-
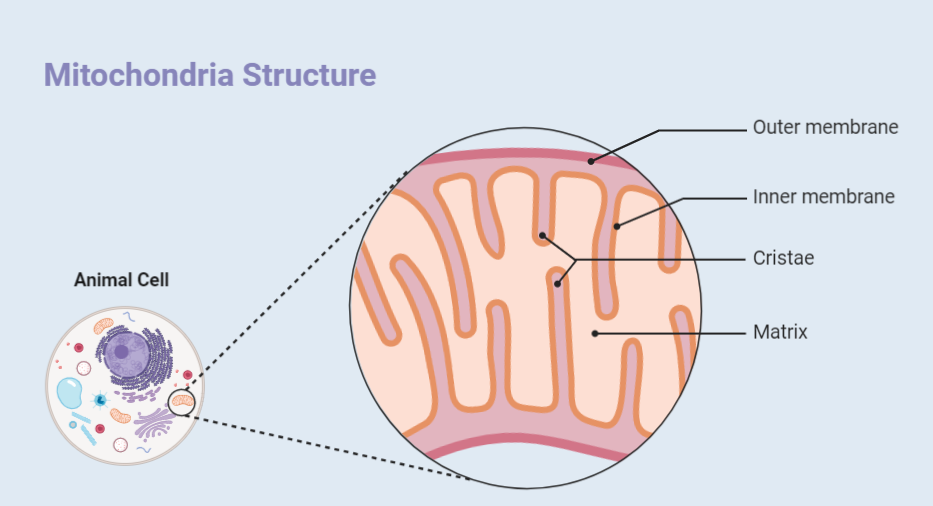
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Due to their essential role in cellular respiration, they are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. Mitochondria have a unique structure consisting of an outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix. They…
-
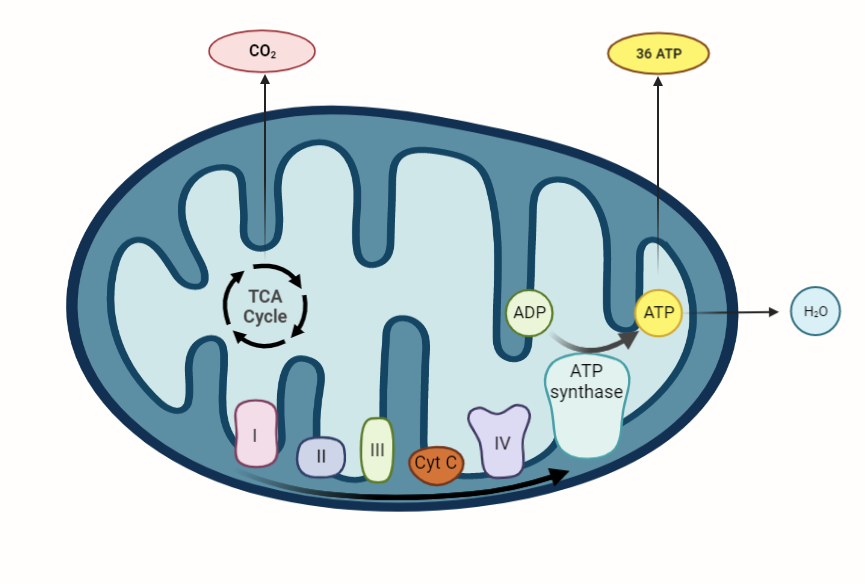
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
The chemiosmotic hypothesis proposed by Peter Mitchell in 1961 is a widely accepted model that explains how living organisms convert energy from electron transfer reactions into ATP synthesis. This hypothesis revolutionized our understanding of how cells generate ATP, the universal energy currency of living systems, and it is a fundamental principle of bioenergetics. The chemiosmotic…
-
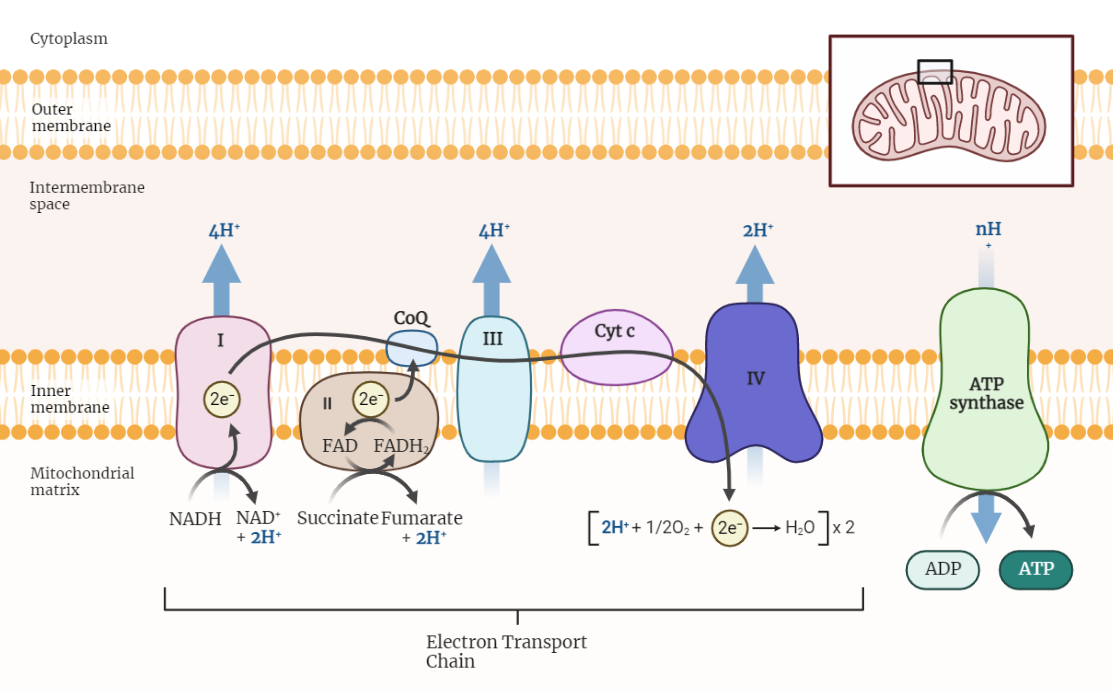
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a fundamental process in cellular energy production. It involves the synthesis of ATP through the electron transport chain (ETC) and chemiosmosis. The ETC, consisting of protein complexes, facilitates the flow of electrons and generates a proton gradient. This proton gradient is harnessed by ATP synthase to produce ATP. The efficiency of oxidative…
Categories
- Anatomy (9)
- Animal Form and Functions (38)
- Animal Physiology (65)
- Biochemistry (33)
- Biophysics (25)
- Biotechnology (52)
- Botany (42)
- Plant morphology (6)
- Plant Physiology (26)
- Cell Biology (107)
- Cell Cycle (14)
- Cell Signaling (21)
- Chemistry (9)
- Developmental Biology (36)
- Fertilization (13)
- Ecology (5)
- Embryology (17)
- Endocrinology (10)
- Environmental biology (3)
- Genetics (59)
- DNA (27)
- Inheritance (13)
- Histology (3)
- Hormone (3)
- Immunology (29)
- life science (76)
- Material science (8)
- Microbiology (18)
- Virus (8)
- Microscopy (18)
- Molecular Biology (113)
- parasitology (6)
- Physics (3)
- Physiology (11)
- Plant biology (26)
- Uncategorized (7)
- Zoology (112)
- Classification (6)
- Invertebrate (7)




