Table of Contents
I. Introduction
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a crucial physiological process that occurs in multicellular organisms.
It plays a key role in the development and maintenance of tissue homeostasis, as well as in the response to cellular stress and damage.
Dysregulation of apoptosis can lead to various diseases, including cancer and autoimmunity.
II. Mechanisms of Apoptosis
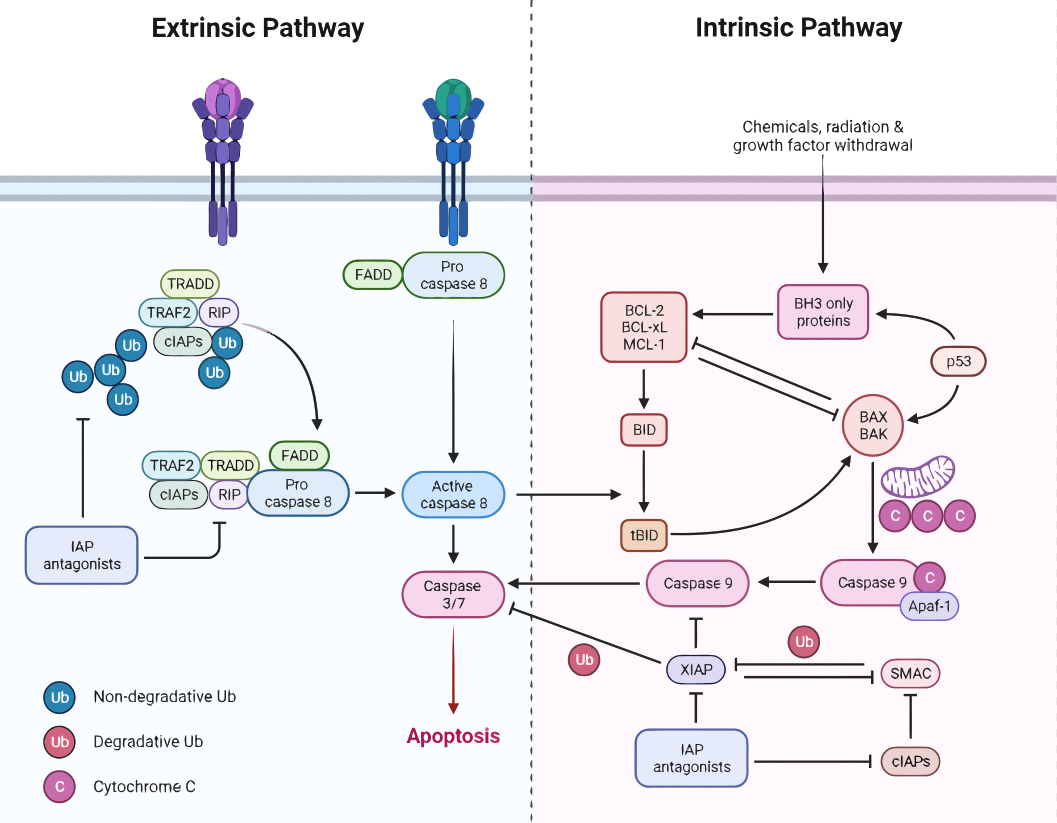
A. Extrinsic pathway
- The extrinsic pathway is triggered by signals from outside the cell, such as death receptors on the cell surface.
- These receptors bind to their ligands, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and Fas ligand, and activate the caspase cascade, a series of proteases that ultimately lead to the destruction of the cell.
- The initiator caspase in this pathway is caspase 8, which activates the executioner caspases, caspase 3 and caspase 7.
B. Intrinsic pathway
- The intrinsic pathway is activated by signals from within the cell, such as DNA damage or mitochondrial dysfunction.
- It involves the release of pro-apoptotic molecules from the mitochondria, such as cytochrome c, which activate the caspase cascade.
- The initiator caspase in this pathway is caspase 9, which activates the executioner caspases, caspase 3 and caspase 7.

III. Execution of Apoptosis
Once activated, the executioner caspases cleave and degrade a variety of cellular proteins, leading to the characteristic morphological changes of apoptosis, such as cell shrinkage, nuclear condensation, and formation of apoptotic bodies.
These changes ensure the efficient removal of the dying cell by phagocytes, to prevent inflammation and tissue damage.
IV. Regulation of Apoptosis
- Apoptosis is tightly regulated at multiple levels, to ensure proper timing and specificity of cell death.
- Pro-survival molecules, such as Bcl-2 and IAPs, can inhibit the intrinsic pathway by blocking the release of pro-apoptotic molecules from the mitochondria.
- On the other hand, pro-apoptotic molecules, such as Bax and Bak, can promote the intrinsic pathway by promoting the release of pro-apoptotic molecules from the mitochondria.
V. Conclusion
Apoptosis is a complex and highly regulated process that plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and responding to cellular stress and damage.
Understanding the molecular mechanisms of apoptosis is essential for the development of therapies for various diseases, including cancer and autoimmunity.