Table of Contents
Introduction to Organs of the Immune System
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from invading pathogens. These organs of immune system play a crucial role in the immune response by providing a physical location for the activation, maturation, and storage of immune cells. In this study note, we will discuss the different organs that make up the immune system, their functions, and their interactions with each other.
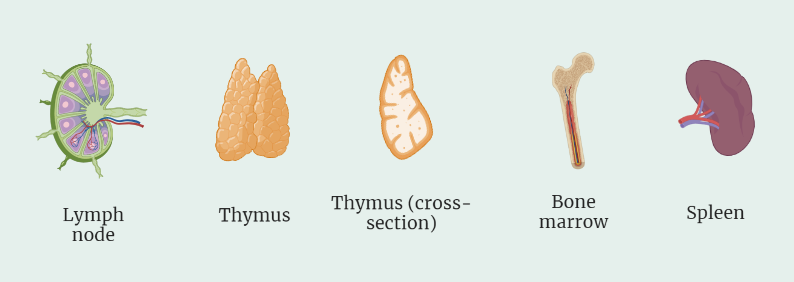
Bone Marrow
- Bone marrow is the primary site of hematopoiesis, or the production of all blood cells, including white blood cells.
- It contains stem cells that give rise to all the different types of white blood cells, including granulocytes, agranulocytes, and lymphocytes.
Thymus
- The thymus is an organ located in the upper chest that is involved in the maturation and selection of T cells.
- It is responsible for the development of T cells from immature cells called thymocytes, and the selection of T cells that are able to recognize self-antigens.
Spleen
- The spleen is an organ located in the upper left abdomen that plays a role in the immune response by filtering the blood and removing damaged or abnormal cells.
- It also contains immune cells, including lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, that are involved in the immune response.
Lymph Nodes
- Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that are located throughout the body and are involved in the immune response by filtering lymph and trapping foreign particles.
- They also contain immune cells, including lymphocytes and dendritic cells, that are involved in the immune response.
Lymphatic vessels
- Lymphatic vessels are a network of vessels that transport lymph, a fluid that contains immune cells, throughout the body.
- They also contain immune cells, including lymphocytes and dendritic cells, that are involved in the immune response.
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) is a collection of immune cells and tissues that are associated with mucous membranes, such as the gut, lung, and nasal passages.
- They are involved in the immune response by providing a first line of defense against pathogens and other foreign particles.
Conclusion
The immune system is composed of a diverse range of organs that work together to protect the body from invading pathogens. These organs include the bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). Each of these organs plays a specific role in the immune response, and their interactions with each other are crucial for the effective functioning of the immune system.