it provides structural support, cell shape, and motility. Functionally versatile, the cytoskeleton plays crucial roles in cell division, endocytosis, and exocytosis. Regulated by specific proteins, its dynamic nature underlies various cellular processes.…
-
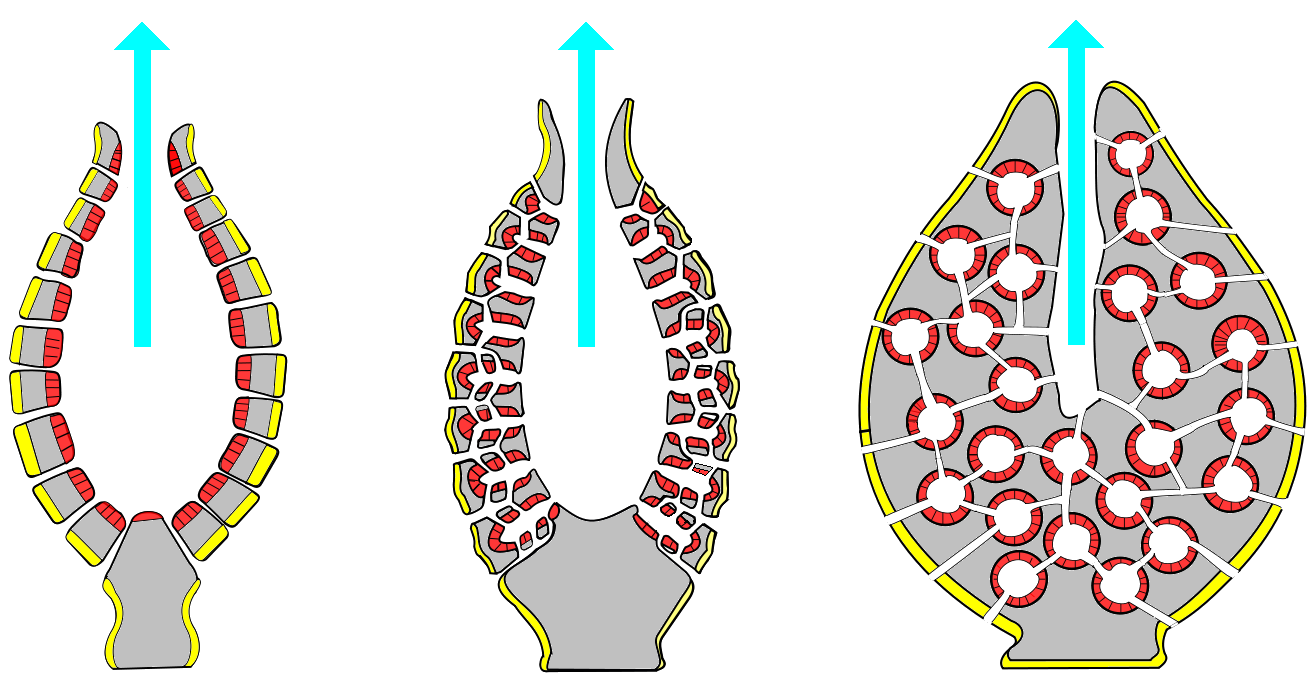
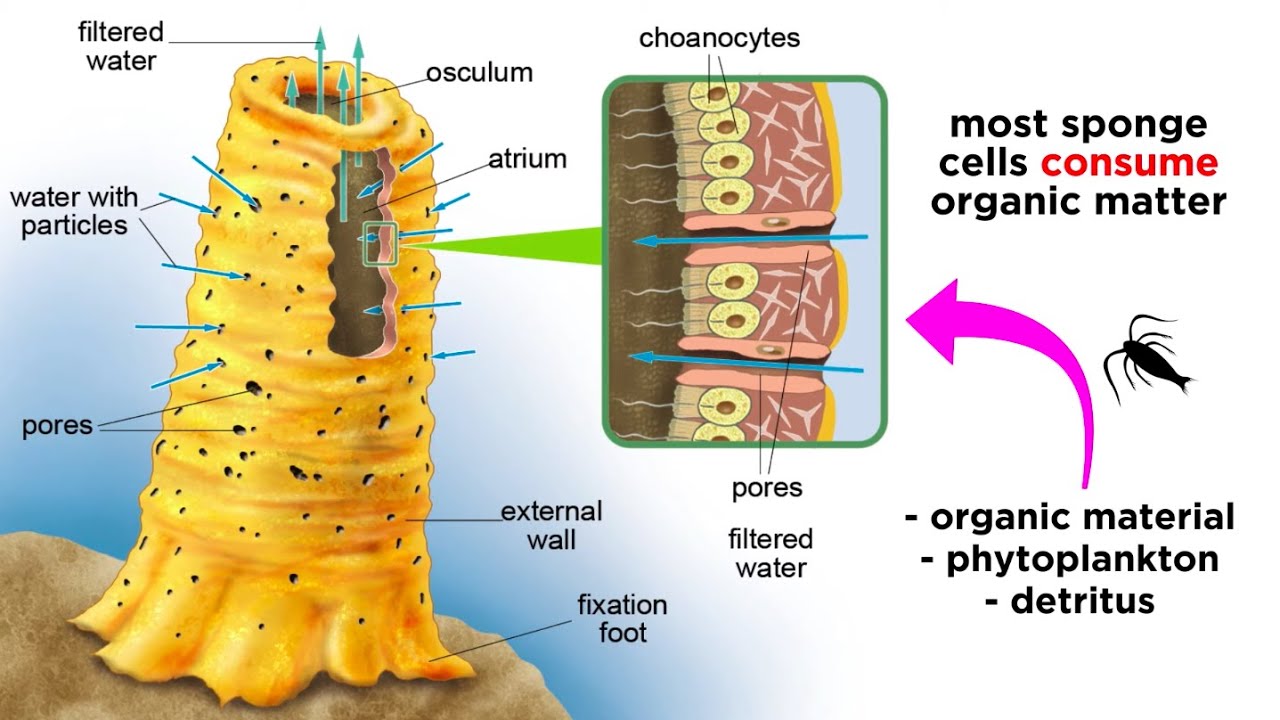
Canal System in Porifera
Porifera, also known as sponges, are a diverse group of aquatic animals that are characterized by their porous body structure and the presence of a system of canals and channels. The canal system in porifera is a key feature that allows for the efficient movement of water and nutrients throughout the sponge’s body. The canal…
-
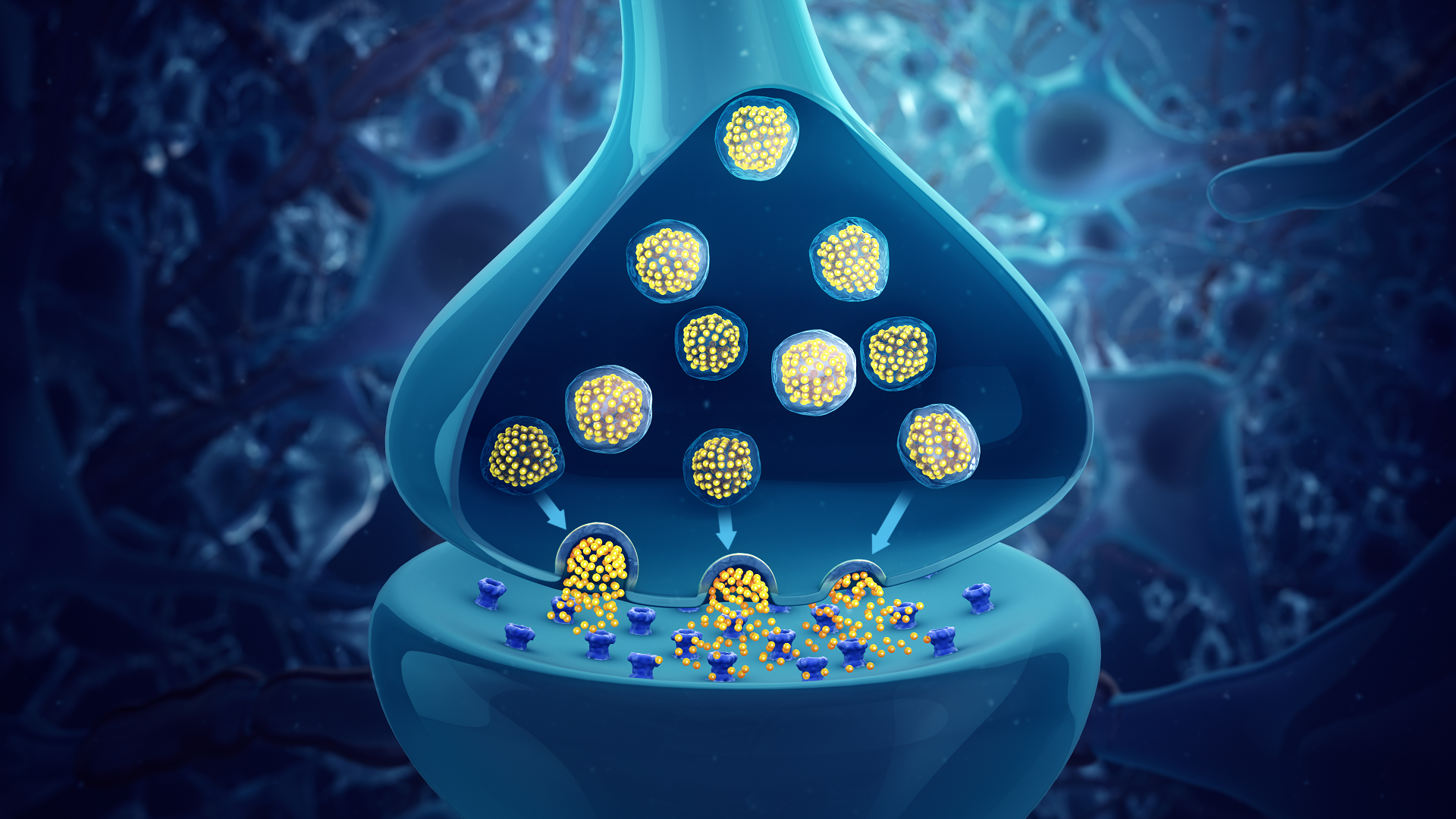
