Table of Contents
Introduction to Inflammation
Inflammation is a complex biological response that occurs in response to injury, infection, or other forms of tissue damage. It is a crucial defense mechanism that is activated by the immune system to eliminate pathogens and other foreign particles and promote healing. In this study note, we will discuss the key components and mechanisms of inflammation, the different types of inflammation, and the role of inflammation in disease.
Key Components and Mechanisms of Inflammation
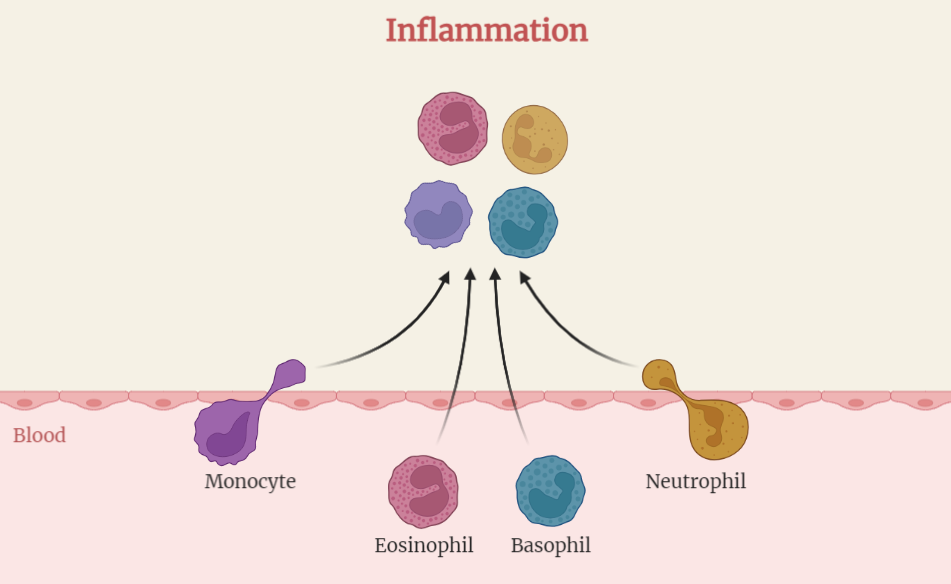
- Inflammation is a complex process that involves a wide range of immune cells, signaling molecules, and other factors.
- The key components and mechanisms of inflammation include the activation of immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and the recruitment of immune cells to the site of injury or infection.
Different Types of Inflammation
- Inflammation can be divided into two main types: acute inflammation and chronic inflammation.
- Acute inflammation is a short-term response that occurs in response to injury or infection and is characterized by the rapid onset of symptoms, such as redness, swelling, and pain.
- Chronic inflammation is a long-term response that can occur in response to chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions and is characterized by the persistence of symptoms over a prolonged period of time.
Role of Inflammation in Disease
- Inflammation plays a crucial role in the immune response and is essential for the elimination of pathogens and other foreign particles.
- However, when inflammation becomes chronic or excessive, it can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the development of various diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases.
- In some cases, chronic inflammation can also lead to the development of chronic conditions, such as osteoarthritis, asthma, and even cancer.
- Additionally, chronic inflammation can also worsen certain diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity.
Inflammation markers
- Inflammation markers are molecules that can be measured in blood or other body fluids to indicate the presence and level of inflammation in the body.
- Examples of inflammation markers include C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).
Inflammation treatment
- Inflammation treatment typically involves the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids.
- Other treatments may include the use of immunosuppressive drugs, or biologic therapies that target specific inflammatory pathways.
- In addition, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy diet, and stress management can also help to reduce inflammation in the body.
Conclusion
Inflammation is a complex biological response that occurs in response to injury, infection, or other forms of tissue damage. It is a crucial defense mechanism that is activated by the immune system to eliminate pathogens and other foreign particles and promote healing. Inflammation can be divided into two main types: acute inflammation and chronic inflammation. When inflammation becomes chronic or excessive, it can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the development of various diseases. The treatment of inflammation typically involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs and lifestyle changes. Understanding the key components and mechanisms of inflammation, the different types of inflammation, and the role of inflammation in disease is crucial for the development of effective treatments and strategies for controlling and preventing inflammation-related diseases.