Table of Contents
I. Introduction
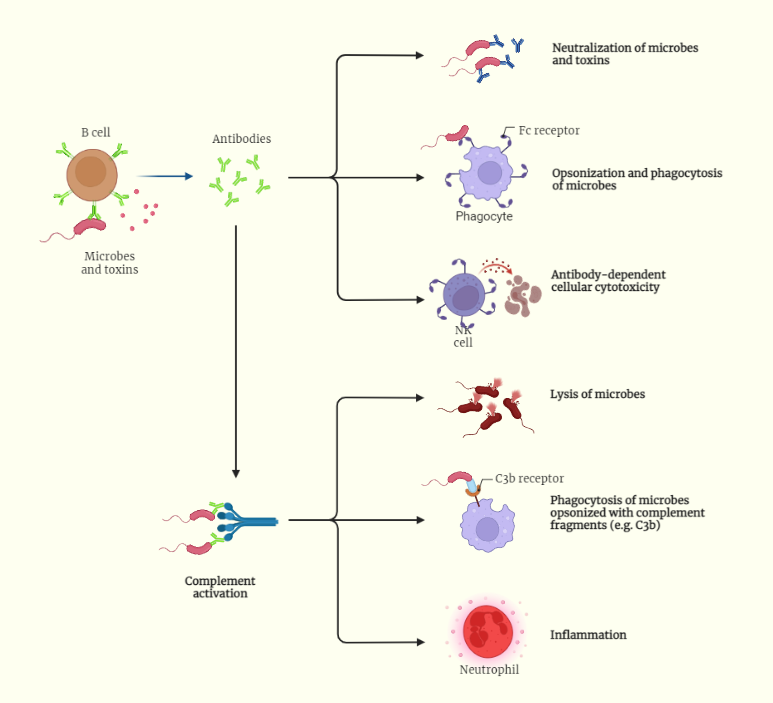
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are a class of proteins. The functions of antibodies play very critical role in the immune response.
- They are produced by B-lymphocytes and are able to specifically bind to a wide variety of antigens.
- Antibodies have a number of functions that help to protect the body from infection and disease.
II. Neutralization
- One of the primary functions of antibodies is to neutralize pathogens.
- This is accomplished through the binding of antibodies to the antigenic determinants (epitopes) of the pathogen, which can prevent the pathogen from infecting host cells or from carrying out its normal functions.
- For example, antibodies can neutralize viruses by binding to the viral envelope, preventing the virus from entering host cells, or by binding to the viral capsid, preventing the virus from releasing its genetic material.
III. Opsonization
- Another important function of antibodies is opsonization, which refers to the ability of antibodies to mark pathogens for phagocytosis.
- This is accomplished through the binding of antibodies to the surface of pathogens, which can then be recognized and engulfed by phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils.
- Opsonization can also enhance the efficacy of the complement system, which helps to kill pathogens.
IV. Complement Activation
- Antibodies can also activate the complement system, which is a group of proteins that work together to help clear pathogens from the body.
- Complement activation is triggered by the binding of antibodies to pathogens and results in the formation of a cascade of reactions that can lead to the lysis of pathogens and the recruitment of inflammatory cells to the site of infection.
V. Allergic Reactions
- Another function of antibodies is in the context of allergic reactions, which are characterized by an abnormal response to normally harmless antigens.
- In an allergic reaction, IgE antibodies bind to allergens, which are then recognized by Fc receptors on the surface of mast cells and basophils.
- This leads to the release of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine, which can cause symptoms such as itching, hives, and difficulty breathing.
VI. Memory
- Antibodies also play a role in the development of immunity, through the formation of memory B-cells that can rapidly produce antibodies upon subsequent exposure to the same antigen.
- This allows the body to mount a faster and more effective immune response in the event of a repeat infection.
VII. Conclusion
- Antibodies are a class of proteins that play a critical role in the immune response.
- Antibodies have a number of functions that help to protect the body from infection and disease, including neutralization, opsonization, complement activation, allergic reactions, and memory.
- The ability of antibodies to bind specifically to antigens allows them to target pathogens and foreign particles, while minimizing damage to host cells and tissues.