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are essential chemical messengers that play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in the brain and throughout the body. They are involved in functions such as mood, sensation, movement, and cognition. The imbalances or disruptions in neurotransmitter function can lead to a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders. This article provides an…
-
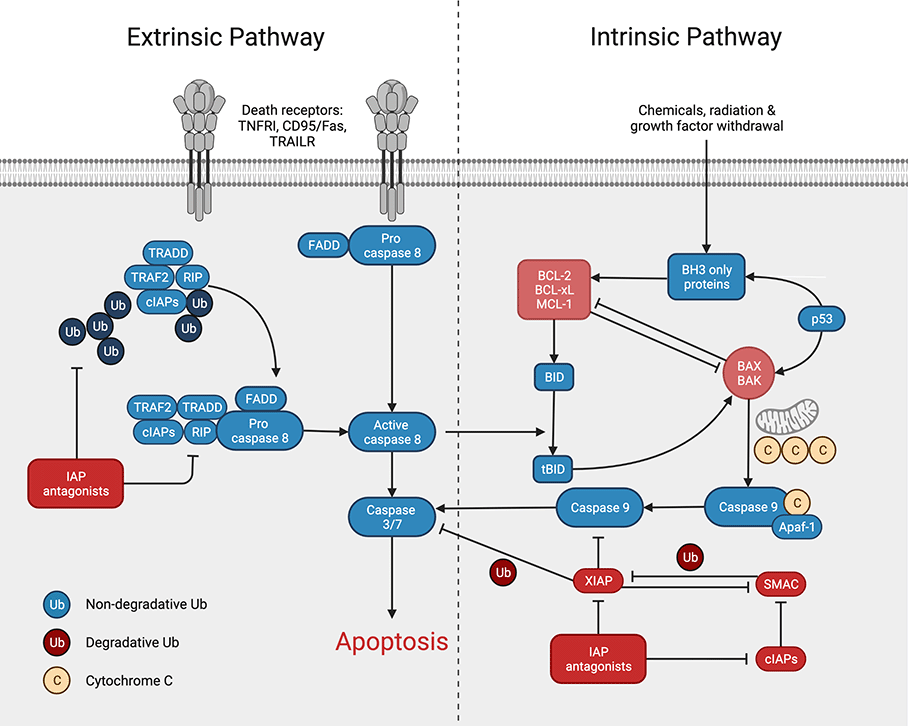
Apoptotic Pathway
Apoptotic pathways, the intricate networks regulating programmed cell death, are vital for various biological processes and disease outcomes. Understanding these pathways, including the intrinsic and extrinsic routes, sheds light on cell death mechanisms and their implications in health and disease. The interplay between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins and the activation of caspases shape the fate…
-
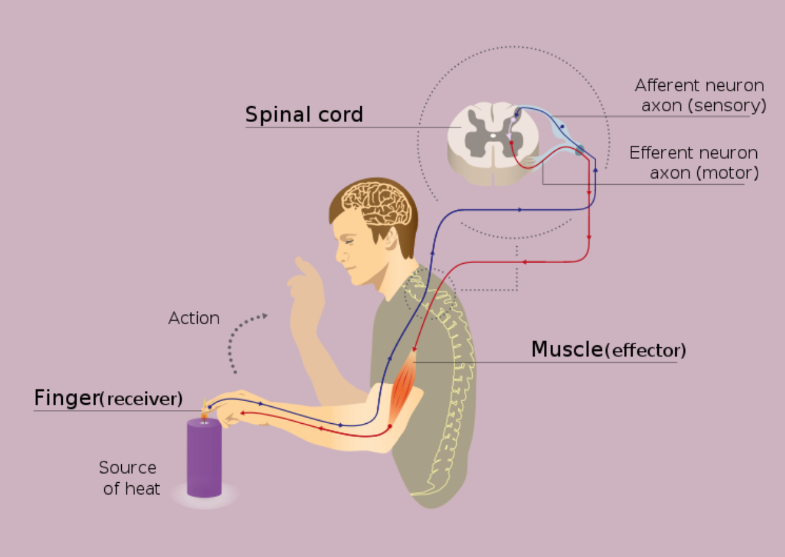
The reflex action and reflex ARC
The reflex arc is a rapid and involuntary movement in response to a stimulus, and it is a critical process for the survival of many species, including humans. It involves a series of sensory, motor, and interneurons that allow for a quick and coordinated response to a stimulus. The reflex arc consists of five components,…
-
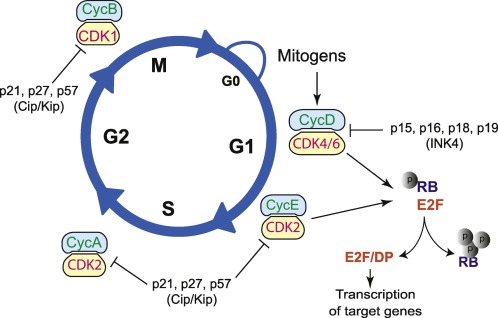
Eukaryotic cell cycle regulation
The cell cycle is a precisely regulated process essential for cell growth and division. It consists of four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and mitosis. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate cell division and maintaining genomic integrity. The cell cycle is governed by various checkpoints that assess DNA integrity, availability of growth…
-
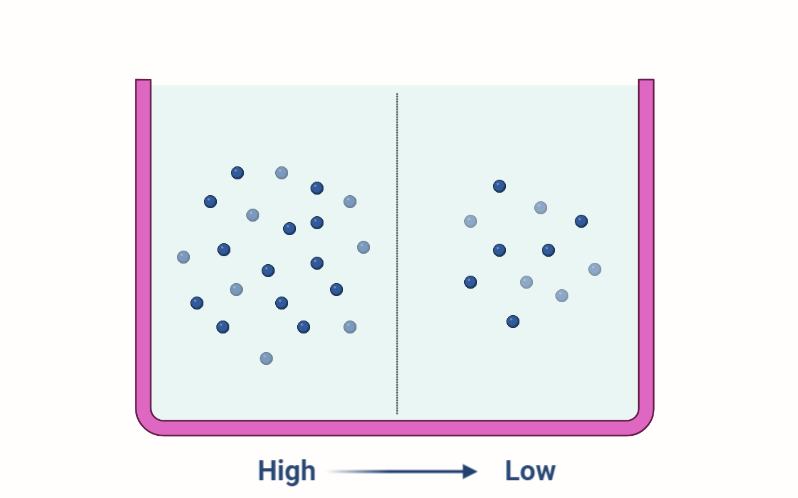
Osmosis
Osmosis is a process that occurs naturally in all living things, including plants and animals. It is a type of passive transport that involves the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This movement of water molecules helps maintain the balance…
-
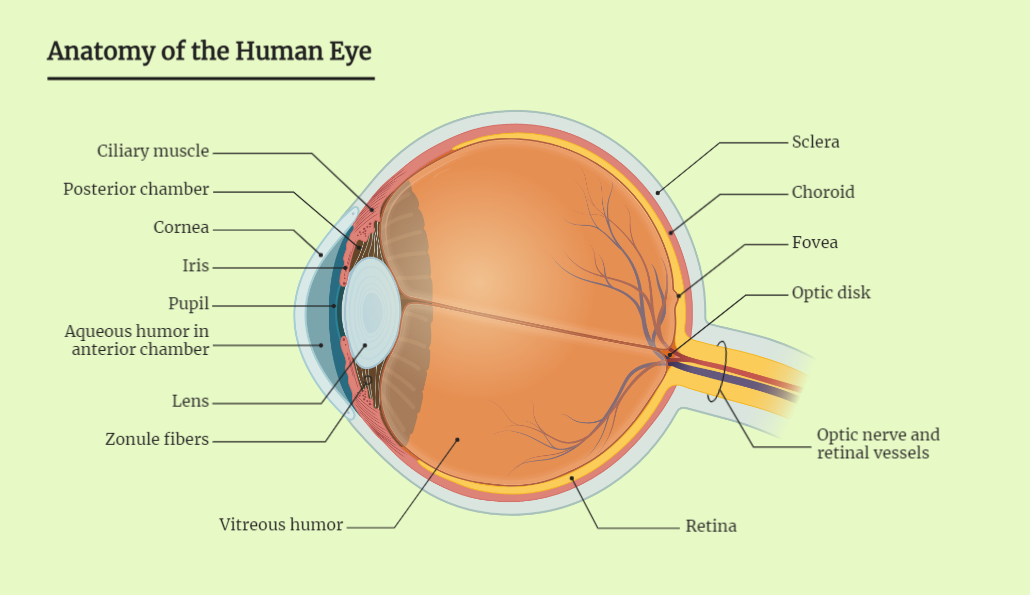
The human eye
The human eye is a remarkable organ that enables us to see and interpret visual information. It consists of several structures, including the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, optic nerve, and vitreous humor, which work together to allow us to perceive the world around us. The physiology of the human eye involves complex processes such…
-

Peroxisome: Structure and Function
Peroxisomes are small, spherical organelles found in eukaryotic cells that play a crucial role in cellular metabolism. They are enclosed by a single membrane and contain enzymes responsible for specific metabolic reactions, such as the metabolism of lipids and the detoxification of harmful substances. Peroxisomes are distinct from lysosomes, as they do not degrade macromolecules.…
-
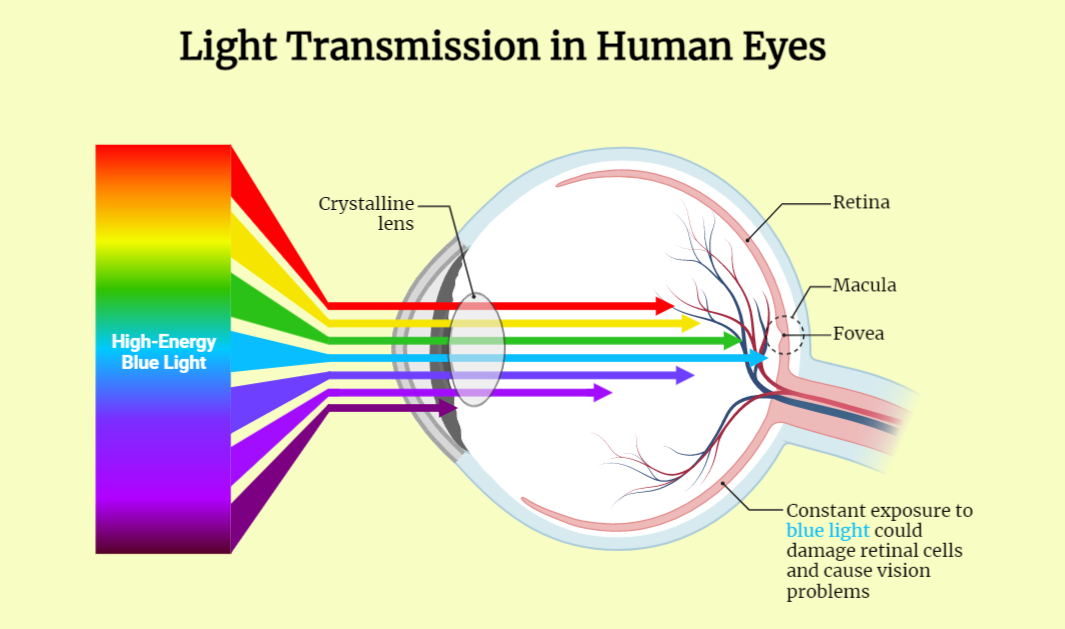
Mechanism of Vision
The process of vision is complex and involves multiple mechanisms that work together to allow us to see and interpret visual information. From the anatomy of the eye to the neural processing of visual signals, this study chapter explores the different aspects of the mechanism of vision. It covers topics such as light refraction, phototransduction,…
-

Restriction Endonucleases
Restriction endonucleases, the DNA-cutting enzymes, are indispensable in molecular biology research. Classified into four types based on recognition sites, Type II enzymes stand out as the most widely used. They cleave DNA at specific sequences, generating fragments with blunt or sticky ends. Despite their complexity, Type I and III enzymes have limited use due to…
-
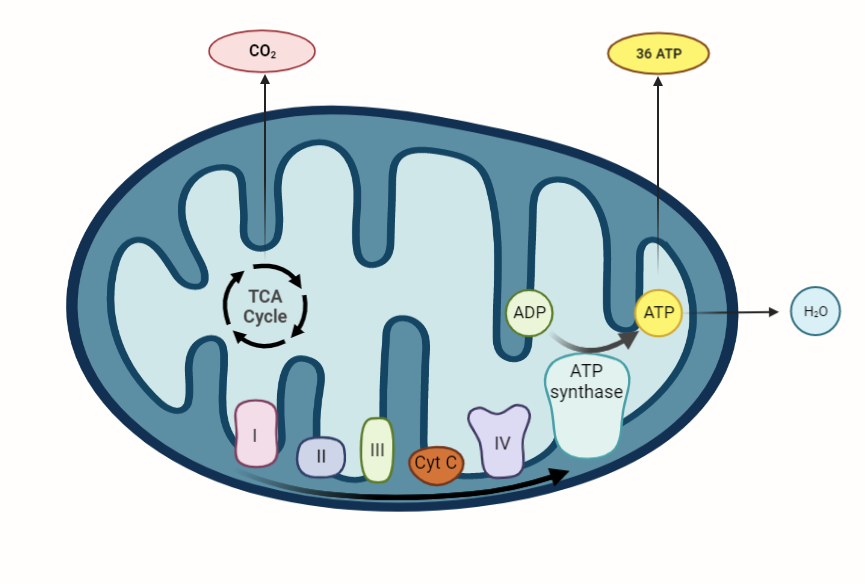
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
The chemiosmotic hypothesis proposed by Peter Mitchell in 1961 is a widely accepted model that explains how living organisms convert energy from electron transfer reactions into ATP synthesis. This hypothesis revolutionized our understanding of how cells generate ATP, the universal energy currency of living systems, and it is a fundamental principle of bioenergetics. The chemiosmotic…
-
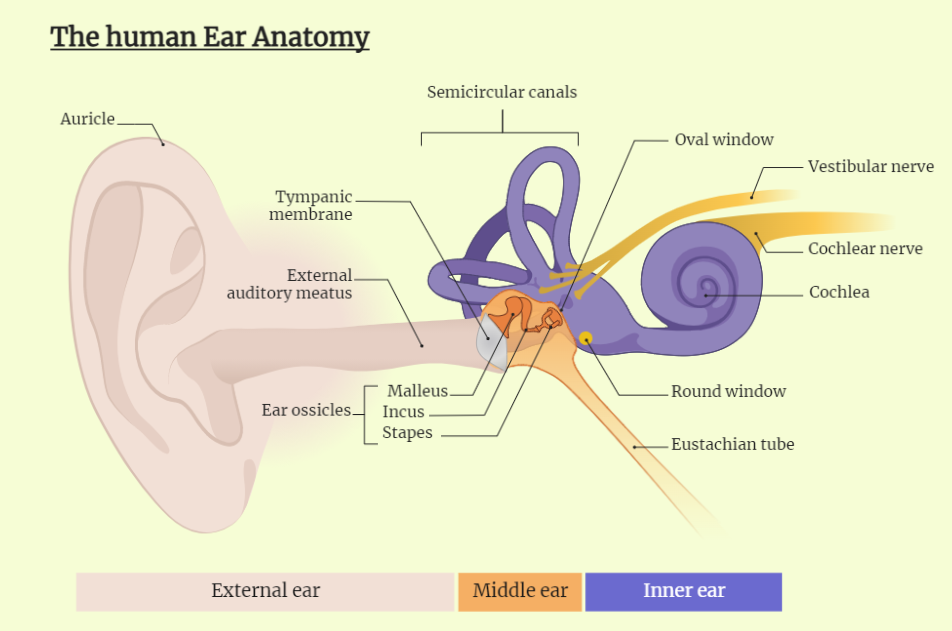
The Human Ear
The human ear is an intricate and essential part of our auditory system, responsible for our sense of hearing and balance. This study chapter delves into the anatomy of the ear, how we hear sounds, the types of hearing loss, and the management and treatment options available. It also covers common ear disorders and diseases…
-

Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife conservation is a crucial endeavor aimed at managing and safeguarding wild animals and their habitats. Preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem services are key reasons behind its significance, along with supporting human well-being. However, various threats, such as habitat destruction, climate change, overexploitation, invasive species, and pollution, pose challenges to wildlife. To combat these issues,…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)